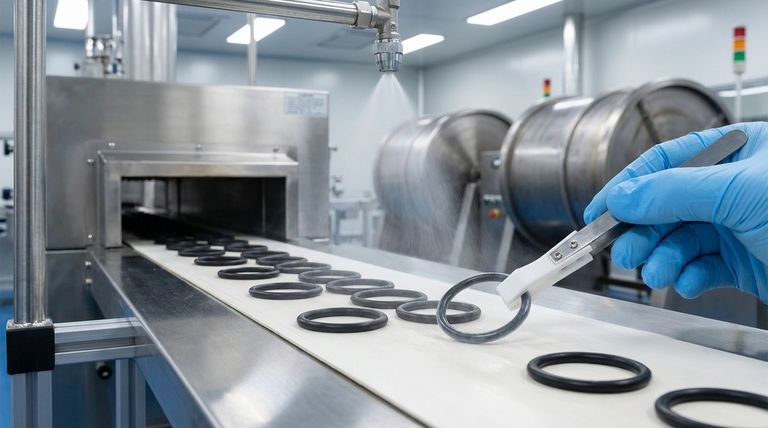
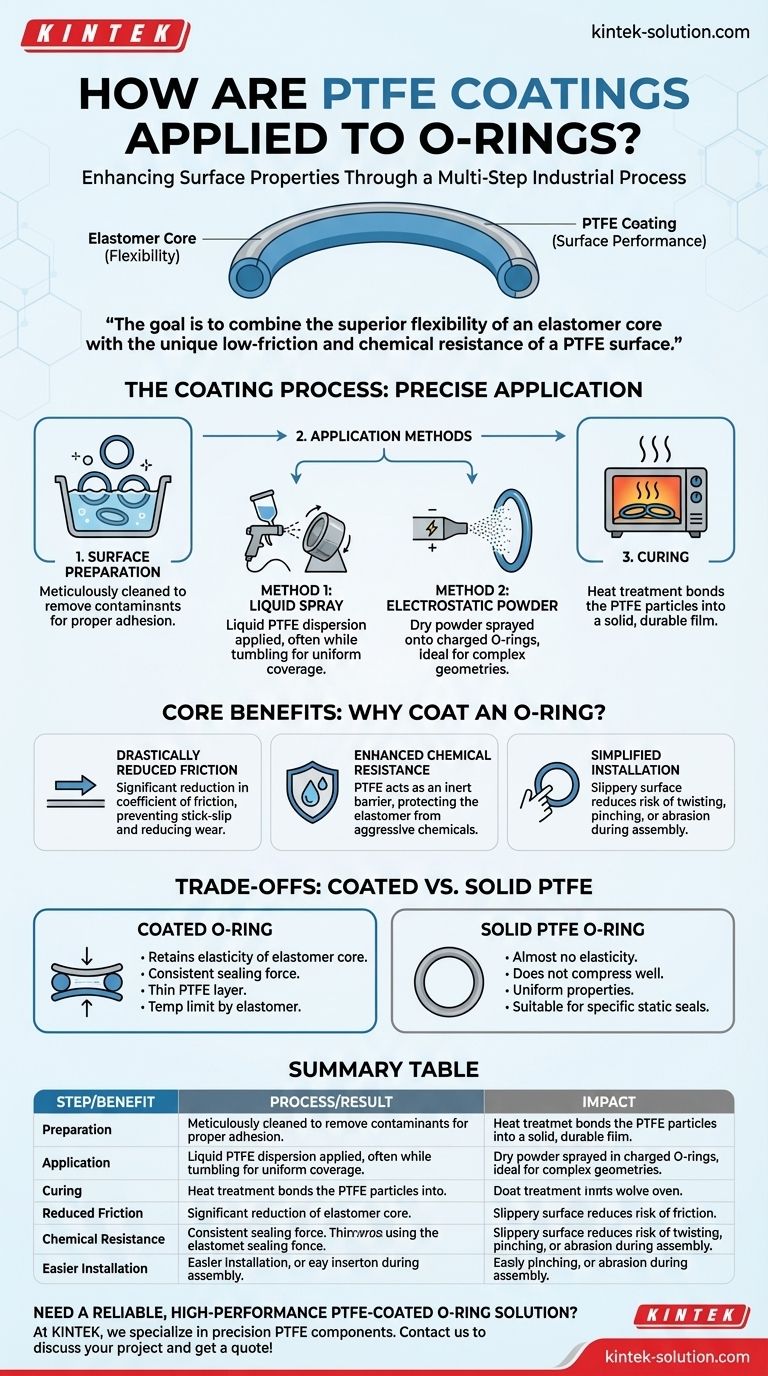
At its core, applying a PTFE coating to an O-ring is a multi-step industrial process designed to enhance its surface properties. The most common method involves spraying a liquid dispersion of PTFE particles directly onto the O-rings, often while they are tumbled in a large drum to ensure even coverage, followed by a heat-curing cycle to permanently bond the coating.
The fundamental goal is not to create a PTFE O-ring, but to combine the superior flexibility and sealing capability of an elastomer core with the unique low-friction and chemical resistance of a PTFE surface.

