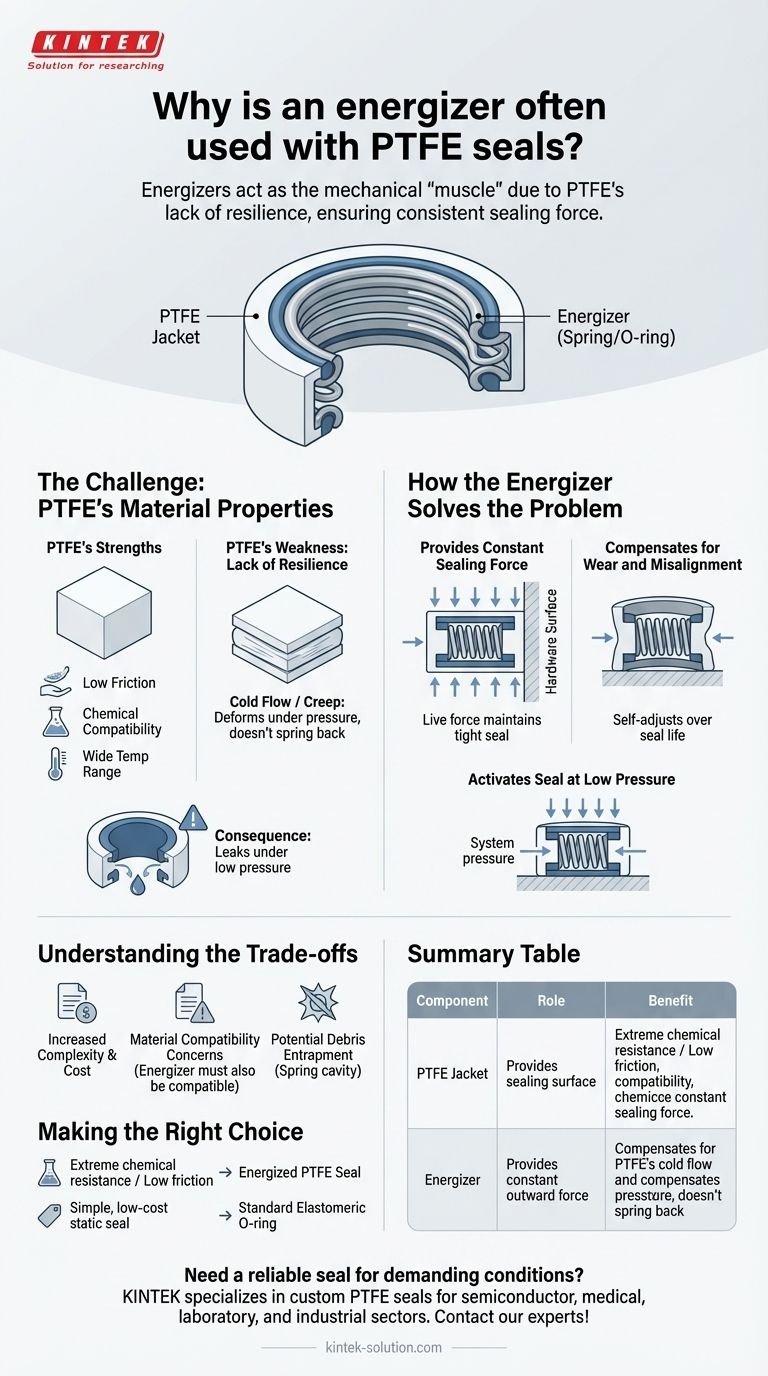
Energizers are a critical component in PTFE seals because the Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material itself lacks the necessary resilience, or "memory," to maintain a consistent sealing force. The energizer provides this constant outward push, ensuring the seal lips remain in firm contact with the hardware surfaces.
The energizer acts as the mechanical "muscle" for the seal. It provides the continuous spring force that the rigid, low-friction PTFE jacket cannot, creating a high-performance seal that leverages the distinct advantages of both materials.

The Challenge: PTFE's Material Properties
To understand the need for an energizer, we must first look at the inherent strengths and weaknesses of PTFE as a sealing material.
