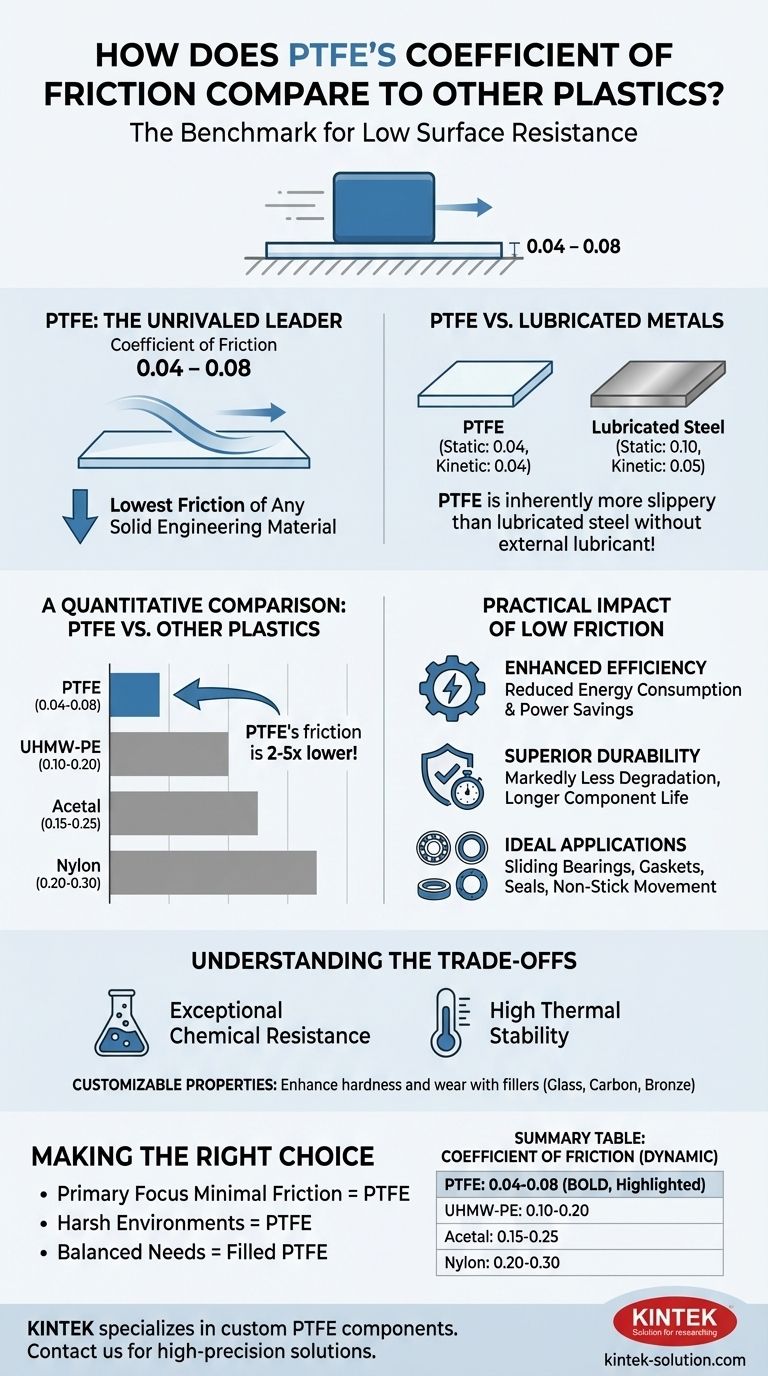
To put it directly, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, significantly outperforming virtually all other plastics and even lubricated metals. Its typical dynamic coefficient of friction ranges from 0.04 to 0.08, which is drastically lower than materials like Nylon (0.20–0.30) or Acetal (0.15–0.25). This property establishes PTFE as the benchmark material for applications where minimizing surface resistance is critical.
The core takeaway is not just that PTFE is "slicker," but that its uniquely low coefficient of friction translates directly into tangible engineering benefits: reduced wear, lower energy consumption, and longer operational life for components.

A Quantitative Comparison: PTFE vs. Other Materials
Understanding the numbers reveals just how significant PTFE's low-friction advantage truly is. It doesn't just lead the category of engineering plastics; it stands in a class of its own.
