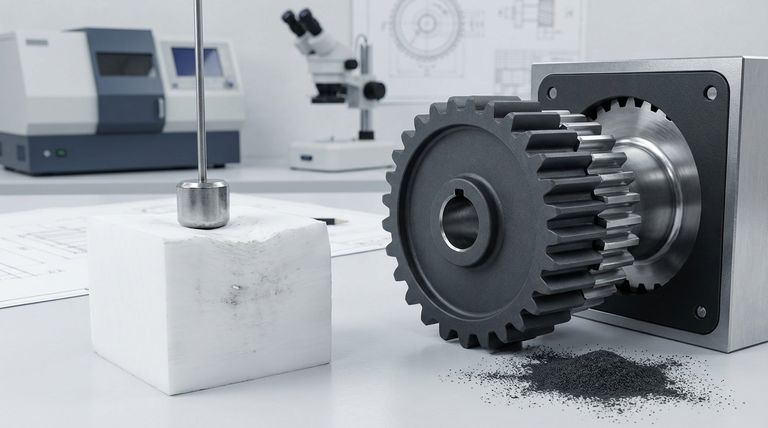
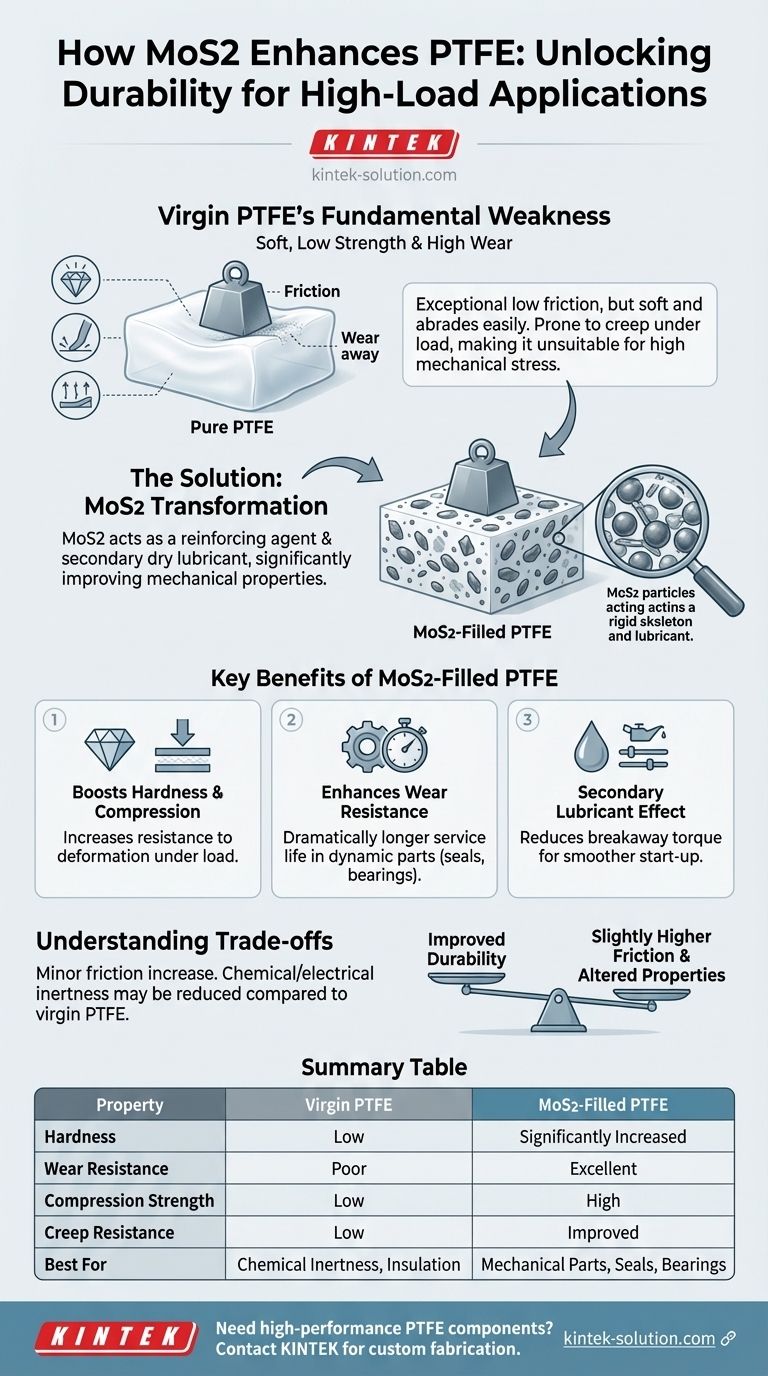
In short, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is added to PTFE to significantly improve its hardness, wear resistance, and slipperiness, especially under mechanical load. This filler acts as a solid lubricant that also reinforces the soft PTFE matrix, creating a composite material with far greater durability and strength than its virgin counterpart.
