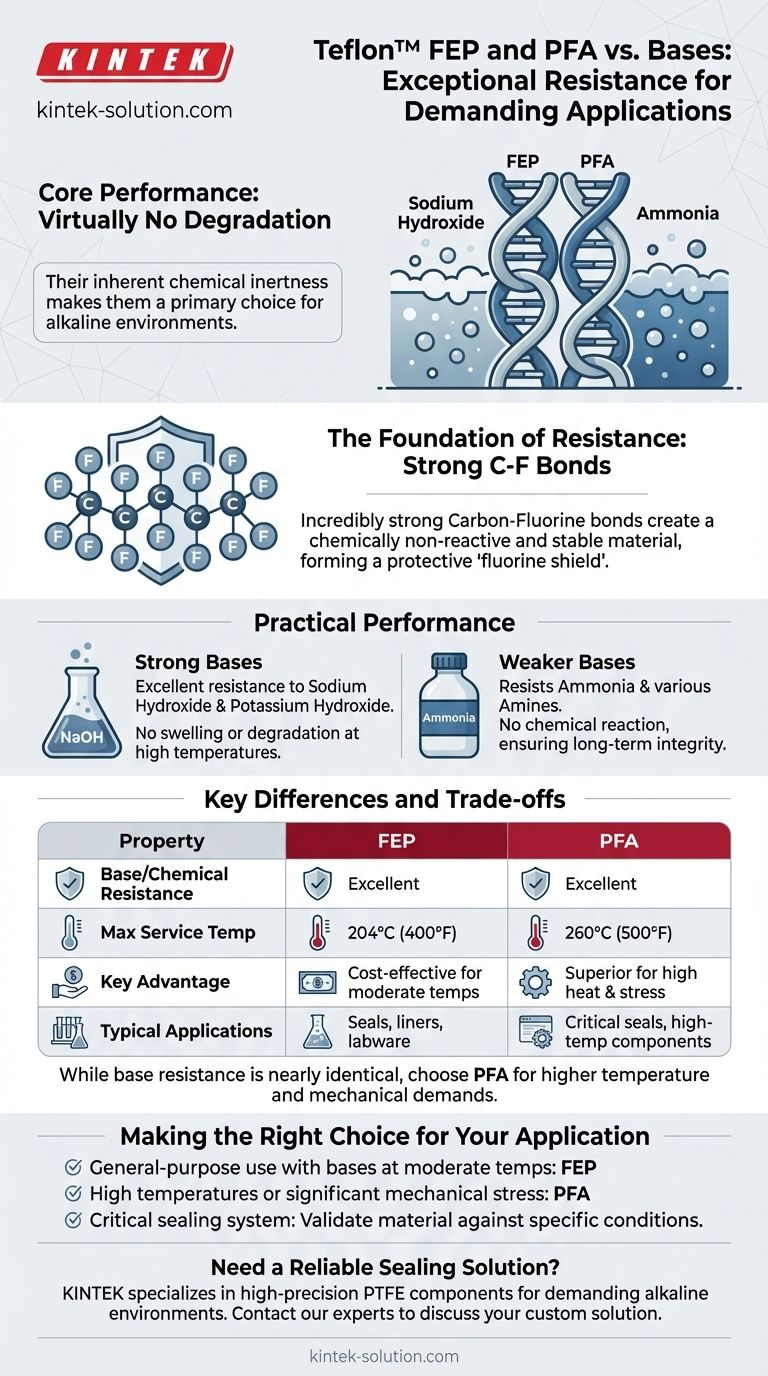
In short, both Teflon™ FEP and PFA offer exceptional resistance to bases. These materials are rated for high performance and show virtually no degradation when exposed to common bases like sodium hydroxide and ammonia. Their inherent chemical inertness makes them a primary choice for demanding applications involving alkaline environments.
The core reason for this superior performance lies in their molecular structure. The incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds that form the backbone of both FEP and PFA create a chemically non-reactive and stable material, making them suitable for sealing or containing even the most aggressive bases.

