At its core, PTFE reduces adsorption in chromatography vials because of its extremely low surface energy. This property makes the surface chemically inert and "non-stick," preventing analytes from binding to the vial's interior and ensuring more of your sample is accurately measured.
The true value of PTFE in chromatography is not just in preventing sample loss from adsorption. It is a critical component for ensuring total sample integrity by also creating a chemically inert barrier that minimizes contamination and a secure seal that prevents evaporation.
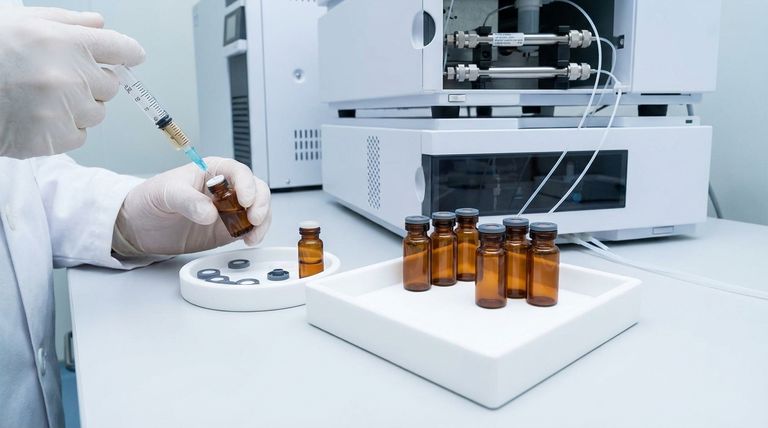

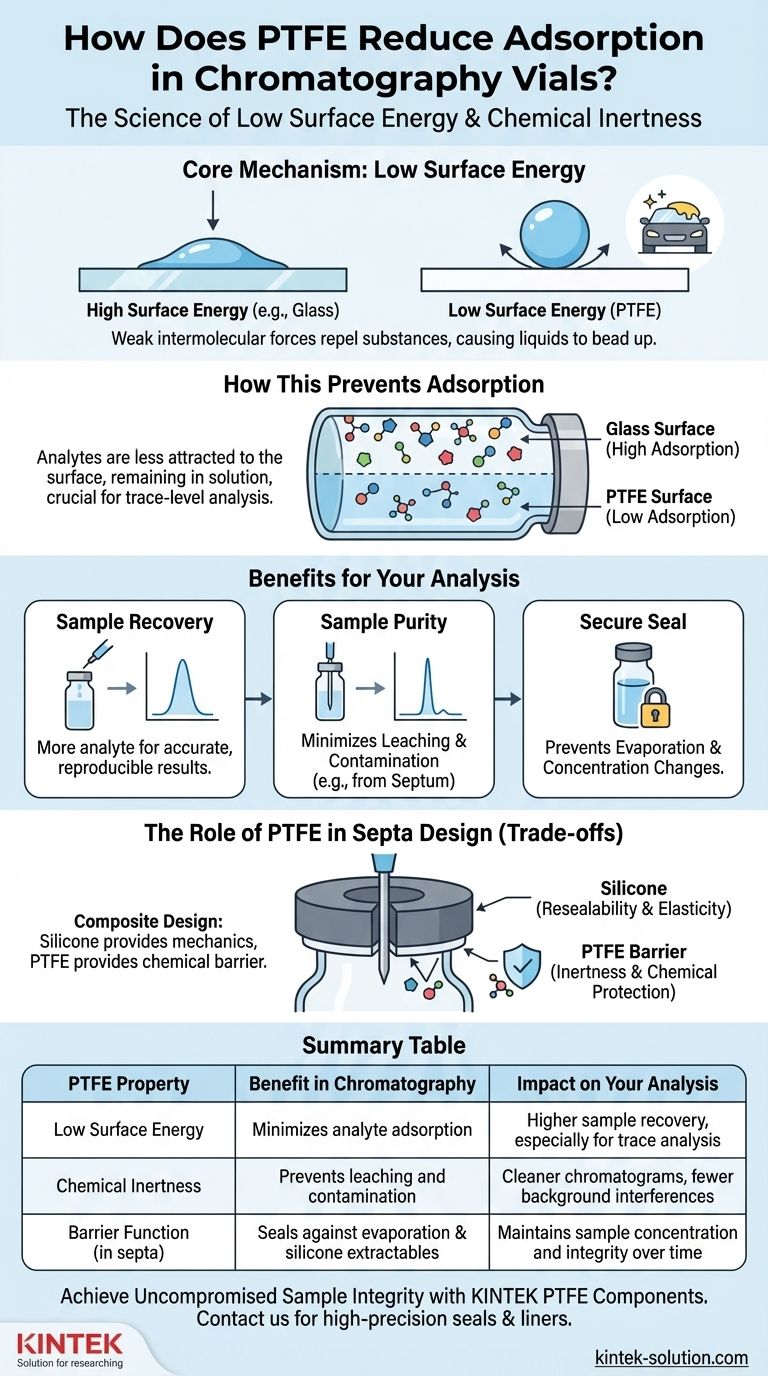
The Core Mechanism: Low Surface Energy
At the molecular level, the effectiveness of PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) comes down to a single, powerful principle: its exceptionally low surface energy. Understanding this is key to understanding its role in your lab.
