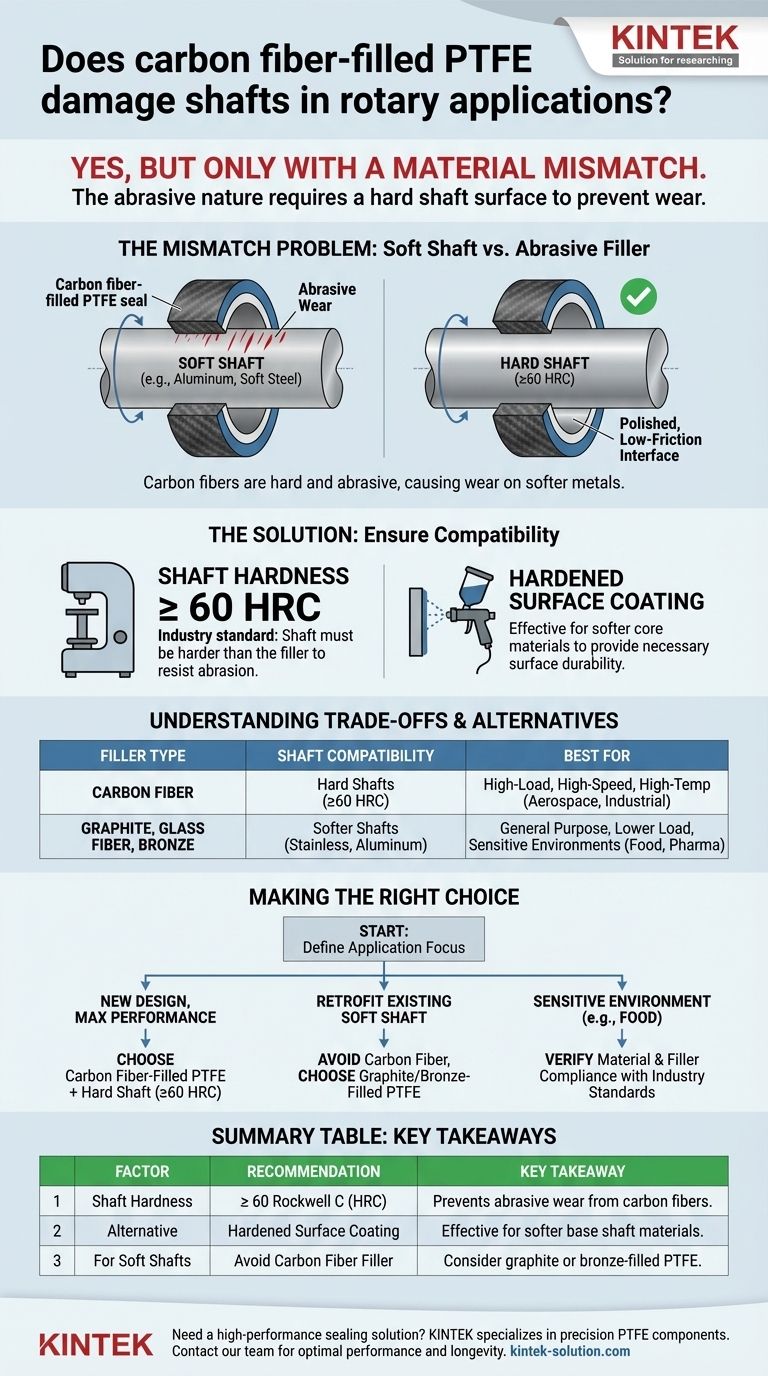
Yes, carbon fiber-filled PTFE can damage shafts, but only when there is a mismatch between materials. The abrasive nature of carbon fibers requires a shaft with a sufficiently hard surface to prevent wear. For optimal performance, the shaft should have a hardness of at least 60 Rockwell C (HRC) or be treated with a hardened surface coating.
The potential for shaft damage does not stem from the PTFE base material, but from a critical mismatch between the abrasive carbon fiber filler and a soft shaft. The solution is to ensure the shaft's surface hardness is specified to work with the filler, creating a durable, low-friction system.

The Role of Fillers in PTFE Performance
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE is known for its extremely low friction but is also mechanically soft. This softness can lead to deformation (creep) under load and limits its use in demanding applications. Fillers are added to enhance specific properties.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
Fillers are not just additives; they fundamentally change the material's behavior. Adding carbon fiber dramatically increases the compressive strength, stiffness, and overall wear resistance of the PTFE composite.
