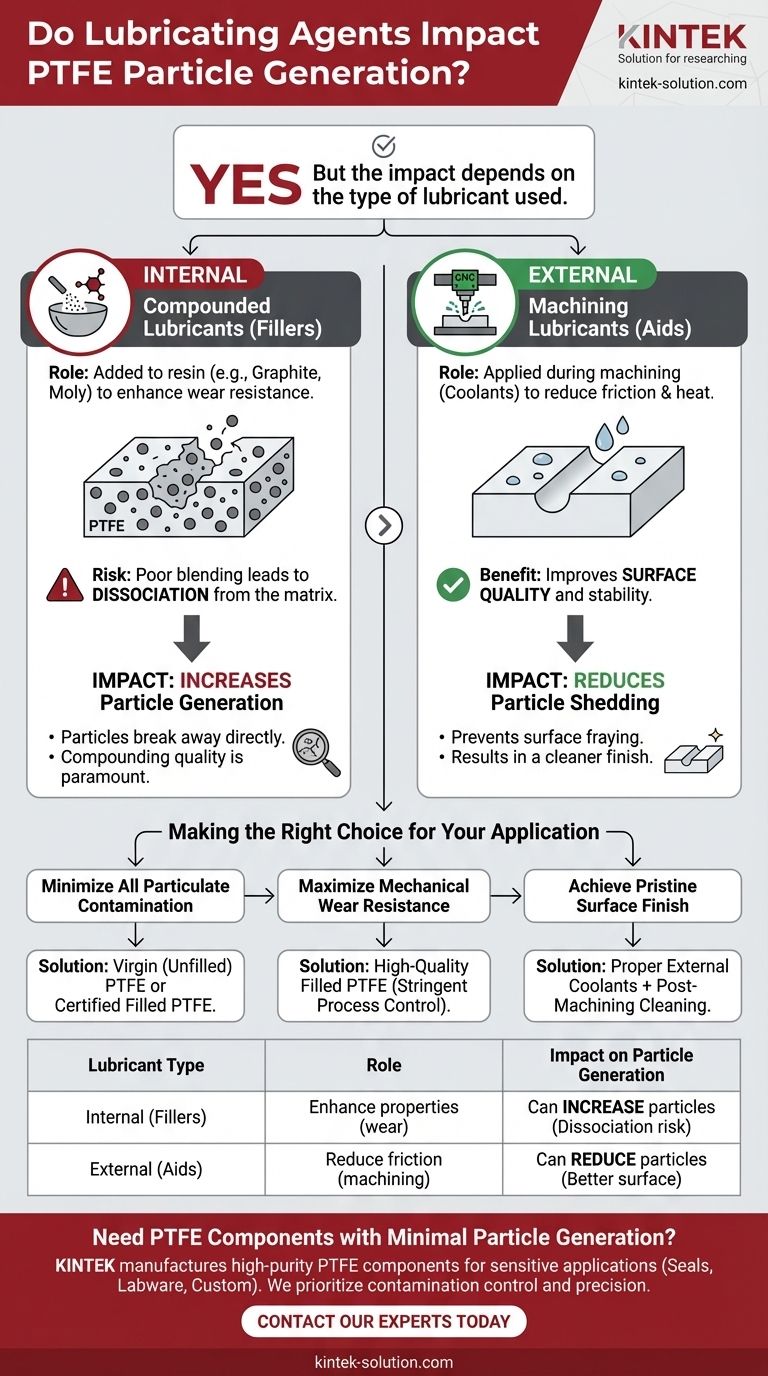
Yes, lubricating agents absolutely impact particle generation in PTFE, but the nature of that impact depends entirely on whether the lubricant is mixed into the material or applied externally during machining. Internally compounded dry lubricants like graphite can break away from the PTFE matrix if not perfectly blended, directly causing particle generation. Conversely, external lubricants used during manufacturing can reduce friction and improve surface quality, potentially reducing the material's tendency to shed particles later on.
The critical factor is not the presence of a lubricant, but its role and integration. Improperly compounded internal lubricants are a direct source of particle contamination, whereas external machining lubricants can actually improve the integrity of the finished part's surface.

