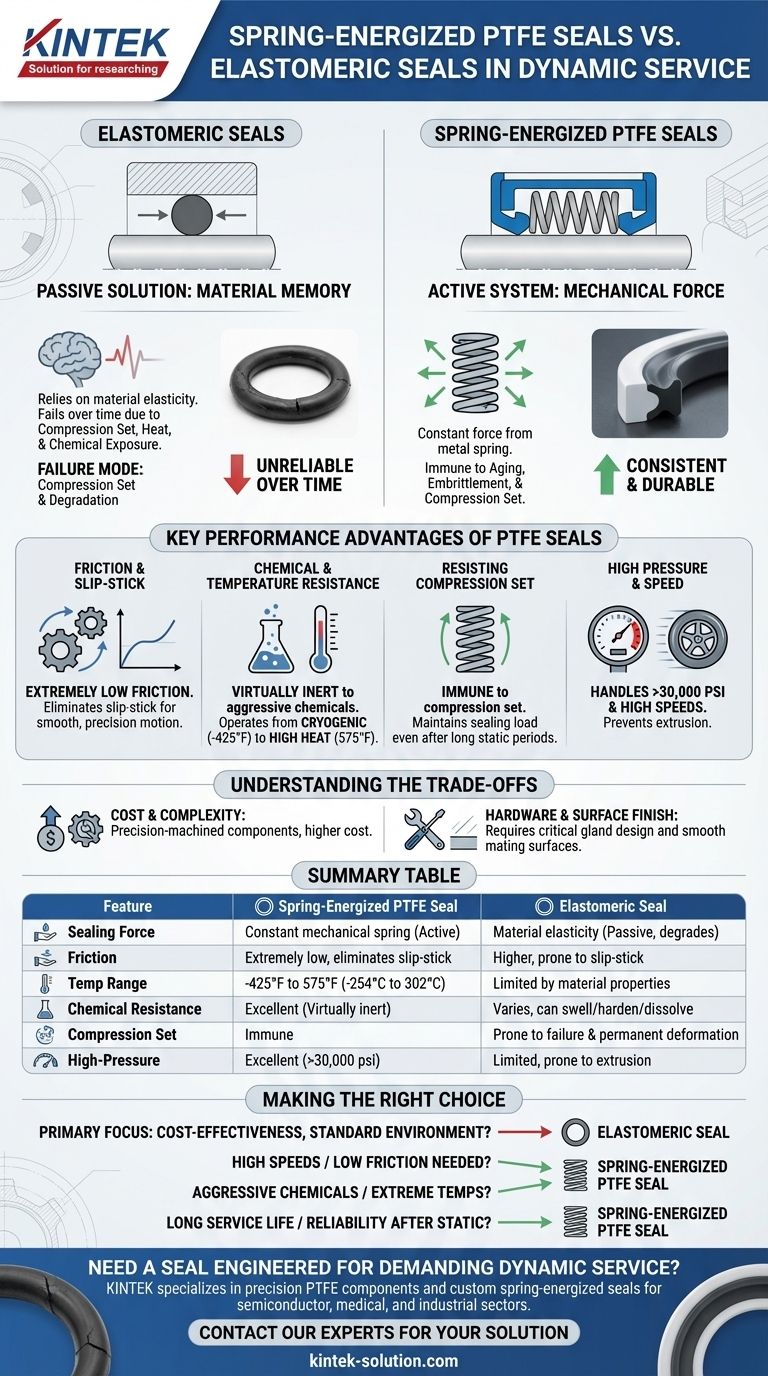
In dynamic service, spring-energized PTFE seals fundamentally outperform elastomeric seals in applications involving extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, high pressures, or the need for very low friction. While elastomeric seals rely on material memory for sealing force, which degrades over time, PTFE seals use a mechanical spring to provide a constant, reliable force, making them the superior choice for demanding, high-performance systems.
The core difference is simple: elastomeric seals are a passive solution relying on material properties that can fail, while spring-energized PTFE seals are an active system engineered for consistent performance where conventional seals cannot survive.

The Fundamental Difference: Mechanical Force vs. Material Memory
To understand the performance gap, you must first understand how each seal generates its sealing force. Their core mechanisms are fundamentally different and dictate their ideal use cases.
How Elastomeric Seals Work
Elastomeric seals, like O-rings, function by being compressed into a gland. They rely entirely on the material's inherent elasticity, or "memory," to push back against the mating surfaces and create a seal.
This reliance on material properties is also their primary weakness in dynamic applications. Over time, factors like heat, chemical exposure, and sustained compression cause the elastomer to lose its memory.
This phenomenon is known as compression set, where the seal permanently deforms and can no longer exert enough force to prevent leaks.
How Spring-Energized PTFE Seals Work
Spring-energized seals are a two-part system: a precision-machined jacket made of low-friction PTFE and an internal energizing spring.