The Foundation of Resistance: Why FEP and PFA Excel
The outstanding performance of FEP (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene) and PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) is not an accident; it is a direct result of their unique fluoropolymer chemistry.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At the molecular level, these materials are built on a chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded to fluorine atoms.
The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This immense bond strength makes the polymer chain exceptionally stable and resistant to being broken apart by chemical attack.
A Protective Fluorine Shield
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. They effectively form a tight, continuous sheath around the carbon backbone.
This "fluorine shield" physically blocks chemicals, like bases, from reaching and reacting with the more vulnerable carbon chain.
Practical Performance in Basic Environments
This molecular stability translates directly into reliable real-world performance when handling both strong and weak bases.
Resistance to Strong Bases
Materials like FEP and PFA show excellent resistance to strong bases (alkalis) such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
Even at high concentrations and elevated temperatures (within the material's operating limits), they will not swell, weaken, or degrade.
Performance with Weaker Bases
The same principle of inertness applies to weaker bases, such as ammonia and various amines.
There is no risk of chemical reaction or material degradation, ensuring long-term integrity of components like O-rings, gaskets, or linings.
Understanding the Key Differences and Trade-offs
While their chemical resistance to bases is nearly identical, the choice between FEP and PFA often depends on other operational factors.
The Primary Factor: Temperature
The most significant difference between the two materials is their maximum service temperature.
PFA generally has a higher temperature rating (up to 260°C / 500°F) compared to FEP (up to 204°C / 400°F). This makes PFA the superior choice for high-heat applications.
Mechanical Properties
PFA typically offers slightly better mechanical properties, such as resistance to stress cracking and creep (deformation under load), especially at elevated temperatures.
For applications involving high mechanical stress in addition to chemical exposure, PFA provides a greater margin of safety.
Chemical Resistance Parity
For the specific purpose of resisting bases, their performance is effectively equal. A base that does not attack FEP will not attack PFA.
The decision between them should be driven by the temperature and mechanical demands of the application, not by a difference in their resistance to bases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Base Application
Your selection should be based on the complete operational environment, not just the chemical compatibility.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose use with bases at moderate temperatures: FEP is an extremely reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your application involves high temperatures or significant mechanical stress: PFA is the more robust option, providing a crucial safety margin.
- If you are designing a critical sealing system: Always validate your material choice against the specific concentration, temperature, and pressure of your application.
By leveraging the inherent chemical stability of these fluoropolymers, you can engineer a highly reliable solution for nearly any challenge involving basic media.
Summary Table:
| Property | FEP | PFA |
|---|---|---|
| Base/Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Max Continuous Service Temp | 204°C (400°F) | 260°C (500°F) |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective for moderate temps | Superior for high heat & stress |
| Typical Applications | Seals, liners, labware | Critical seals, high-temp components |
Need a Reliable Sealing Solution for Aggressive Bases?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including FEP and PFA seals, liners, and custom labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components withstand demanding alkaline environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and receive a custom solution tailored for performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- PTFE Deep Evaporating Dishes Customizable Laboratory and Industrial Solutions
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What advantages do the low friction and non-stick properties of PTFE gaskets provide? Boost System Reliability and Purity
- What additional properties do PTFE O-rings require besides thermal resistance? Master Chemical and Mechanical Sealing
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE lined and hard seal butterfly valves? Ensure Optimal Performance and Safety
- What makes PTFE lip seals suitable for aerospace applications? Unmatched Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How do composite bellows compare to PTFE bellows? Choose the Right Bellow for Your Application
- What is PTFE and what are its common applications? Discover the Versatile High-Performance Polymer
- What cooling and lubrication techniques are recommended for PTFE machining? Master Heat Control for Precision Parts
- What types of PTFE products are available for fluid handling solutions? Your Guide to High-Purity Components



















