In essence, fillers are added to PTFE to fundamentally enhance its mechanical and thermal properties. While virgin PTFE is exceptionally low-friction and chemically inert, it is also soft and prone to deforming under load. Fillers introduce crucial characteristics like vastly improved wear resistance, dimensional stability, and hardness, transforming PTFE into a robust composite material for demanding engineering applications.
While virgin PTFE offers unmatched chemical resistance and lubricity, it lacks the structural integrity for many mechanical uses. Fillers act as a reinforcing matrix, transforming PTFE from a soft polymer into a high-performance engineering composite with drastically improved resistance to wear, creep, and heat.

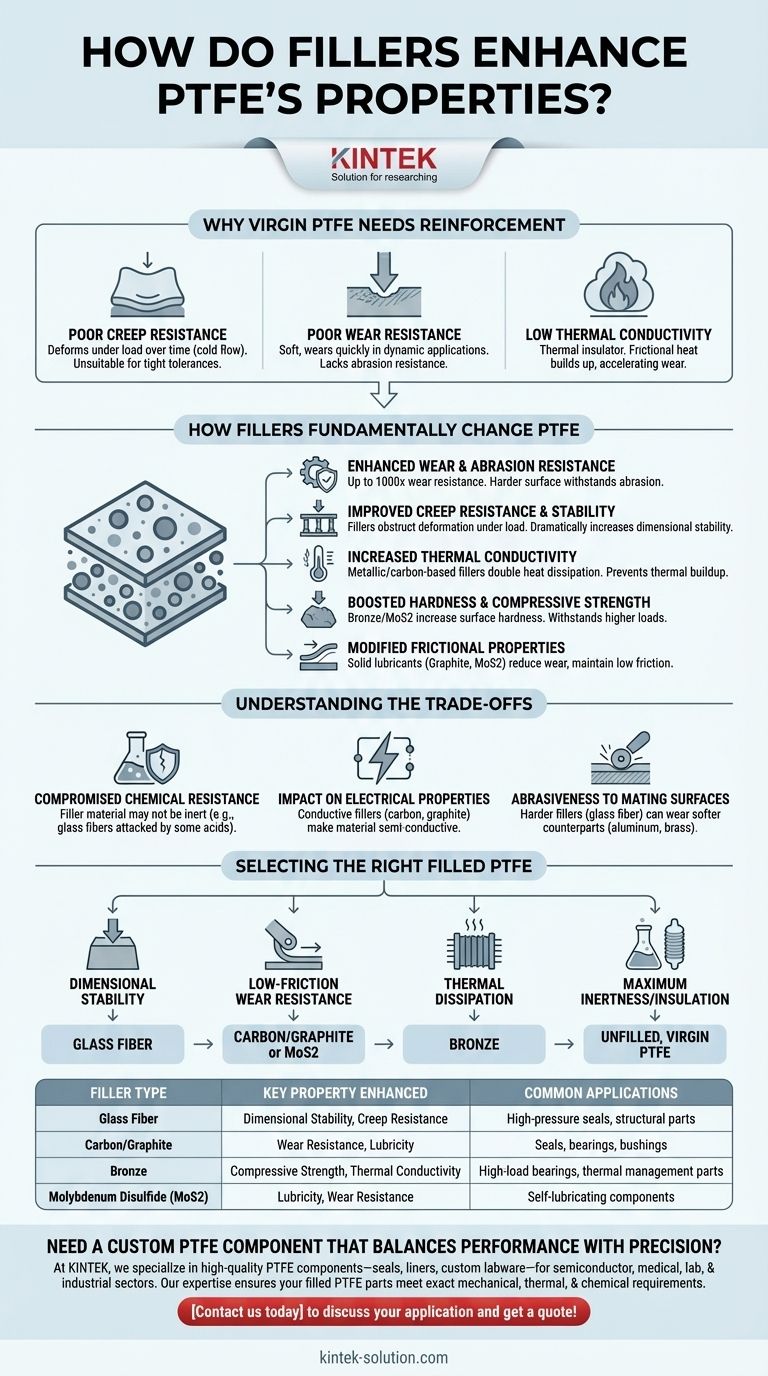
Why Virgin PTFE Needs Reinforcement
To understand the role of fillers, we must first recognize the inherent limitations of pure, or "virgin," PTFE.
