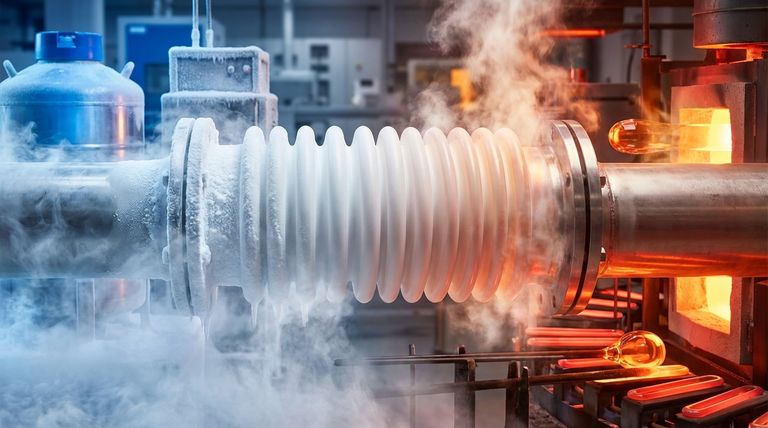
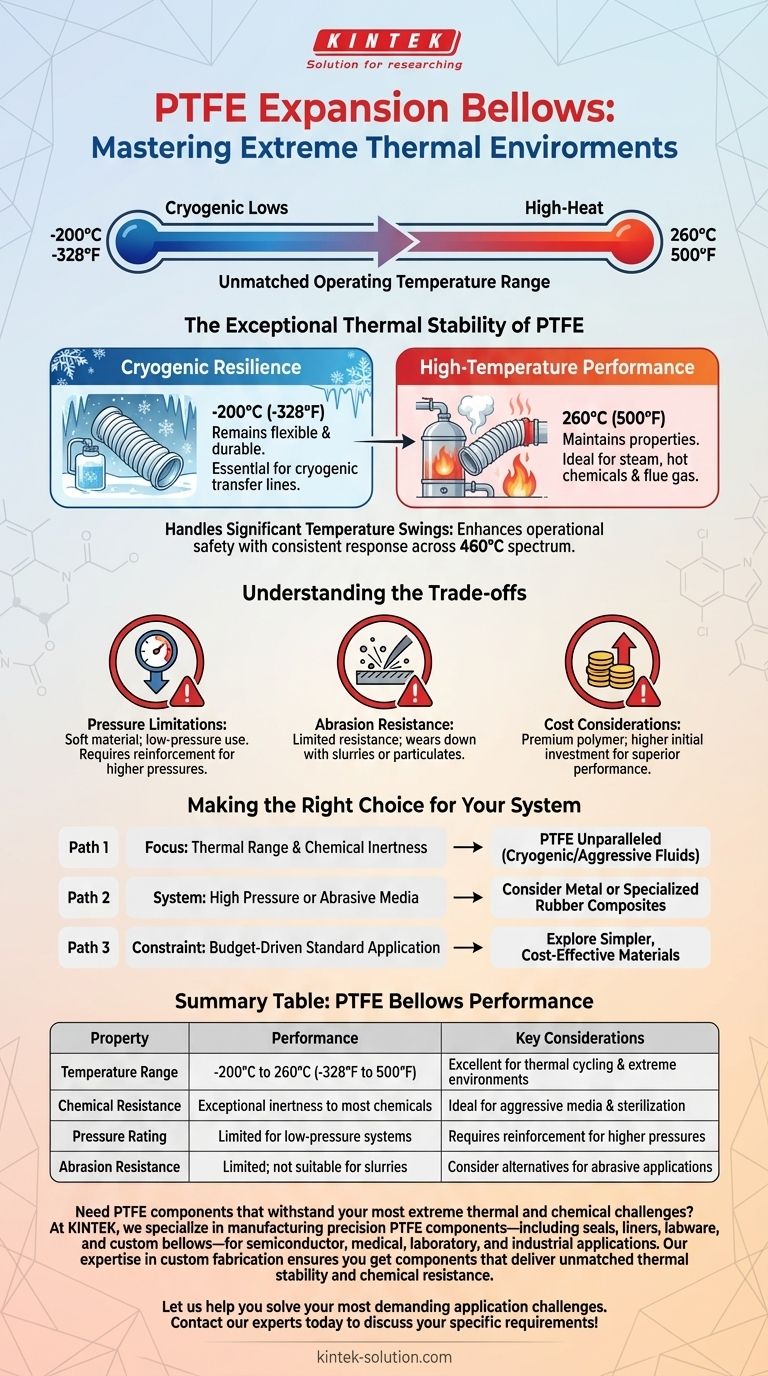
When selecting materials for demanding thermal environments, PTFE expansion bellows offer an exceptionally wide and reliable operating temperature range. They are engineered to function consistently from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat applications of 260°C (500°F). This stability ensures their structural integrity and performance are not compromised by extreme thermal cycling.
The core value of PTFE bellows lies in their unmatched temperature range and chemical inertness. However, this thermal resilience must be carefully weighed against their inherent limitations in handling high pressure and physical abrasion.

The Exceptional Thermal Stability of PTFE
The molecular structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is what gives it such a remarkable tolerance for extreme temperatures. This makes it a go-to material for applications where other elastomers or plastics would fail.
High-Temperature Performance
PTFE maintains its key properties without degradation up to 260°C (500°F). This makes it highly suitable for processes involving steam, hot chemicals, or flue gas systems. For example, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, these bellows can endure repeated high-temperature sterilization cycles without cracking or losing flexibility.
Cryogenic Resilience
Unlike many materials that become brittle and fail at low temperatures, PTFE remains flexible and durable down to -200°C (-328°F). This unique characteristic makes it an essential component in cryogenic transfer lines and other ultra-low temperature applications.
Why a Wide Range Matters
The ability to perform reliably across a 460°C spectrum allows a single component to handle processes with significant temperature swings. This simplifies system design and enhances operational safety by providing a consistent, predictable material response.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its thermal performance is outstanding, PTFE is not the universal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper material selection.
Pressure Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material and lacks the inherent mechanical strength for high-pressure applications. Unreinforced bellows are generally used in low-pressure systems. For higher pressures, specially engineered or reinforced designs are required.
Abrasion Resistance
The material has limited resistance to abrasive media. In systems transporting slurries or high-velocity particulates, PTFE can wear down more quickly than harder materials like metal or certain rubber composites.
Cost Considerations
PTFE is a premium polymer. Consequently, its expansion bellows are often more expensive than those made from common elastomers like rubber. The higher initial cost is justified by its superior performance in extreme chemical and thermal environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct expansion bellow requires balancing performance needs with operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is thermal range and chemical inertness: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for applications like cryogenic transfer or processing aggressive, high-temperature fluids.
- If your system involves high pressure or abrasive media: You must consider alternatives like metal bellows or specialized rubber composites that are designed for mechanical strength.
- If budget is the driving constraint for a standard application: Simpler materials may offer a more cost-effective solution, provided they meet the temperature and chemical demands of the system.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a decision to prioritize its unmatched thermal and chemical resistance for applications where other materials would fail.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Bellows Performance | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Excellent for thermal cycling and extreme environments |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional inertness to most chemicals | Ideal for aggressive media and sterilization |
| Pressure Rating | Limited for low-pressure systems | Requires reinforcement for higher pressures |
| Abrasion Resistance | Limited; not suitable for slurries/particulates | Consider alternatives for abrasive applications |
Need PTFE components that withstand your most extreme thermal and chemical challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom bellows—for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get components that deliver unmatched thermal stability and chemical resistance, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you solve your most demanding application challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















