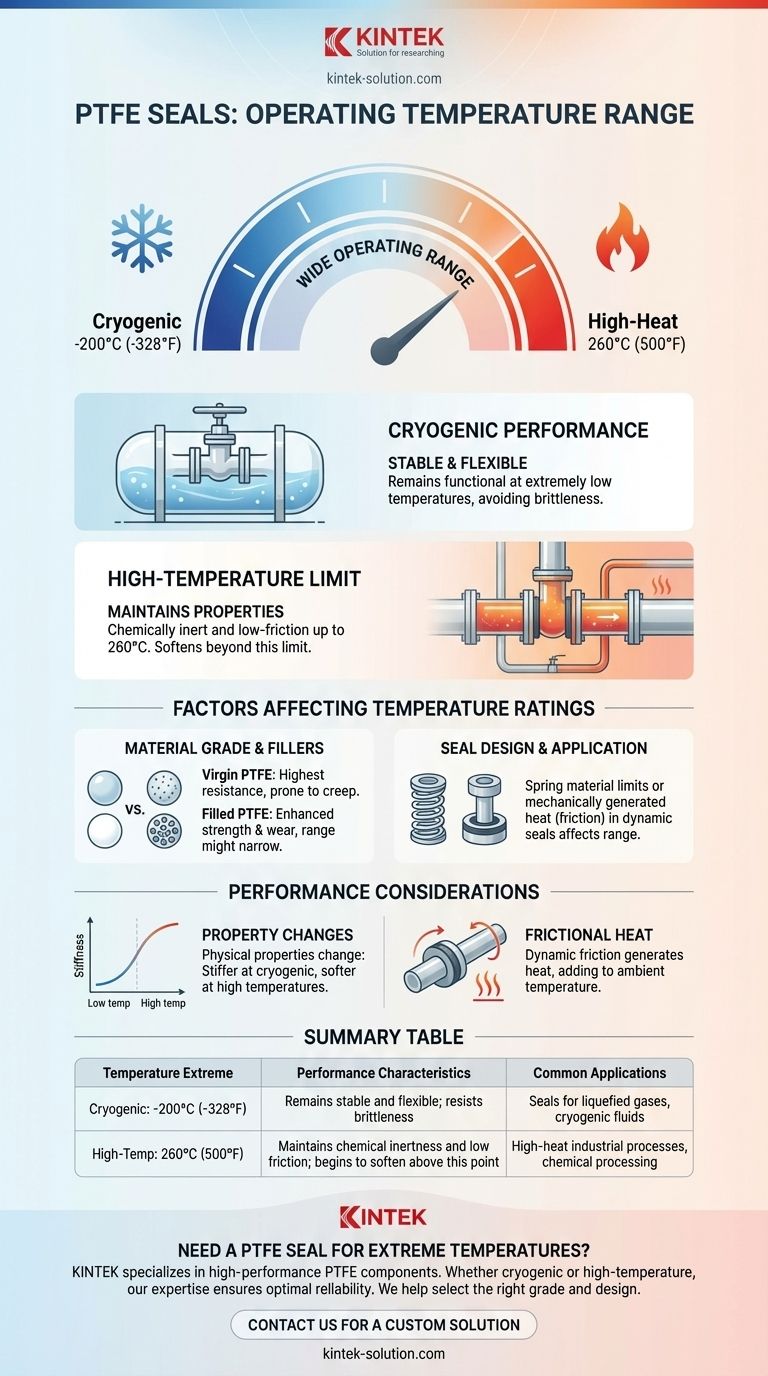
In short, PTFE seals operate within a remarkably wide temperature range. A reliable general range is from -200°C (-328°F) up to 260°C (500°F). This capability allows them to be used in everything from cryogenic applications to high-heat industrial processes.
The specific operating temperature of a PTFE seal is not just about the PTFE material itself. The final rating depends heavily on the specific grade of PTFE used, the inclusion of filler materials, and the design of the seal assembly.

The Source of PTFE's Thermal Stability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fluoropolymer with unique properties that give it exceptional performance at both temperature extremes. Understanding why it works so well provides the context for its application limits.