This enhancement allows the material to maintain its shape under heavy loads and at high rotational speeds, making it ideal for high-performance seals and bushings.
The Source of the Abrasion
The wear potential comes directly from the properties that make carbon fiber so effective. The fibers are extremely hard and strong.
When paired with a shaft made of a softer metal, these hard fibers can act as a fine abrasive, gradually wearing down the shaft's surface over time. The soft PTFE base material itself does not cause this wear.
The Critical Factor: Shaft and Seal Compatibility
The key to preventing damage is not to avoid carbon fiber-filled PTFE, but to ensure the entire system is designed for compatibility. The interaction between the seal material and the shaft surface is paramount.
The Mechanism of Wear
In a rotary application, the seal or bushing is in constant contact with the spinning shaft. If the hard carbon fibers in the PTFE composite are harder than the shaft's surface, they will slowly abrade the metal, especially at the high surface speeds PTFE can handle (up to 35 m/s).
The 60 Rockwell C Guideline
To prevent this abrasive action, the shaft surface must be harder than the filler. The industry-standard recommendation is a shaft surface hardness of 60 Rockwell C (HRC) or higher.
At this hardness level, the shaft is more than capable of resisting the abrasive effect of the carbon fibers. Instead of the shaft wearing down, the seal and shaft surfaces polish each other, resulting in a very low-friction, long-lasting interface.
The Alternative: Surface Coatings
If the core material of the shaft is not hard enough and cannot be through-hardened, applying a hardened surface coating is an effective and common solution. This provides the necessary surface durability without changing the underlying shaft.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing carbon fiber-filled PTFE involves balancing its superior performance characteristics against the requirement for a compatible shaft.
When Carbon Fiber Is the Right Choice
Carbon fiber-filled PTFE excels in high-load, high-speed, and high-temperature applications. Its low thermal expansion and high strength prevent extrusion and maintain a tight seal where other materials would fail. This is why it's trusted in demanding sectors like aerospace and high-performance manufacturing.
When to Consider Alternatives
If you are working with an existing system that has a soft shaft (e.g., common grades of stainless steel or aluminum), and hardening the shaft is not feasible, carbon fiber-filled PTFE is not the appropriate choice. This is often the case in food or pharmaceutical applications where specific, softer metals are required.
Other Filler Options
For softer shafts, other fillers provide a balance of properties without being abrasive. Materials filled with graphite, glass fiber, or bronze offer different performance profiles that may be better suited for applications where the shaft cannot be hardened.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material combination from the start is essential for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of your machinery.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance in a new design: Pair carbon fiber-filled PTFE seals or bushings with a shaft designed to have a surface hardness of at least 60 HRC.
- If your primary focus is retrofitting a system with an existing soft shaft: Avoid carbon fiber-filled PTFE and choose a PTFE composite with a less abrasive filler, such as graphite.
- If your primary focus is operation in a sensitive environment (e.g., food processing): Verify that both the shaft material and the specific PTFE filler comply with industry standards and are compatible with each other.
Proper material pairing is the key to unlocking the high-performance benefits of filled PTFE without compromising component longevity.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Recommendation | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Shaft Hardness | ≥ 60 Rockwell C (HRC) | Prevents abrasive wear from carbon fibers. |
| Alternative | Hardened Surface Coating | Effective solution for softer base shaft materials. |
| For Soft Shafts | Avoid Carbon Fiber Filler | Consider graphite or bronze-filled PTFE instead. |
Need a high-performance sealing solution that won't damage your equipment?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including carbon fiber-filled seals and bushings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our experts can help you select or custom-fabricate the perfect material pairing for your specific shaft and application requirements—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Ensure optimal performance and longevity. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the common types of glass reinforcements used in PTFE-based materials? Optimize Performance for Your Application
- What is a Teflon O-ring and what is its primary function? A Guide to Superior Sealing
- What is a PTFE ball valve and how does it function? The Ultimate Guide to Corrosion-Resistant Flow Control
- How is structured PTFE manufactured? The Process Behind High-Performance PTFE Components
- What delivery services are available for PTFE gasket orders? Get Emergency 24-Hour Turnaround
- Why are ePTFE gaskets not recommended for abrasive environments? Protect Your Seals from Premature Failure
- What are the key dielectric properties of PTFE that make it suitable for wires and cables? Ensuring Signal Integrity in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common industrial applications of PTFE in the chemical sector? Ensure Safety and Reliability with PTFE Components



















