In any demanding industrial piping system, the choice of expansion joint material dictates reliability and longevity. While rubber offers flexibility and metal provides strength, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) expansion joints occupy a unique and critical position. They combine near-universal chemical resistance with a wide operating temperature range, making them the superior choice for systems handling corrosive media under extreme thermal conditions.
An engineer's choice often appears to be between the flexibility of rubber and the high-pressure tolerance of metal. However, the deep need is for reliability in harsh environments. PTFE resolves this by offering a solution that excels where both rubber and metal fail: resisting chemical attack and temperature extremes simultaneously.

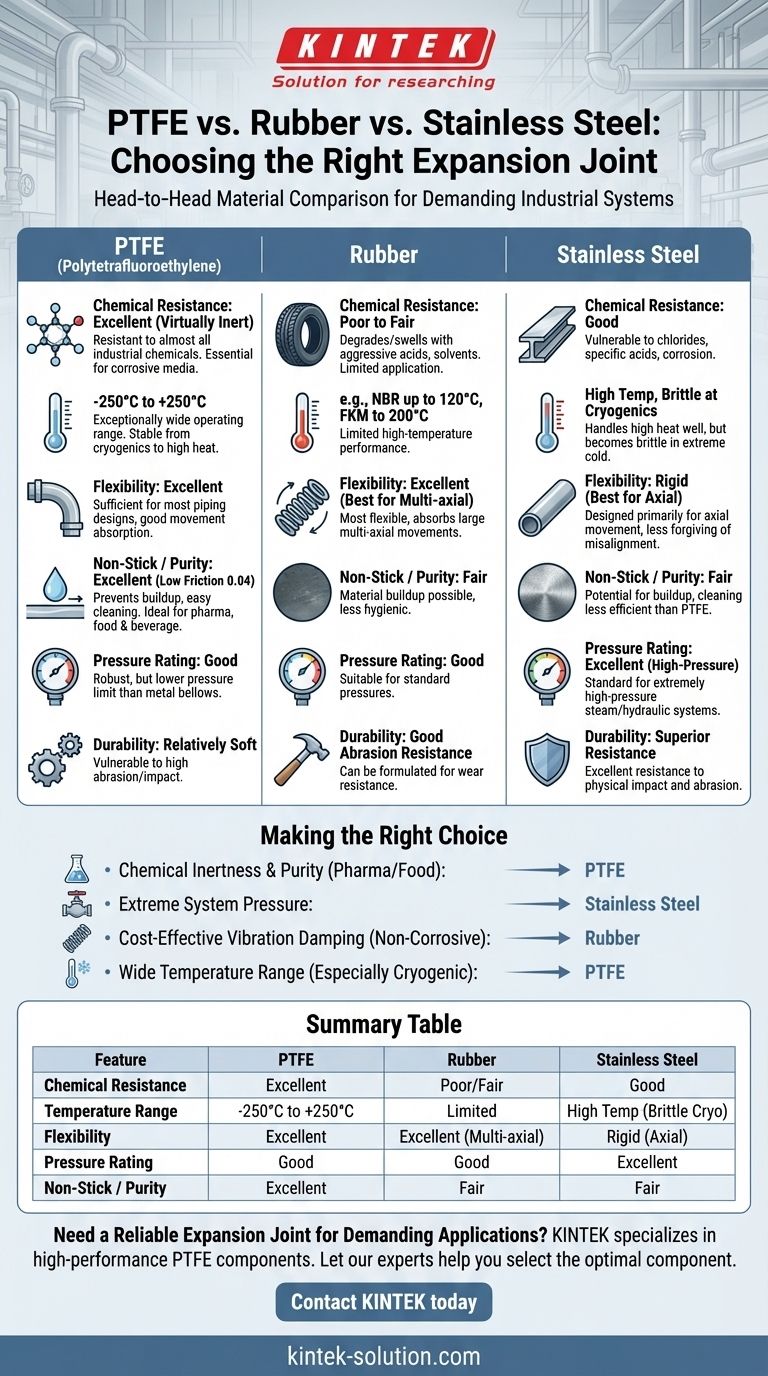
A Head-to-Head Material Comparison
To select the right expansion joint, you must evaluate how each material performs against your system's specific demands. The differences between PTFE, rubber, and stainless steel are not subtle; they are fundamental.
Chemical Resistance: PTFE's Defining Strength
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to almost all industrial chemicals, a property no rubber or standard metal can claim. This makes it essential for applications in chemical processing plants.
While specialized elastomers exist, most rubber compounds will degrade, swell, or fail when exposed to aggressive acids, solvents, or caustics. Stainless steel, while robust, is vulnerable to corrosion from chlorides, acids, and other specific chemical agents.