Performance in Cryogenic Conditions
The molecular structure of PTFE remains stable and functional even at extremely low temperatures. This makes it a primary choice for seals in applications involving liquefied gases and other cryogenic fluids, where many other elastomers would become brittle and fail.
The High-Temperature Limit
As temperatures rise, PTFE maintains its chemical inertness and low-friction properties. The upper limit of 260°C (500°F) is generally considered the maximum for continuous service, as the material begins to soften and lose mechanical strength beyond this point. Some sources may cite peak temperatures up to 300°C (572°F), but this is typically for very short, intermittent exposure.
Why You See Different Temperature Ratings
You will often encounter varying temperature ranges in technical data sheets. This is not an error; it reflects the fact that not all PTFE seals are created equal. Several factors modify the base material's performance.
Pure PTFE vs. Filled Compounds
Virgin (pure) PTFE offers the highest temperature resistance and chemical inertness. However, it can be prone to cold flow (creep) and has lower wear resistance.
Filled PTFE incorporates materials like carbon, glass fiber, or bronze to enhance specific properties. These fillers improve mechanical strength, reduce creep, and increase wear resistance, but they can sometimes slightly narrow the acceptable temperature range or change other characteristics.
The Impact of Seal Design
The overall design of the seal assembly is a critical factor. For example, a spring-energized seal uses a metal spring to provide a consistent sealing force. The operating temperature of the entire seal may be limited by the spring material, not just the PTFE jacket.
Similarly, a piston seal operates in a dynamic environment where friction generates heat. Its listed temperature range, such as -54°C to 204°C (-65°F to +400°F), may be more conservative to account for this mechanically generated heat and pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply operating within the range is not enough; performance at the extremes involves important considerations.
Material Properties Change with Temperature
Even within its safe operating range, the physical properties of PTFE change. At the cryogenic end, the material becomes stiffer and less flexible. At the high-temperature end, it becomes softer and more susceptible to extrusion, especially under high pressure.
Frictional Heat Must Be Considered
In dynamic applications like rotary or piston seals, the friction between the seal and the moving surface generates significant heat. This self-generated heat must be added to the ambient system temperature to ensure the seal does not exceed its maximum limit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Always consult the manufacturer's specific data sheet for the exact seal you are considering. However, you can use these general guidelines to steer your selection.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic service: A virgin PTFE or a specially formulated cryogenic grade is likely the best choice for maximum flexibility at low temperatures.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature dynamic sealing: A filled PTFE compound will provide the necessary mechanical strength and wear resistance to perform reliably under heat and pressure.
- If your primary focus is general industrial use: A standard PTFE seal will perform exceptionally well, but pay close attention to the interplay between pressure, temperature, and speed in your specific system.
Ultimately, choosing the right seal requires looking beyond a single number and understanding the full context of your application.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Extreme | Performance Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cryogenic: -200°C (-328°F) | Remains stable and flexible; resists brittleness | Seals for liquefied gases, cryogenic fluids |
| High-Temp: 260°C (500°F) | Maintains chemical inertness and low friction; begins to soften above this point | High-heat industrial processes, chemical processing |
Need a PTFE Seal for Extreme Temperatures?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require standard seals or custom-fabricated solutions for cryogenic or high-temperature environments, our expertise in precision production ensures optimal performance and reliability.
We can help you select the right PTFE grade and seal design to meet your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical resistance requirements—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE and non-PTFE laminates? Optimize Performance vs. Cost
- Why are PTFE expansion bellows considered a cost-effective long-term investment? Reduce Total Cost of Ownership
- What are the advantages of Teflon washers? Achieve Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What is the main difference between PTFE and expanded PTFE? Unlock the Right Material for Your Application
- What makes PTFE V-rings effective seals? A Guide to Robust, Low-Friction Sealing
- What are the electrical conductivity and chemical resistance properties of PTFE and nylon? Key Differences for Your Application
- How is PTFE typically processed in manufacturing? A Guide to Molding, Sintering & Machining
- What are some best practices for using a Teflon sheet? Ensure Flawless Heat Press Results Every Time



