The Coating Process Explained
To achieve a durable and effective coating, the application process must be precise. It involves preparing the O-ring, applying the coating material, and curing it to create a permanent bond.
The Foundation: Surface Preparation
Before any coating is applied, the O-rings must be meticulously cleaned. Any contaminants like mold-release agents or dust will prevent proper adhesion, leading to coating failure.
Method 1: Liquid Spray Application
The most prevalent technique for O-rings uses a liquid PTFE dispersion. This mixture is applied using conventional compressed air spray guns, similar to painting. For bulk processing, O-rings are often tumbled in a large, rotating barrel while the coating is sprayed, ensuring a uniform layer on all surfaces.
Method 2: Electrostatic Powder Application
For certain fluoropolymers like PFA or FEP, a dry powder coating is used. The O-rings are given an electrical charge, and the oppositely charged powder is sprayed towards them. This electrical attraction pulls the powder evenly onto the part's surface, which is especially useful for more complex geometries.
The Final Step: Curing
After the coating is applied, the O-rings are heated in an industrial oven. This crucial step, known as curing, bakes the coating, causing the PTFE particles to melt, flow together, and form a solid, bonded film on the elastomer's surface.
Why Coat an O-Ring? The Core Benefits
Adding a PTFE coating fundamentally changes the O-ring's surface interaction without compromising the sealing performance of its elastomeric core.
Drastically Reduced Friction
The primary benefit is a significant reduction in the coefficient of friction. This is critical in dynamic applications to prevent stick-slip behavior, reduce wear, and lower the force needed for movement.
Enhanced Chemical Resistance
The PTFE layer acts as a chemically inert barrier. It protects the underlying elastomer (like FKM or EPDM) from brief or incidental contact with aggressive chemicals that would otherwise cause it to swell or degrade.
Simplified Installation
The slippery surface makes O-rings much easier to install, particularly in automated assembly lines. It reduces the risk of the O-ring being twisted, pinched, or abraded during installation, which is a common cause of seal failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Coated vs. Solid PTFE
It is critical to distinguish between a PTFE-coated elastomer O-ring and a solid PTFE O-ring. They serve very different purposes and have different limitations.
Elasticity and Sealing Force
A coated O-ring retains the elasticity and memory of its elastomer core. It can compress to fill imperfections and exert a consistent sealing force, making it ideal for most standard sealing applications.
A solid PTFE O-ring is rigid and has almost no elasticity. It does not compress well and is therefore unsuitable for dynamic seals or applications that require the "squeeze" of a traditional O-ring to function.
Coating Durability
The PTFE coating is a very thin layer. In highly abrasive dynamic applications, this layer can eventually wear away, exposing the elastomer beneath and losing its low-friction benefits. A solid PTFE part offers uniform properties throughout its material.
Temperature Limitations
The maximum operating temperature of a coated O-ring is dictated by its elastomer core material, not the PTFE. If the core material cannot handle the heat, the seal will fail, regardless of the coating's high-temperature stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right solution depends entirely on the specific demands of your sealing environment.
- If your primary focus is low-friction dynamic sealing or easier installation: A PTFE-coated elastomer O-ring is the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is sealing in a high-abrasion environment: You may need to consider a more robust solid seal material, but be aware of the trade-offs in elasticity.
- If your primary focus is static sealing against extremely aggressive chemicals: A solid PTFE O-ring might be an option, but a perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) O-ring often provides a more reliable sealing solution.
Ultimately, a PTFE coating is an exceptional surface treatment that solves specific engineering challenges related to friction and chemical exposure.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Key Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Surface Cleaning | Removes contaminants for proper adhesion |
| 2. Application | Liquid Spray or Electrostatic Powder | Ensures uniform, even coating coverage |
| 3. Curing | Heat Treatment | Bonds PTFE into a durable, solid film |
| Primary Benefit | Result | Application Impact |
| Reduced Friction | Lower coefficient of friction | Prevents stick-slip in dynamic seals |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert PTFE barrier | Protects elastomer core from degradation |
| Easier Installation | Slippery surface | Reduces risk of twisting or pinching |
Need a reliable, high-performance PTFE-coated O-ring solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom-coated O-rings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals deliver superior low-friction performance and chemical resistance, tailored to your specific application requirements—from prototype to high-volume production.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the role of PTFE sheets in sublimation printing? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results
- What are the characteristics of virgin PTFE bushings? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- How have recent innovations improved Teflon gland packing technology? From Passive Seals to Smart Systems
- Why is chemical inertness important for PTFE coated fasteners? Ensure Long-Term Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What standards are referenced for PTFE O-rings? Ensure Interchangeability & Superior Performance
- What cost advantages do PTFE lined butterfly valves offer? Achieve Superior Corrosion Resistance at Lower Costs
- What material can enhance the benefits of ring-type gaskets? Boost Performance with PTFE in Harsh Environments
- What modifications are available for PTFE plastics? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications



















