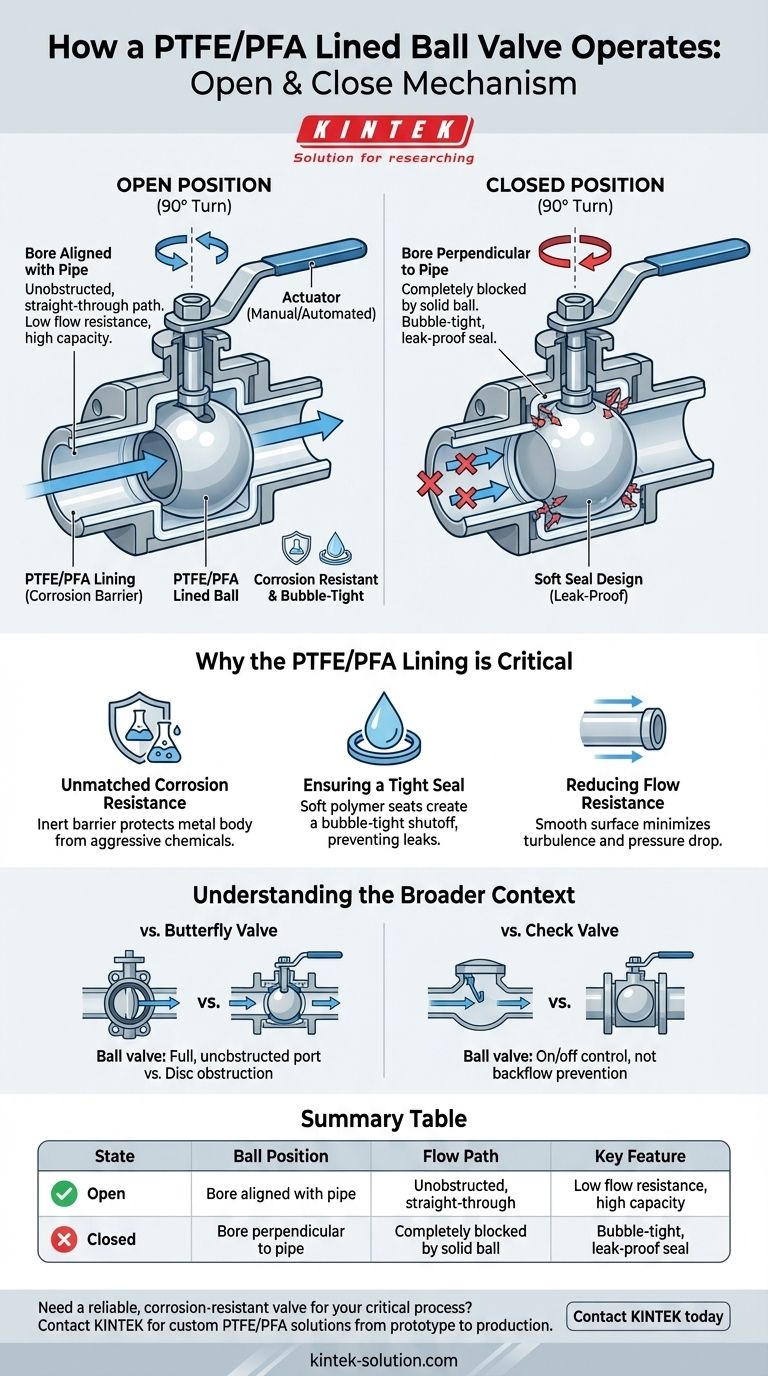
At its core, a PTFE/PFA lined ball valve operates through a simple quarter-turn mechanism. A spherical ball with a hole, known as a bore, is positioned within the valve body. When an actuator rotates this ball 90 degrees, the bore aligns with the pipe's inlet and outlet to allow flow, or it turns perpendicular to the pipe to block it completely.
The true value of a PTFE/PFA lined ball valve lies in its combination of a mechanically simple and reliable design—the rotating ball—with the superior chemical resistance of a protective polymer lining. This pairing creates a highly effective solution for controlling the flow of aggressive and corrosive media.

