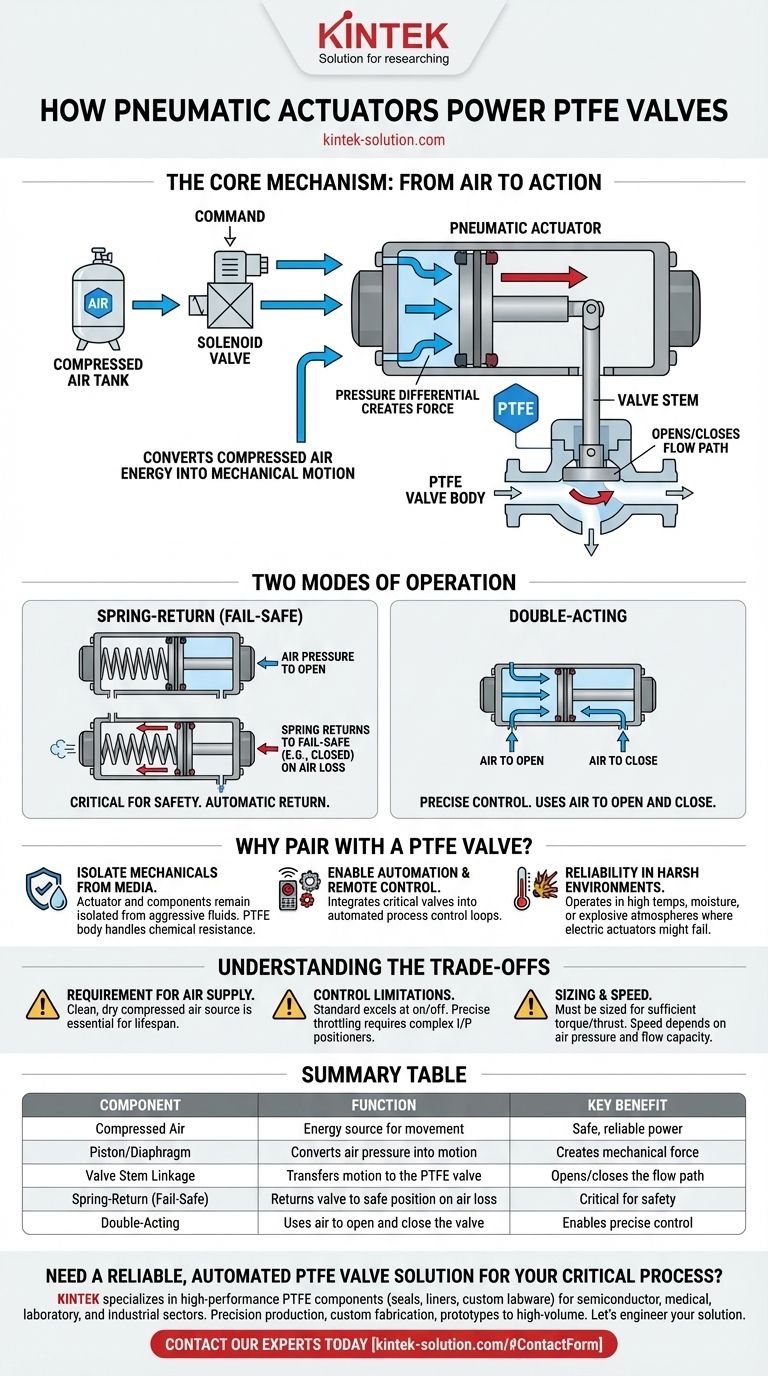
At its core, a pneumatic actuator functions by using compressed air to create mechanical force, which automatically opens or closes the connected PTFE valve. It replaces manual hand-turning with a reliable, remotely controlled system driven by air pressure acting on an internal piston or diaphragm.
The essential role of a pneumatic actuator is to convert the potential energy of compressed air into the kinetic energy of mechanical motion. This allows a chemically inert PTFE valve to be operated automatically and remotely, crucial for modern industrial process control.
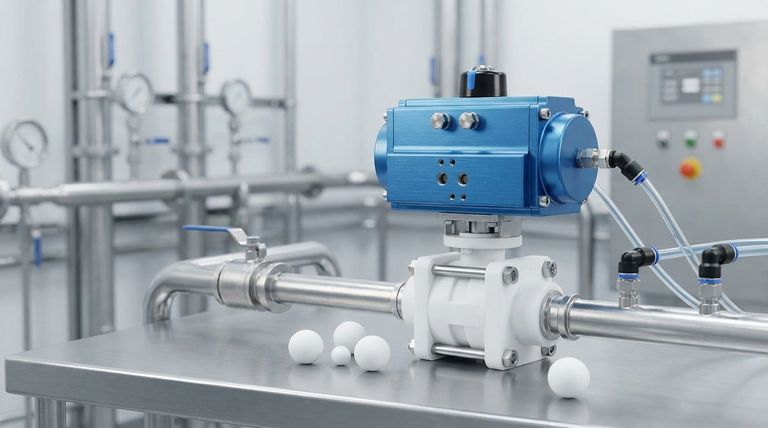

The Core Mechanism: From Air to Action
Understanding the actuator's function involves breaking it down into a few simple, sequential steps. The entire operation is a clean and direct conversion of pneumatic pressure into physical work.
