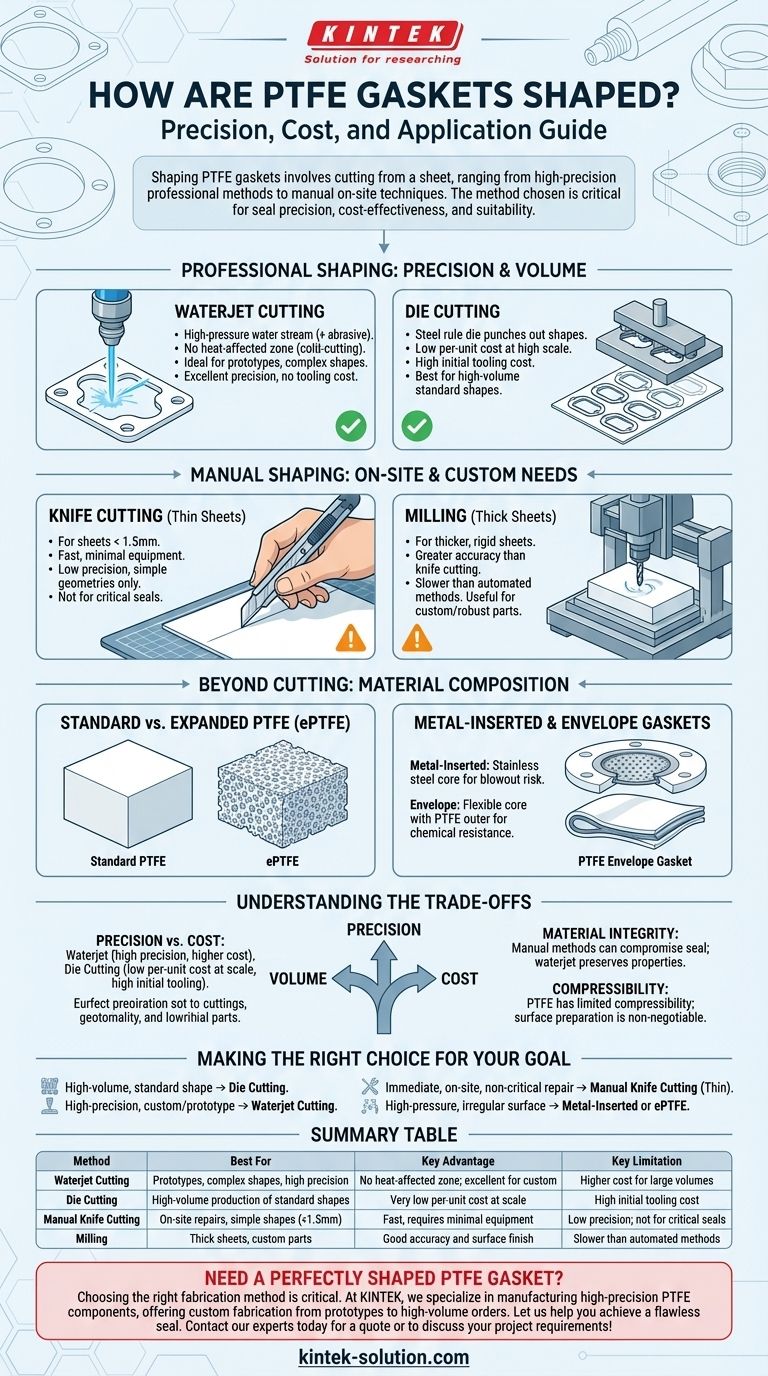
At its core, shaping a PTFE gasket involves cutting it from a sheet of material. This can be accomplished through high-precision professional methods like waterjet or die cutting, or it can be done manually for less critical applications by using a knife for thin sheets and milling for thicker sections.
The method used to shape a PTFE gasket is not just about achieving a specific form; it's a critical decision that directly impacts the seal's precision, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for the intended application.

Professional Shaping Methods: Precision and Volume
For applications demanding high precision, repeatability, and reliability, professional fabrication is the standard. These methods ensure the gasket meets exact specifications, which is crucial for effective sealing.
Waterjet Cutting
A waterjet uses a highly pressurized stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive, to cut through the PTFE sheet. This computer-controlled process is exceptionally precise.
Because it is a cold-cutting method, there is no heat-affected zone, meaning the material properties of the PTFE at the edge of the gasket are not altered. This makes it ideal for complex shapes, prototypes, and one-off requirements.
Die Cutting
Die cutting is the go-to method for high-volume production of standardized gaskets. A sharp steel rule, bent into the desired shape (the "die"), is pressed onto the PTFE sheet to punch out the gasket.