The spring, not the jacket material, provides the primary sealing force. It exerts a constant, consistent radial load on the PTFE lips, forcing them against the sealing surfaces.
This design decouples the sealing force from the material's memory. The metal spring is immune to aging, embrittlement, and compression set, ensuring reliable sealing for the life of the component.
Key Performance Advantages in Dynamic Service
This fundamental design difference gives spring-energized PTFE seals a decisive edge in several critical performance areas common in dynamic systems.
Overcoming Friction and Slip-Stick
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction. This dramatically reduces drag and heat generation in high-speed rotary or reciprocating applications.
Crucially, it eliminates slip-stick, a phenomenon where high-friction elastomeric seals can adhere to the mating surface, causing jerky, uncontrolled motion. This is unacceptable in precision systems.
Unmatched Chemical and Temperature Resistance
PTFE jackets are virtually inert to all industrial chemicals, solvents, acids, and bases. This eliminates the need for extensive fluid compatibility checks required for elastomers, which can swell, harden, or dissolve when exposed to the wrong media.
These seals operate reliably in an exceptionally wide temperature range, from cryogenic conditions (-425°F / -254°C) up to high-heat applications (575°F / 302°C), where elastomers would become brittle or degrade completely.
Resisting Compression Set and Aging
Because the metal spring provides the force, the seal is immune to compression set. It maintains a consistent sealing load whether the system is in motion or has been sitting static for long periods.
This prevents the common failure mode where an elastomeric seal takes a set and leaks upon startup after a period of inactivity.
Handling High Pressure and Speed
The constant force from the spring ensures the sealing lip remains in firm contact with the mating surface, even under high pressures (over 30,000 psi) and high surface speeds.
This robust design prevents the seal from being extruded into clearance gaps, a common failure point for elastomers under high pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a spring-energized seal is an engineering decision, and it's critical to understand the trade-offs to make the right choice.
Cost and Complexity
Spring-energized PTFE seals are precision-machined components. They are inherently more complex and costly to manufacture than a standard molded elastomeric O-ring.
Hardware and Surface Finish
While robust, these seals perform best with specific hardware considerations. Gland design and surface finish on the mating components are critical to ensure a long, leak-free service life. They are generally less forgiving of poor surface conditions than a soft elastomer.
When Elastomers Are the Right Choice
For countless static or low-demand dynamic applications with moderate temperatures, compatible fluids, and low pressures, an elastomeric seal is often the most cost-effective and perfectly suitable solution. Their value in these scenarios is undisputed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The selection process should be driven entirely by the performance demands and failure risks of your specific system.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a standard environment: An elastomeric seal is the logical and most efficient choice.
- If your application involves high speeds or requires low, consistent friction: The inherent properties of a spring-energized PTFE seal are essential to prevent slip-stick and wear.
- If the seal will be exposed to aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures: A spring-energized PTFE seal is often the only reliable option to ensure system integrity.
- If you require long service life and reliability after long static periods: The PTFE seal's immunity to compression set provides a clear advantage.
Ultimately, the choice requires moving beyond a default component and selecting the seal that is truly engineered to meet the demands of your dynamic system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spring-Energized PTFE Seal | Elastomeric Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Force | Constant mechanical spring | Material elasticity (degrades) |
| Friction | Extremely low, eliminates slip-stick | Higher, prone to slip-stick |
| Temp Range | -425°F to 575°F (-254°C to 302°C) | Limited by material |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Virtually inert) | Varies, can swell/harden |
| Compression Set | Immune | Prone to failure |
| High-Pressure Performance | Excellent (>30,000 psi) | Limited, prone to extrusion |
Need a Seal Engineered for Demanding Dynamic Service?
If your application involves extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, high pressures, or requires very low friction, a standard elastomeric seal may not be sufficient. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom spring-energized seals, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide reliable sealing solutions that deliver:
- Long-term performance in the harshest conditions.
- Consistent, low-friction operation for precision systems.
- Custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume production.
Don't let seal failure risk your system's integrity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a solution engineered for performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How do the non-stick properties of PTFE benefit sealing technology? Enhance Seal Life and Purity
- What are some common industries and applications for PTFE/Teflon machined parts? Solve Harsh Environment Challenges
- What makes ePTFE gaskets effective against gas leakage? The Key to Superior Gas Sealing
- What future trends are expected in Teflon parts machining? AI, Automation, and Sustainability
- How does PTFE Liner perform under heavy loads? Superior Durability for Demanding Applications
- In which industries or applications are PTFE O-rings typically used? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE and EPDM valve seats? Ensure Reliable Fluid Control
- Why might an engineer choose to stick with standard O-rings for long-running applications? Maximize Reliability & Minimize Risk



















