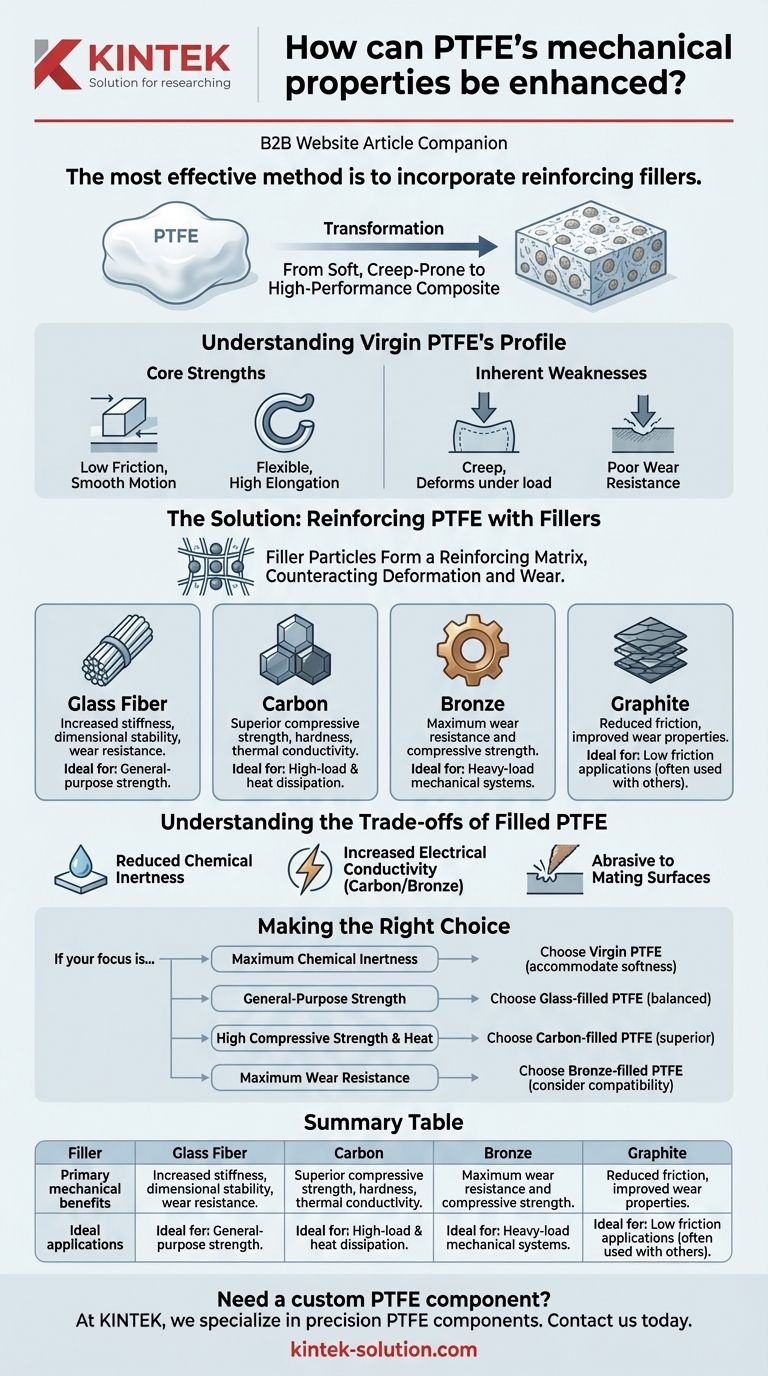
To enhance the mechanical properties of PTFE, the most effective method is to incorporate reinforcing fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or bronze. Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is inherently soft and prone to deforming under load (creep), but these additives create a composite material with significantly improved tensile strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to wear for more demanding applications.
Virgin PTFE excels in low-friction and chemical resistance but often fails in demanding mechanical roles due to its softness and tendency to creep. By adding specific fillers, you fundamentally trade some of its original properties to create a high-performance engineering material tailored for strength and durability.

Understanding Virgin PTFE's Mechanical Profile
The Core Strengths: Low Friction and Flexibility
Virgin PTFE is renowned for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction. Its static and dynamic friction coefficients are nearly identical, which prevents "stick-slip" behavior and allows for incredibly smooth transitions from a standstill to motion.