The Two Roles of Lubricants with PTFE
Understanding particle generation requires differentiating between lubricants used as an integral material filler and those used as a temporary manufacturing aid.
Internally Compounded Lubricants (Fillers)
Many high-performance PTFE variants are not pure but are instead compounds, with materials like graphite or molybdenum disulfide (moly) mixed in.
These "dry lubricants" are added to the PTFE resin before it is processed to enhance properties like wear resistance and compressive strength.
The Risk of Dissociation
The primary cause of particle generation from these materials is dissociation from the PTFE matrix.
If the lubricant filler is not uniformly and thoroughly blended during the compounding process, these particles can become dislodged from the surface of the final component during use. This shedding is a direct form of particle generation.
External Lubricants (Machining Aids)
In contrast, lubricants can also be applied externally during the machining of a PTFE component. These are typically liquid coolants or cutting fluids.
Their purpose is to reduce friction and dissipate heat generated by the cutting tool. This prevents thermal deformation and results in a cleaner, smoother cut.
Enhancing Surface Quality
By enabling a higher quality machining process, external lubricants help create a more stable and uniform surface on the PTFE part.
A smoother, well-finished surface is inherently less likely to fray or shed its own particles during its operational life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While lubricants can offer significant benefits, they also introduce complexities that must be managed to control particle generation.
The Compounding Challenge
For filled PTFE, the quality of the compounding process is paramount.
The risk of particle generation is directly tied to the manufacturer's ability to create a homogenous blend. Sourcing material from a reputable supplier with stringent process controls is the most effective way to mitigate this issue.
Application Sensitivity
The acceptable level of particle generation is dictated by the application.
In semiconductor or medical device manufacturing, any foreign particle can be a critical failure. In a less sensitive industrial application, the enhanced wear resistance from a graphite filler may far outweigh the minor risk of particle shedding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your strategy for managing particle generation depends entirely on the primary goal for your component.
- If your primary focus is minimizing all particulate contamination: Use virgin (unfilled) PTFE or demand rigorous certification of the compounding process for any filled PTFE.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear resistance: Accept that a filled PTFE is likely necessary, but make quality control and uniform compounding a critical specification for your supplier.
- If your primary focus is achieving a pristine surface finish: Ensure proper external coolants and lubricants are used during the machining process, followed by a validated post-machining cleaning procedure.
Ultimately, controlling particle generation in PTFE requires a clear understanding of how and why a lubricating agent is being used.
Summary Table:
| Lubricant Type | Role | Impact on Particle Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Internal (Compounded Fillers) | Added to PTFE resin to enhance wear resistance, compressive strength. | Can increase particles if fillers (e.g., graphite) dissociate from the PTFE matrix due to poor blending. |
| External (Machining Aids) | Applied during machining to reduce friction, improve surface finish. | Can reduce particles by enabling a cleaner cut and a more stable, less friable surface. |
Need PTFE Components with Minimal Particle Generation?
Controlling particle generation is critical for success in semiconductor, medical, and laboratory applications. The right manufacturing partner makes all the difference.
KINTEK manufactures high-purity PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—with a focus on your application's specific contamination control requirements. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring optimal material selection and machining processes for your needs.
Let us help you achieve the integrity your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- How are Teflon-encapsulated O-Rings utilized in heavy equipment and hydraulics? Achieve Superior Sealing and Reduce Downtime
- How does the non-stick surface of PTFE benefit seals? Unlock Self-Cleaning Performance and Reliability
- What are the limitations or challenges of PTFE envelope gaskets? Manage Creep, Installation, and Thermal Expansion
- What is the temperature range for PTFE piston seals? Unlock the True Limits for Your Application
- Why should negative pressure be avoided in PTFE lined butterfly valves? Prevent Catastrophic Liner Collapse
- What are the key characteristics of PTFE plugs? Master Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How does thermal expansion affect PTFE machining? Master Heat Management for Dimensional Accuracy
- How should thin-wall PTFE components be clamped during machining? Prevent Deformation with the Right Fixtures



