PTFE's Exceptional Strengths
PTFE is chosen for its remarkable properties, including an extremely low coefficient of friction, which is ideal for dynamic applications. It also boasts near-universal chemical compatibility and can withstand a very wide range of temperatures.
The Critical Weakness: Lack of Resilience
The primary drawback of PTFE is its poor "memory" or elasticity. Unlike a rubber O-ring that springs back to its original shape after being compressed, PTFE does not.
If you compress a pure PTFE seal, it will hold that new, deformed shape. This phenomenon is often referred to as cold flow or creep.
The Consequence of Cold Flow
In a real-world application, an un-energized PTFE seal would quickly fail. Under the initial installation compression, it would take a set and lose its sealing force, leading to leaks, especially under low-pressure conditions or during temperature cycles.
How the Energizer Solves the Problem
The energizer is a simple, elegant solution that directly counteracts PTFE's lack of resilience. It is typically a metal spring or an elastomeric O-ring that sits in a groove inside the PTFE jacket.
Providing a Constant Sealing Force
The energizer's core function is to provide a continuous, live force that constantly pushes the PTFE seal lips outward against the rod or bore. This ensures a tight seal is maintained even when no system pressure is present.
Compensating for Wear and Misalignment
As the PTFE seal jacket naturally wears down over its service life, the energizer expands to take up the microscopic gap. This self-adjusting capability ensures a reliable seal over millions of cycles. It also helps the seal conform to minor imperfections or misalignments in the hardware.
Activating the Seal at Low Pressure
While high system pressure will help push the seal lips against the hardware, the energizer is crucial for effective sealing at low pressures or in vacuum conditions. It provides the initial force required to create the seal before the system pressure can take over.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the two-component design of an energized seal introduces considerations not present with simpler seals.
Increased Complexity and Cost
An energized seal is inherently more complex and expensive to manufacture than a standard elastomeric O-ring. The design requires careful integration of two different materials.
Material Compatibility Concerns
The energizer material itself—whether stainless steel, Elgiloy, or an FKM O-ring—must also be chemically compatible with the system media. This adds another variable to the material selection process.
Potential for Debris Entrapment
In certain applications, particularly in sanitary or food-grade environments, the cavity that houses the spring can be a potential trap for media or debris. Specialized seal designs exist to mitigate this specific issue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal depends entirely on the demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance or low friction in dynamic systems: An energized PTFE seal is an outstanding solution that overcomes the material's natural limitations.
- If your primary focus is reliable sealing across wide temperature or pressure ranges: The energizer provides the consistent force needed to accommodate thermal expansion and pressure fluctuations.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-cost static seal for a compatible fluid: A standard elastomeric O-ring is often the more practical and cost-effective choice.
By combining an energizer with a PTFE jacket, you create a composite seal that delivers performance far beyond what either component could achieve alone.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Jacket | Provides sealing surface | Extreme chemical resistance, low friction, wide temperature range |
| Energizer (Spring/O-ring) | Provides constant outward force | Compensates for PTFE's cold flow, ensures sealing at low pressure, compensates for wear |
Need a reliable seal for demanding conditions? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE seals with precision energizers for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our seals combine the superior chemical and thermal properties of PTFE with the consistent force of an energizer for leak-free operation. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver the exact solution you need. Contact our experts today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of PTFE gaskets? A Guide to Choosing the Right Seal
- Why is the manufacturing cost of PTFE processing machines high? The Engineering Behind High-Performance Polymer Processing
- What are some common examples of non-PTFE, PTFE, and ceramic-filled PTFE laminates? Optimize Your High-Frequency PCB Design
- What types of parts are made from filled granular PTFE resins? Enhance Durability in Demanding Applications
- What are some tips for CNC machining Teflon? Master PTFE Machining for Superior Results
- What are the different grades of PTFE used in rotary shaft seals? Choose the Right Filler for Peak Performance
- What are some common fillers used to improve PTFE properties for valve seats? Boost Performance & Durability
- In which industries are mechanical seals with PTFE rings commonly used? Essential for Harsh Chemical & High-Temp Environments



