The Challenge of "Creep"
Virgin PTFE exhibits poor creep resistance, meaning it deforms permanently over time when subjected to a constant load, a phenomenon also known as cold flow. This makes it unsuitable for holding tight tolerances in components under pressure.
Poor Wear Resistance
Despite its low coefficient of friction, pure PTFE is very soft and wears away quickly in dynamic applications. It lacks the abrasion resistance needed for seals, bearings, or bushings that experience repetitive motion.
Low Thermal Conductivity
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator. In moving parts, this becomes a disadvantage, as frictional heat builds up instead of dissipating, which can accelerate wear and cause component failure.
How Fillers Fundamentally Change PTFE
Fillers are not just additives; they create a composite material where the filler particles provide a structural backbone within the soft PTFE matrix.
Enhancing Wear and Abrasion Resistance
This is the most significant improvement. Research shows that filled PTFE can have up to 1000 times the wear resistance of unfilled PTFE. Fillers like carbon, graphite, and bronze provide a harder surface that withstands abrasion far more effectively.
Improving Creep Resistance and Stability
Fillers like glass fiber physically obstruct the PTFE from deforming under load. This dramatically increases the material's dimensional stability and allows it to be used in high-pressure sealing and structural applications.
Increasing Thermal Conductivity
Metallic and carbon-based fillers are much more thermally conductive than the base polymer. By adding them, the composite's ability to dissipate heat can be doubled, preventing thermal buildup in high-speed or high-load parts.
Boosting Hardness and Compressive Strength
Fillers like bronze and molybdenum disulfide increase the surface hardness and compressive strength of PTFE. This allows the material to withstand higher loads without being crushed or extruded.
Modifying Frictional Properties
While some fillers can slightly increase the static coefficient of friction, others like graphite and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) are solid lubricants. They create a self-lubricating surface that reduces wear and maintains low friction in dynamic systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Adding fillers is an engineering compromise. Enhancing one property often means sacrificing another.
Compromised Chemical Resistance
The primary trade-off is a reduction in chemical inertness. While PTFE itself is resistant to nearly all chemicals, the filler material may not be. For example, glass fibers can be attacked by hydrofluoric acid and strong alkalis.
Impact on Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators available. Adding conductive fillers like carbon or graphite will change this property, making the material semi-conductive or static-dissipative.
Abrasiveness to Mating Surfaces
Harder fillers, particularly glass fiber, can be abrasive to softer mating surfaces like aluminum or brass. The selection of both the filled PTFE and the counterpart material must be considered together.
Selecting the Right Filled PTFE for Your Application
The choice of filler should be driven entirely by the primary demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability under static load: A glass-filled compound is often the most effective and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is low-friction wear resistance in dynamic applications: A carbon-graphite or MoS2-filled compound provides excellent lubricity and durability.
- If your primary focus is thermal dissipation in a high-load environment: A bronze-filled compound offers superior thermal conductivity and compressive strength.
- If your primary focus is preserving maximum chemical inertness and electrical insulation: Unfilled, virgin PTFE remains the superior option, provided its mechanical limitations are acceptable.
By understanding these enhancements and their associated trade-offs, you can select a material precisely tailored to your engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Key Property Enhanced | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | Dimensional Stability, Creep Resistance | High-pressure seals, structural parts |
| Carbon/Graphite | Wear Resistance, Lubricity | Seals, bearings, bushings |
| Bronze | Compressive Strength, Thermal Conductivity | High-load bearings, thermal management parts |
| Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2) | Lubricity, Wear Resistance | Self-lubricating components |
Need a custom PTFE component that balances performance with precision?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication (from prototypes to high-volume orders) ensures your filled PTFE parts meet exact mechanical, thermal, and chemical requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