The Role of Compressed Air
Compressed air serves as the energy source for the actuator. It is supplied via a pneumatic line and controlled by a separate solenoid valve, which directs the air into the actuator's inlet port on command.
The Internal Piston or Diaphragm
Inside the actuator's housing is a piston (for linear or rotary motion) or a flexible diaphragm (typically for linear motion). When compressed air enters the chamber on one side of this component, the pressure differential forces it to move.
Linkage to the Valve Stem
This movement is the "action." The piston or diaphragm is mechanically linked to the valve's stem. As the internal component moves, it drives the valve stem up, down, or in a rotation, thereby opening or closing the flow path inside the PTFE valve body.
Two Modes of Operation
Pneumatic actuators typically come in two primary configurations that determine their behavior, especially when air pressure is lost.
- Spring-Return (Fail-Safe): This design includes a powerful spring. Air pressure works against the spring to move the valve to one position (e.g., open). When the air is vented, the spring automatically forces the valve back to its default "fail-safe" position (e.g., closed). This is critical for safety.
- Double-Acting: This model has air ports on both sides of the piston. Air pressure is used to both open and close the valve. It offers more precise control but lacks an automatic fail-safe position without additional components.
Why Pair a Pneumatic Actuator with a PTFE Valve?
The pairing of a robust mechanical actuator with a chemically inert valve is a deliberate engineering choice driven by the need for both automation and material compatibility.
Isolate Mechanicals from Media
The actuator and its internal components (seals, lubricants, metals) remain completely isolated from the fluid passing through the valve. The PTFE valve body and its wetted parts provide the necessary chemical resistance, while the actuator provides the force without risk of corrosion or contamination.
Enable Automation and Remote Control
PTFE valves are often used in systems handling aggressive or high-purity chemicals where manual operation is either impractical or unsafe. A pneumatic actuator allows these critical valves to be integrated into an automated process control loop, operated from a central control room.
Reliability in Harsh Environments
Pneumatic systems are mechanically simple and highly durable. They can operate reliably in environments with high temperatures, moisture, or even explosive atmospheres where electric actuators might pose a risk or fail prematurely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, pneumatic actuation is not a universal solution. Understanding its operational requirements is key to successful implementation.
Requirement for an Air Supply
The most significant prerequisite is a source of clean, dry, compressed air. The quality and reliability of this air supply directly impact the long-term performance and lifespan of the actuator.
Control Limitations
Standard pneumatic actuators excel at simple on/off control. Achieving precise intermediate positions for flow throttling requires more complex and costly components, such as an I/P positioner, which translates an electrical control signal into variable air pressure.
Sizing and Speed
The actuator must be correctly sized to provide enough torque or thrust to overcome the forces within the valve and the process line. Actuation speed is dependent on air pressure and the flow capacity of the control solenoids and tubing.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct actuator configuration is directly tied to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is safety and reliable on/off control: A spring-return ("fail-safe") actuator is the most robust and dependable choice.
- If your primary focus is precise flow modulation: A double-acting actuator paired with a digital or analog positioner will provide the necessary fine control.
- If your primary focus is operation in a hazardous location: The inherent safety of a pneumatic system, free from electrical sparks, makes it the ideal solution for controlling your PTFE valves.
Ultimately, understanding how a pneumatic actuator works empowers you to design a more reliable, safe, and efficient fluid control system.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Compressed Air | Energy source for movement | Safe, reliable power |
| Piston/Diaphragm | Converts air pressure into motion | Creates mechanical force |
| Valve Stem Linkage | Transfers motion to the PTFE valve | Opens/closes the flow path |
| Spring-Return (Fail-Safe) | Returns valve to safe position on air loss | Critical for safety |
| Double-Acting | Uses air to open and close the valve | Enables precise control |
Need a reliable, automated PTFE valve solution for your critical process?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production and custom fabrication capabilities, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensure you get a valve and actuator system perfectly tailored to your application's safety, control, and environmental requirements.
Let's engineer your solution. Contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are common applications of low-friction PTFE? Solve Friction & Corrosion Challenges
- Why is the non-reactivity of PTFE fasteners important in medical devices? Ensuring Patient Safety and Device Integrity
- How does Reinforced PTFE differ from Virgin PTFE? Unlock the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the qualities of PTFE seals? The Key to Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What is PTFE and why is it used in sealing applications? Unlock Superior Chemical & Temperature Resistance
- What are the drawbacks of PTFE seals? Key Limitations and Design Considerations
- How does the flexibility of PTFE gaskets contribute to their versatility? Sealing Imperfect Surfaces with Ease
- What are the recommended methods for preparing metal surfaces before bonding with PTFE? Achieve a Durable, High-Strength Bond



