While virgin PTFE is exceptionally slippery, it is also soft and deforms easily under pressure. Molybdenum disulfide acts as a crucial reinforcing agent and a secondary dry lubricant, making the composite material much more durable and capable of handling mechanical stress.

The Fundamental Weakness of Virgin PTFE
To understand why fillers like MoS2 are necessary, we must first look at the inherent limitations of pure polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
The Paradox of Low Friction and High Wear
Virgin PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, giving it excellent non-stick and sliding properties.
However, this inherent slipperiness is paired with very low mechanical strength. The material is soft and abrades easily, leading to a high rate of wear.
Low Mechanical Strength and Creep
Pure PTFE has low tensile strength and rigidity. When subjected to a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures, it is prone to "creep," or permanently deforming over time.
This softness makes it unsuitable for most mechanical applications that involve significant pressure or structural demands.
How MoS2 Transforms PTFE's Properties
Adding molybdenum disulfide directly addresses the primary weaknesses of PTFE, creating a high-performance material for demanding applications.
A Boost in Hardness and Compression Strength
The MoS2 particles are distributed throughout the PTFE matrix, acting as a reinforcing agent. This significantly increases the material's hardness and its ability to resist deformation under compressive loads.
Enhanced Wear Resistance
By making the compound harder, MoS2 dramatically reduces the rate at which the material wears away from friction. The resulting surface is far more durable and has a much longer service life in dynamic applications like seals, bearings, and guides.
A Secondary Lubricant Effect
Molybdenum disulfide is, by itself, an excellent dry lubricant. Its inclusion in PTFE enhances the composite's overall lubricating properties.
This is particularly effective at reducing the initial force, or breakaway torque, needed to start movement after a period of rest.
A Synergistic Partnership
MoS2 is frequently used in conjunction with other fillers, such as glass fiber or bronze. This creates a synergistic effect, combining the hardness of MoS2 with the added strength and thermal conductivity of the other materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, adding any filler to PTFE introduces important considerations.
Potential Impact on Coefficient of Friction
Fillers can sometimes slightly increase the static coefficient of friction compared to pure, virgin PTFE.
However, this minor trade-off is almost always outweighed by the immense improvement in wear resistance and dimensional stability under load.
Altered Chemical and Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is valued for its exceptional chemical inertness and its properties as an excellent electrical insulator.
The addition of fillers like MoS2 can alter these characteristics. The final composite may not be suitable for applications where extreme chemical resistance or dielectric strength is the primary requirement.
Choosing the Right PTFE for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires balancing the need for low friction against the demands of the mechanical environment.
- If your primary focus is pure chemical inertness or electrical insulation: Virgin PTFE is the correct choice, provided the mechanical loads are minimal.
- If your primary focus is low-friction wear resistance under moderate loads: MoS2-filled PTFE provides a significant and cost-effective upgrade in durability.
- If your primary focus is high-load structural performance: Consider a PTFE composite with multiple fillers, such as MoS2 combined with glass or bronze, to achieve the necessary strength and wear characteristics.
Understanding these filler interactions allows you to specify a material that moves beyond simple slipperiness to deliver true engineering performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | MoS2-Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Low | Significantly Increased |
| Wear Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Compression Strength | Low | High |
| Creep Resistance | Low | Improved |
| Coefficient of Friction | Very Low | Slightly Higher, but Excellent |
| Best For | Chemical Inertness, Electrical Insulation | Mechanical Parts, Seals, Bearings, Guides |
Need a high-performance PTFE component that can handle mechanical stress?
At KINTEK, we specialize in custom fabricating PTFE components (including MoS2-filled and other advanced composites) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We can help you select the perfect material and produce precision parts from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using PTFE gaskets in high-pressure applications? Ensure a Reliable, Leak-Free Seal
- What are the key features of PTFE lined valves? Maximize Safety and Cut Costs with Corrosion-Resistant Valves
- What are the advantages of using PTFE-lined expansion joints? Achieve Superior Corrosion and Temperature Resistance
- What are PTFE-based materials composed of for RF PCB stackups? A Guide to Engineered Composites
- Why are glass-filled PTFE rods used in medical devices? Enhanced Strength and Biocompatibility for Critical Applications
- How does a PTFE lined wafer check valve function? A Guide to Reliable Backflow Prevention
- What are the temperature ranges for PTFE, PEEK, and POM ball valve seats? A Guide to Material Selection
- How does the large expansion coefficient of PTFE material affect processing? Master Dimensional Stability



