What is Surface Energy?
Think of surface energy as the level of attraction a surface has for other molecules. A high-energy surface, like clean glass, readily attracts substances, causing water to spread out.
A low-energy surface, like PTFE, has very weak intermolecular forces. This repels most substances, causing liquids like water to bead up and roll off, just as on a freshly waxed car.
How This Prevents Adsorption
Analytes dissolved in a solvent are in a constant state of interaction. When they encounter the vial's inner surface, they are less attracted to the low-energy PTFE than they are to remaining in the solution.
This lack of attraction is crucial. It means your analytes, especially at very low concentrations, are far less likely to "stick" to the vial walls, a common cause of sample loss.
The Impact on Sample Recovery
By minimizing adsorption, PTFE directly improves sample recovery. More of the analyte you prepared remains in the sample when it is injected into the instrument.
This is absolutely critical for trace-level analysis, where even the smallest amount of sample loss can lead to inaccurate or non-reproducible results.
Beyond Adsorption: Ensuring Total Sample Purity
While preventing adsorption is a primary benefit, PTFE's chemical properties contribute to overall data integrity in other essential ways, particularly when used in vial septa.
Minimizing Leaching and Extractables
Septa, the seals in the vial cap, are often made of a PTFE/silicone composite. The PTFE layer acts as a vital chemical barrier.
It prevents leachables—chemicals from the softer silicone layer—from dissolving into your sample and causing contamination. This ensures that the only peaks you see in your chromatogram come from your sample, not your equipment.
Creating a Secure Seal Against Evaporation
The chemical resistance and physical properties of PTFE help create a secure and reliable seal when the cap is tightened.
This protects the sample from evaporation. If the solvent evaporates, the concentration of your analyte changes, invalidating any quantitative analysis. A proper PTFE-faced septum maintains the sample's prepared concentration over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional material, its application in chromatography involves intelligent design, most notably in the construction of septa.
The Role of Silicone in Septa
Pure PTFE can be somewhat rigid. To create a seal that can be reliably pierced by an autosampler needle multiple times, it is bonded to a layer of silicone.
The silicone provides the softness and elasticity required for a tight seal and excellent resealability after puncture.
Why the PTFE Layer is Critical
The design of a PTFE/silicone septum ensures that only the inert PTFE layer ever makes contact with your sample. The silicone provides the mechanical function, while the PTFE provides the chemical protection.
This composite structure offers the best of both worlds: the inertness of PTFE and the resealing capability of silicone, ensuring sample purity and integrity even during long analytical runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Selecting the right vial and septum combination is a critical decision based on your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is trace-level analysis: A vial and septum with a high-quality PTFE barrier is non-negotiable to prevent sample loss and ensure accurate quantification.
- If your primary focus is sample purity for sensitive methods (like LC-MS): The inertness of PTFE is essential to prevent leaching and the introduction of extractables that could interfere with your results.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput or long sequences: A well-designed PTFE/silicone septum is crucial for maintaining a reliable seal after multiple injections, preventing evaporation and cross-contamination.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE is a foundational step toward achieving reliable and reproducible analytical results.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Property | Benefit in Chromatography | Impact on Your Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Low Surface Energy | Minimizes analyte adsorption | Higher sample recovery, especially for trace analysis |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents leaching and contamination | Cleaner chromatograms, fewer background interferences |
| Barrier Function (in septa) | Seals against evaporation and silicone extractables | Maintains sample concentration and integrity over time |
Achieve Uncompromised Sample Integrity with KINTEK PTFE Components
Struggling with sample loss, contamination, or unreliable results in your chromatography workflows? The root cause may be your vial components.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware specifically for demanding applications in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial settings. Our components are engineered to provide the critical inert barrier your sensitive analyses require, ensuring maximum sample recovery and data accuracy.
Whether you need custom prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise in PTFE fabrication delivers the reliability your lab depends on.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and request a quote. Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components



