Temperature Operating Range: A Game of Extremes
PTFE offers an exceptionally wide working temperature range, from cryogenic lows of -250°C (-418°F) up to 250°C (482°F). This far exceeds the capabilities of most common elastomers.
For comparison, standard NBR rubber is limited to about 120°C (248°F), and even high-performance FKM (Viton) tops out around 200°C (392°F). While some metals handle higher temperatures, they can become brittle at the cryogenic levels where PTFE remains stable.
Flexibility and Movement Absorption
An expansion joint must absorb thermal movement, vibration, and system misalignment. In this category, rubber is the most flexible material, capable of absorbing large multi-axial movements.
PTFE offers excellent flexibility, sufficient for the vast majority of piping system designs. Metal bellows, by contrast, are far more rigid. They are primarily designed for axial movement and are less forgiving of lateral or angular misalignments.
Friction and Purity: The Non-Stick Advantage
PTFE possesses the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid engineering material, often cited as low as 0.04. This creates a non-stick surface that is critical for purity and performance.
In pharmaceutical or food and beverage applications, this prevents material buildup and allows for easy, reliable cleaning. This low-friction property also reduces the force required to actuate the joint, minimizing stress on the piping system. Rubber and metal surfaces do not share this inherent non-stick characteristic.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every scenario. Acknowledging the limitations of PTFE is key to making an informed engineering decision.
Pressure Handling Capabilities
The primary advantage of metal bellows expansion joints is their ability to withstand extremely high pressures. Standard PTFE expansion joints, while robust, generally have lower pressure ratings than their metal counterparts. For high-pressure steam or hydraulic systems, metal is often the default choice.
Physical Abrasion and Durability
PTFE is a relatively soft material. In pipelines carrying abrasive slurries or high-velocity particulates, a specialized abrasion-resistant rubber liner might offer a longer service life. Metal joints also provide superior resistance to physical impact and abrasion compared to any polymer-based joint.
Initial Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
PTFE is a high-performance material, and its initial procurement cost is typically higher than that of a standard rubber expansion joint. However, in a corrosive environment, its vastly superior lifespan and the prevention of costly downtime often result in a significantly lower total cost of ownership.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Your selection must align directly with the primary operational challenge your system faces.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness and purity: PTFE is the unparalleled choice, essential for aggressive chemicals, pharmaceuticals, or food-grade applications.
- If your primary focus is handling extreme system pressure: A stainless steel or other metal alloy expansion joint remains the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective vibration damping in a non-corrosive system: A standard rubber expansion joint provides the most economical solution.
- If your primary focus is a wide temperature range, especially cryogenic: PTFE offers superior performance and stability over almost all rubber alternatives.
By understanding these core material trade-offs, you can specify an expansion joint that ensures the long-term integrity and efficiency of your piping system.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE | Rubber | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Virtually Inert) | Poor to Fair (Degrades) | Good (Vulnerable to Chlorides/Acids) |
| Temperature Range | -250°C to +250°C | Limited (e.g., NBR to 120°C) | High Temp (Brittle at Cryogenics) |
| Flexibility | Excellent | Excellent (Best for Multi-axial) | Rigid (Best for Axial) |
| Pressure Rating | Good | Good | Excellent (High-Pressure) |
| Non-Stick / Purity | Excellent (Low Friction) | Fair | Fair |
Need a Reliable Expansion Joint for Demanding Applications?
Choosing the right material is critical for your system's reliability and longevity. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, precision PTFE components like seals, liners, and custom expansion joints for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand the challenges of harsh environments. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific chemical, temperature, and pressure requirements, maximizing your system's uptime and efficiency.
Let our experts help you select the optimal component. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What industrial applications commonly use PTFE packing? Essential Sealing Solutions for Demanding Industries
- What are the electrical applications of PTFE sheets? Unlock Superior Insulation for Demanding Electronics
- What is a PTFE gasket? The Ultimate Seal for Extreme Chemicals and Temperatures
- How does the lifespan of PTFE oil seals compare to other types? Achieve 10,000-50,000 Hours of Reliability
- Why is Teflon's heat resistance important in food processing? Ensure Safety and Efficiency
- What industries benefit from using PTFE rod in bearings and bushings? Enhance Performance in Demanding Environments
- How do rubber gaskets compare to PTFE gaskets? Choose the Right Seal for Your Application
- What are the common plumbing applications of PTFE? Ensure Leak-Proof, Durable Seals



