The Core Mechanism: A Simple Quarter-Turn
The operation of a ball valve is remarkably straightforward, which is a key reason for its widespread use in industrial applications. The entire function hinges on the rotation of the internal ball.
The "Open" Position: Unobstructed Flow
When the valve is open, the hole, or bore, through the center of the ball is aligned directly with the valve's inlet and outlet. This creates a straight, clear path for the fluid, resulting in very low flow resistance and high flow capacity.
The "Close" Position: A Solid Barrier
To close the valve, the ball is rotated a quarter-turn (90 degrees). This rotation moves the bore perpendicular to the direction of flow, presenting the solid, un-bored surface of the ball as a barrier that effectively stops the fluid.
Actuation and Control
The rotation of the ball is controlled by an external actuator connected to a stem. This can be a simple manual lever or handwheel for local operation, or it can be automated with an electric or pneumatic (gas source) actuator for remote or automated control systems.
Why the PTFE/PFA Lining is Critical
While the mechanical operation is simple, the lining is what enables this valve to perform in demanding chemical environments. The PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) or PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) layer is the component that comes into direct contact with the process fluid.
Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
The primary function of the lining is to create an inert barrier between the corrosive fluid and the valve's metal body (typically steel). This protects the structural components from attack by strong acids, alkalis, salts, and other aggressive chemicals, ensuring high chemical stability and a long service life.
Ensuring a Tight Seal
The seats, which are the components the ball presses against to stop flow, are also made from these soft polymer materials. This soft seal design allows the ball to create a bubble-tight shutoff, providing excellent sealing performance and preventing leaks.
Reducing Flow Resistance
The smooth, low-friction surface of the PTFE/PFA lining allows fluids to pass through with minimal turbulence or pressure drop. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces wear and tear on the valve's internal components over time.
Understanding the Broader Context
To fully appreciate the role of a lined ball valve, it's helpful to understand how it compares to other common valve types used in similar applications.
Ball Valves vs. Butterfly Valves
A lined butterfly valve also uses a quarter-turn mechanism but operates with a thin disc that rotates in the flow path. While effective, the disc is always present in the flow, causing some obstruction even when fully open. Ball valves, by contrast, offer a full, unobstructed port when open.
The Role of Check Valves
It's important to distinguish on/off valves from flow-directing valves. A lined check valve is designed for a completely different purpose: to allow fluid to flow in only one direction and automatically prevent any backflow. A ball valve provides no inherent protection against reverse flow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve depends entirely on the specific requirements of your system.
- If your primary focus is reliable on/off control of highly corrosive fluids: The robust chemical barrier of a PTFE/PFA lined ball valve is an ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the lowest possible pressure drop when the valve is open: The full-bore design of a ball valve offers superior performance over a butterfly valve.
- If your primary focus is ensuring a leak-proof, bubble-tight seal in the closed position: The soft-seat design inherent to lined ball valves provides exceptionally reliable sealing.
Ultimately, understanding the synergy between the simple quarter-turn mechanism and its protective polymer lining empowers you to deploy this valve with confidence in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Operation State | Ball Position | Flow Path | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open | Bore aligned with pipe | Unobstructed, straight-through | Low flow resistance, high capacity |
| Closed | Bore perpendicular to pipe | Completely blocked by solid ball | Bubble-tight, leak-proof seal |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve for your critical process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE and PFA components, including custom-lined ball valves for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our valves combine the simplicity of a quarter-turn mechanism with the superior chemical resistance of our polymer linings to ensure long-lasting, leak-proof performance with aggressive media.
Whether you require a standard design or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, we prioritize precision and durability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the tolerances for PTFE balls based on size? Precision vs. Standard Grade Explained
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What are the properties of Teflon balls? Unlock Elite Chemical & Friction Resistance
- What are the common applications of PTFE balls? Leverage Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What size range do PTFE balls come in? A Guide from 3mm to 100mm



