While there is an initial tooling cost to create the die, the per-unit cost becomes very low at scale. This makes it the most economical choice for producing hundreds or thousands of identical gaskets.
Manual Shaping: On-Site and Custom Needs
In maintenance, repair, or prototyping scenarios, it is sometimes necessary to shape a gasket on-site from a stock sheet of PTFE.
Knife Cutting for Thin Sheets
For thin PTFE sheets (typically under 1.5mm or 1/16"), a sharp utility knife can be used. This method is fast and requires minimal equipment.
However, it lacks the precision of automated methods and is only suitable for simple geometries and less demanding, non-critical sealing applications.
Milling for Thick Sheets
Thicker, more rigid sheets of PTFE can be shaped using a milling machine. This offers much greater accuracy and a better surface finish than manual knife cutting.
This approach is useful for creating robust, thick gaskets or custom components when a waterjet is not available.
Beyond Cutting: Material Composition Matters
How a gasket is "shaped" also depends on its fundamental construction. Not all PTFE gaskets start as a simple, solid sheet.
Standard vs. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Standard PTFE is a solid, dense material. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE), by contrast, is created through a process that introduces a porous, flexible microstructure.
This soft, conformable nature allows ePTFE to create a tight seal even on irregular or damaged flange surfaces with less bolt load, offering a different kind of "fit" than a rigid, cut gasket.
Metal-Inserted and Envelope Gaskets
For high-pressure services where blowout is a risk, gaskets can be manufactured with integrated metal components.
Metal-inserted PTFE gaskets contain a perforated stainless steel core, while PTFE envelope gaskets feature a flexible core material with a PTFE outer layer. These are pre-formed solutions designed for specific, challenging applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right approach requires balancing three key factors: precision, volume, and cost.
Precision vs. Cost
Waterjet cutting offers the highest precision for any shape but can be more expensive for large production runs. Die cutting is highly economical at scale but requires an upfront investment in tooling and is not practical for prototypes.
Material Integrity
Manual cutting, especially with a dull blade, can create nicks or uneven edges that compromise the seal. Heat-generating methods (which are not used for PTFE) could alter its chemical resistance, which is why waterjet is a preferred method.
The Challenge of Compressibility
PTFE has limited compressibility compared to other materials. This means that even a perfectly shaped gasket will fail if the flange surfaces are not clean, smooth, and parallel. Proper surface preparation is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine the best shaping method and material type for your gasket.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of a standard shape: Die cutting offers the lowest per-unit cost and excellent repeatability.
- If your primary focus is a high-precision, custom, or prototype gasket: Waterjet cutting provides exceptional accuracy for any geometry with no tooling costs.
- If your primary focus is an immediate, on-site repair of a non-critical seal: Manually cutting a thin PTFE sheet is a viable, temporary solution.
- If your primary focus is sealing a high-pressure or irregular surface: Specify a pre-formed metal-inserted gasket or a conformable expanded PTFE (ePTFE) material.
Ultimately, understanding these shaping methods and material options empowers you to specify a gasket solution that ensures both a perfect fit and long-term seal integrity.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waterjet Cutting | Prototypes, complex shapes, high precision | No heat-affected zone; excellent for custom shapes | Higher cost for large volumes |
| Die Cutting | High-volume production of standard shapes | Very low per-unit cost at scale | High initial tooling cost |
| Manual Knife Cutting | On-site repairs, simple shapes, thin sheets (<1.5mm) | Fast, requires minimal equipment | Low precision; not for critical seals |
| Milling | Thick sheets, custom parts when waterjet unavailable | Good accuracy and surface finish | Slower than automated methods |
Need a Perfectly Shaped PTFE Gasket?
Choosing the right fabrication method is critical for seal integrity, performance, and cost. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, using the optimal shaping technique for your specific application to ensure a perfect fit and long-term reliability.
Let us help you achieve a flawless seal. Contact our experts today for a quote or to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How often should PTFE sliding bearings be lubricated? A 3-Year Guide to Structural Integrity
- How is PTFE used in the automotive industry? Enhancing Vehicle Reliability and Performance
- What thickness options are available for PTFE gaskets? Select the Right Seal for Your Application
- How does the chemical resistance of PTFE gaskets benefit ball valve applications? Ensure Leak-Free, Non-Contaminating Seals
- What is the purpose of a piston seal? Ensure Peak Performance in Your Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- What is a PTFE gasket and what are its primary properties? Unlock Superior Chemical and Thermal Sealing
- How should seals and gaskets be maintained in PTFE butterfly valves? A Proactive Guide to Prevent Downtime
- How can the susceptibility to creep and cold flow in PTFE washers be addressed? Improve Stability with Filled PTFE or Metal Backing



















