In short, PTFE gaskets are preferred in high-temperature environments due to their exceptional thermal stability, allowing them to maintain their shape and sealing integrity at continuous service temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). Unlike many other polymers that would degrade or melt, PTFE remains durable and chemically resistant under significant thermal stress, ensuring a reliable, long-lasting seal in demanding applications.
The preference for PTFE in high-temperature applications stems not just from its heat resistance alone, but from its unique combination of thermal stability, chemical inertness, and consistent sealing performance across an extremely wide temperature range.

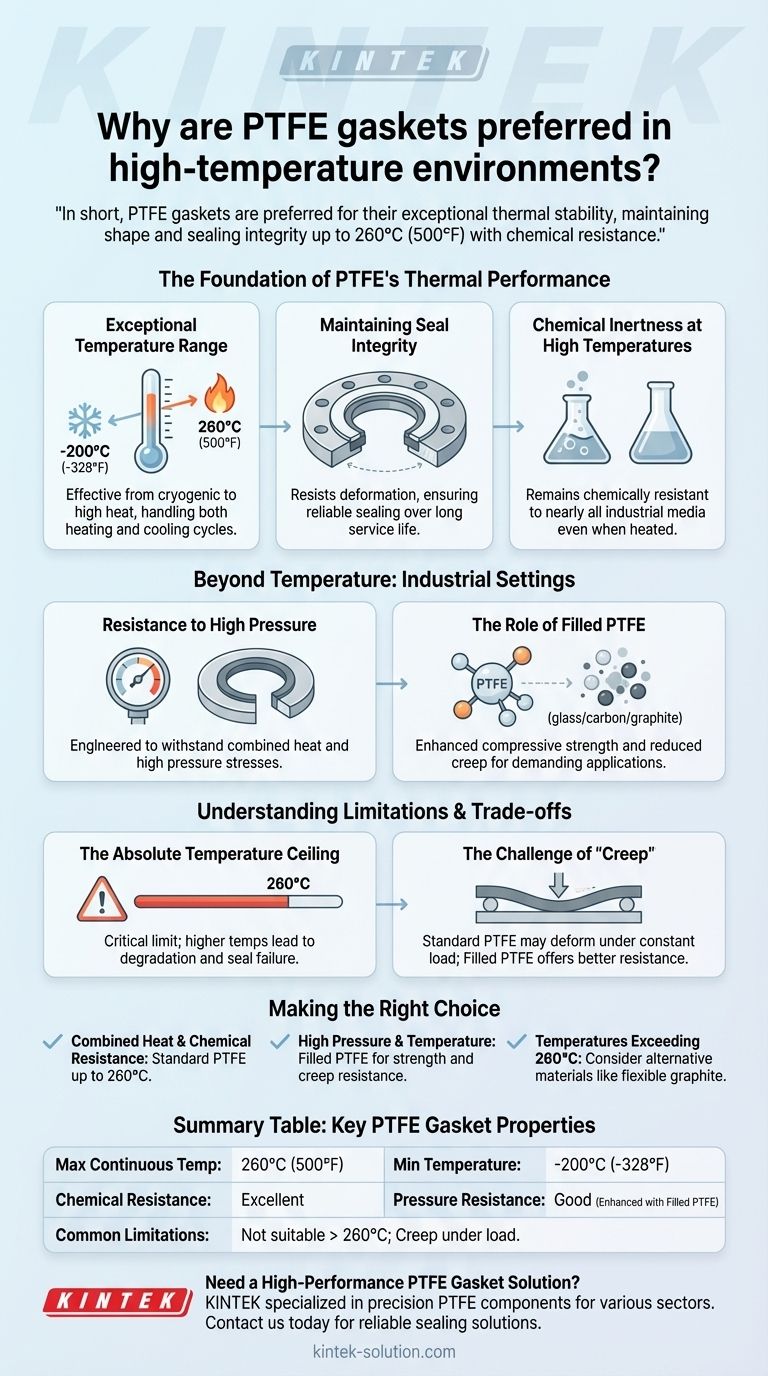
The Foundation of PTFE's Thermal Performance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) possesses a unique molecular structure that gives it properties that are highly valuable in industrial sealing applications.
Exceptional Temperature Range
PTFE gaskets operate effectively across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic conditions at -200°C (-328°F) all the way up to 260°C (500°F). This stability at both extremes is rare among sealing materials.
This means a single material can be specified for processes that involve both heating and cooling cycles without concern for material failure.
Maintaining Seal Integrity Under Heat
A primary function of a gasket is to create a reliable seal between two surfaces. PTFE maintains its shape and mechanical properties when exposed to high heat below its threshold.
It resists deformation, ensuring it continues to fill imperfections in flange surfaces and prevent leaks. This durability leads to a longer service life and reduces the need for frequent replacements in systems like heat exchangers or high-powered engines.
Chemical Inertness at High Temperatures
Many industrial processes involve not just heat, but also corrosive chemicals. PTFE is famously inert and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents.
Crucially, it retains this chemical resistance even at elevated temperatures, a condition where other materials might become more susceptible to chemical attack.
Beyond Temperature: Why PTFE Excels in Industrial Settings
While temperature resistance is the primary driver, other properties make PTFE a superior choice in the context of a complete industrial system.
Resistance to High Pressure
High-temperature applications are often also high-pressure applications. PTFE gaskets are engineered to withstand these combined stresses.
Their ability to create a strong seal with relatively low surface compression helps maintain the integrity of the joint without leaking under pressure.
The Role of Filled PTFE
For applications requiring even greater performance under mechanical stress, filled PTFE gaskets are used.
By adding materials like glass, carbon, or graphite to the virgin PTFE, characteristics like compressive strength and thermal conductivity are enhanced. This makes them ideal for high-pressure or mechanically demanding settings where pure PTFE might be too soft.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect for every situation. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging where PTFE may not be the right choice.
The Absolute Temperature Ceiling
The 260°C (500°F) limit is a critical design constraint. If temperatures in your system will spike or consistently operate above this point, PTFE will begin to degrade and fail.
Prolonged exposure near its upper limit, especially over large gasket surfaces, can lead to decomposition and a loss of the seal.
The Challenge of "Creep"
Standard PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under a constant compressive load over time (a condition known as creep or cold flow), it can slowly deform, potentially reducing the sealing pressure on the gasket.
This is why filled PTFE variants are often specified for critical high-pressure applications, as the filler material significantly improves the gasket's resistance to creep.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires analyzing your full operating conditions—not just the temperature.
- If your primary focus is combined heat and chemical resistance: Standard PTFE is an excellent choice for applications up to 260°C (500°F) involving aggressive media.
- If your primary focus is high pressure and temperature: A filled PTFE gasket (e.g., glass or carbon-filled) will provide the necessary strength and creep resistance to ensure a durable seal.
- If your temperatures will exceed 260°C (500°F): You must consider alternative materials, such as flexible graphite or specialized metallic gaskets, as PTFE is not suitable.
Ultimately, choosing the right gasket is about matching the material's specific properties to the precise demands of your environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | PTFE Gasket Performance |
|---|---|
| Max Continuous Temperature | 260°C (500°F) |
| Min Temperature | -200°C (-328°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, even at high temperatures |
| Pressure Resistance | Good, enhanced with filled PTFE variants |
| Common Limitations | Not suitable above 260°C; standard PTFE may experience creep under constant load |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Gasket Solution?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require standard PTFE for unmatched chemical resistance or filled PTFE for enhanced strength and creep resistance in high-pressure environments, we deliver reliable, long-lasting sealing solutions tailored to your exact operating conditions.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your gaskets meet the precise demands of your high-temperature application.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components



