It is also highly flexible, with a very high elongation at break (200-400%). This allows it to conform to surfaces, making it an excellent material for seals.
The Inherent Weaknesses: Creep and Poor Wear Resistance
The primary mechanical weakness of unfilled PTFE is creep. This is the tendency for the material to deform permanently when subjected to a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures.
This softness also results in relatively low wear and abrasion resistance. In applications with repetitive motion or contact with abrasive surfaces, virgin PTFE will wear away quickly.
The Solution: Reinforcing PTFE with Fillers
How Fillers Fundamentally Change the Material
Fillers create a composite structure. The small, hard particles or fibers of the filler material form a reinforcing matrix within the softer PTFE, directly counteracting its tendency to deform and wear.
This addition transforms PTFE from a soft, compliant material into a robust engineering plastic capable of bearing significant loads.
Common Fillers and Their Primary Benefits
Different fillers are chosen to enhance specific properties:
- Glass Fiber: This is a common, general-purpose filler. It significantly increases stiffness, dimensional stability, and wear resistance.
- Carbon: Adding carbon increases compressive strength, hardness, and wear resistance. It also improves thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat in high-speed applications.
- Bronze: This filler provides the greatest improvement in wear resistance and compressive strength, making it ideal for high-load mechanical systems.
- Graphite: Often used in combination with other fillers (like carbon), graphite reduces the coefficient of friction and improves wear properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Filled PTFE
The Impact on Chemical Resistance
The primary trade-off is a potential reduction in chemical inertness. Virgin PTFE is resistant to nearly all chemicals, but fillers like glass or bronze can be attacked by certain aggressive media.
Changes in Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator. The addition of carbon or bronze makes the composite material more electrically conductive, which can be a critical design consideration.
Considerations for Mating Surfaces
Abrasive fillers, particularly glass fiber, can increase the wear rate of the mating surface they slide against. This is especially true for softer materials like aluminum or other plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness and purity: Virgin PTFE is the only option; your design must accommodate its mechanical softness.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose strength and stability: Glass-filled PTFE offers a balanced improvement in wear resistance and reduced creep.
- If your primary focus is high compressive strength and heat dissipation: Carbon-filled PTFE provides superior hardness, load capacity, and thermal conductivity.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance under heavy loads: Bronze-filled PTFE delivers the highest performance but requires careful consideration of chemical compatibility.
Ultimately, selecting the right PTFE composite is about precisely matching the filler to your specific mechanical challenge.
Summary Table:
| Filler Type | Primary Mechanical Benefits | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Fiber | Increased stiffness, dimensional stability, wear resistance | General-purpose strength and stability |
| Carbon | Superior compressive strength, hardness, thermal conductivity | High-load applications and heat dissipation |
| Bronze | Maximum wear resistance and compressive strength | Heavy-load mechanical systems |
| Graphite | Reduced friction, improved wear properties (often used with other fillers) | Applications requiring low friction and wear resistance |
Need a custom PTFE component that balances strength, wear resistance, and chemical compatibility?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require virgin PTFE for ultimate chemical purity or a reinforced composite for demanding mechanical applications, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our expertise enhance your project's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is a PTFE sliding rubber bearing pad and its primary use? Essential for Bridge & Building Movement
- How does the durability of PTFE expansion bellows compare to rubber alternatives? Maximize Lifespan in Harsh Environments
- How does FR4 PCB material compare to PTFE in terms of electrical properties? Choose the Right Material for Your Application.
- What are the advantages of bronze-filled PTFE bushes? Boost Load Capacity & Wear Resistance
- What design parameter must be considered when applying wide contact to spring-activated PTFE lip seals? Prevent Bell Mouthing to Avoid Catastrophic Leakage
- What is the temperature range for PTFE oil seals and conventional oil seals? A Guide to Extreme vs. Standard Performance
- How do PTFE coated fasteners perform in marine and offshore environments? Superior Corrosion Protection for Critical Assets
- What types of fluids can PTFE O-Rings repel? The Ultimate Guide to Chemical Resistance



