The Unrivaled Leader in Low Friction
When measured, the difference is stark. PTFE's coefficient of friction is lower than that of any other solid engineering material.
- PTFE: 0.04 – 0.08
- UHMW-PE: 0.10 – 0.20
- Acetal: 0.15 – 0.25
- Nylon: 0.20 – 0.30
This demonstrates that other common plastics exhibit two to five times more friction than PTFE.
How PTFE Measures Up to Metals
Perhaps the most telling comparison is against lubricated steel. PTFE's static and kinetic friction (0.04) is even lower than lubricated steel, which has a kinetic coefficient of friction of 0.05 and a static coefficient of 0.10.
This means a PTFE surface is inherently more slippery than a lubricated metal one, without requiring any external lubricant.
The Practical Impact of Low Friction
A low coefficient of friction is more than a technical specification; it is a feature that solves fundamental engineering challenges related to efficiency, durability, and performance.
Enhanced Efficiency and Energy Savings
In any system with moving parts, friction is a direct cause of energy loss. By minimizing this resistance, PTFE reduces the energy required to operate machinery.
In high-speed applications like impellers or sliding bearings, this reduction in energy consumption can be substantial, leading to significant power savings over the component's life.
Superior Durability and Component Lifespan
Friction directly causes wear and tear on material surfaces. PTFE's non-stick, low-friction nature means that parts sliding against it experience markedly less degradation.
This results in a longer service life for both the PTFE component and any material it comes into contact with, reducing maintenance frequency and replacement costs.
Ideal for Non-Stick and Sliding Applications
These properties make PTFE the premier choice for a range of specific uses where low friction is paramount. Common applications include sliding bearings, gaskets, seals, and other components that require smooth, non-stick movement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its friction performance is unmatched, selecting a material requires a holistic view. The decision to use PTFE is often solidified by its other elite properties, as the application's environment is just as important as its mechanical function.
Exceptional Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually impervious to almost all industrial solvents and corrosive chemicals. It consistently outperforms other high-performance plastics like Nylon and even PEEK in its ability to withstand harsh chemical environments.
High Thermal Stability
Beyond its chemical resilience, PTFE also offers excellent performance across a wide range of temperatures. This allows it to maintain its structural integrity and low-friction properties in conditions where other plastics would fail.
Customizable Properties
Pure PTFE is relatively soft. However, its properties, such as hardness and wear resistance, can be enhanced by adding fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze. This makes it a versatile material that can be tailored to specific industrial needs without sacrificing its core low-friction benefit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the right material depends entirely on the primary goal of your design.
- If your primary focus is minimal friction and energy efficiency: PTFE is the undisputed best choice, offering the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material.
- If your primary focus is operating in a corrosive chemical or high-temperature environment: PTFE's chemical and thermal stability make it a superior and highly reliable option.
- If your primary focus is balancing friction with specific mechanical needs: A filled grade of PTFE may provide the necessary hardness and wear resistance while maintaining excellent low-friction characteristics.
Choosing PTFE is choosing a material engineered to overcome the fundamental challenges of friction, wear, and environmental hostility.
Summary Table:
| Material | Coefficient of Friction (Dynamic) |
|---|---|
| PTFE | 0.04 – 0.08 |
| UHMW-PE | 0.10 – 0.20 |
| Acetal | 0.15 – 0.25 |
| Nylon | 0.20 – 0.30 |
Need a component with the lowest possible friction?
PTFE's unique properties deliver critical benefits for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors:
- Reduce energy consumption and operational costs.
- Extend component lifespan with superior wear resistance.
- Ensure reliable performance in harsh chemical and thermal environments.
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us engineer a solution that maximizes your efficiency and durability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered non-reactive? The Power of an Unbreakable Molecular Bond
- What is PTFE and how is it produced? The Science Behind a High-Performance Polymer
- What are the key specifications of PTFE material? Unlock Its Extreme Performance & Limits
- What happens when PTFE is incinerated? The Hidden PFAS Pollution Risk
- What certifications does the manufacturer of PTFE products hold? The ISO 9001 Assurance for Quality
- What are filled PTFE materials and what are their benefits? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What quality control measures are used in PTFE production? Ensure Material Integrity for Your Application
- Is Teflon used in medical applications? Leverage Its Biocompatibility and Low Friction



















