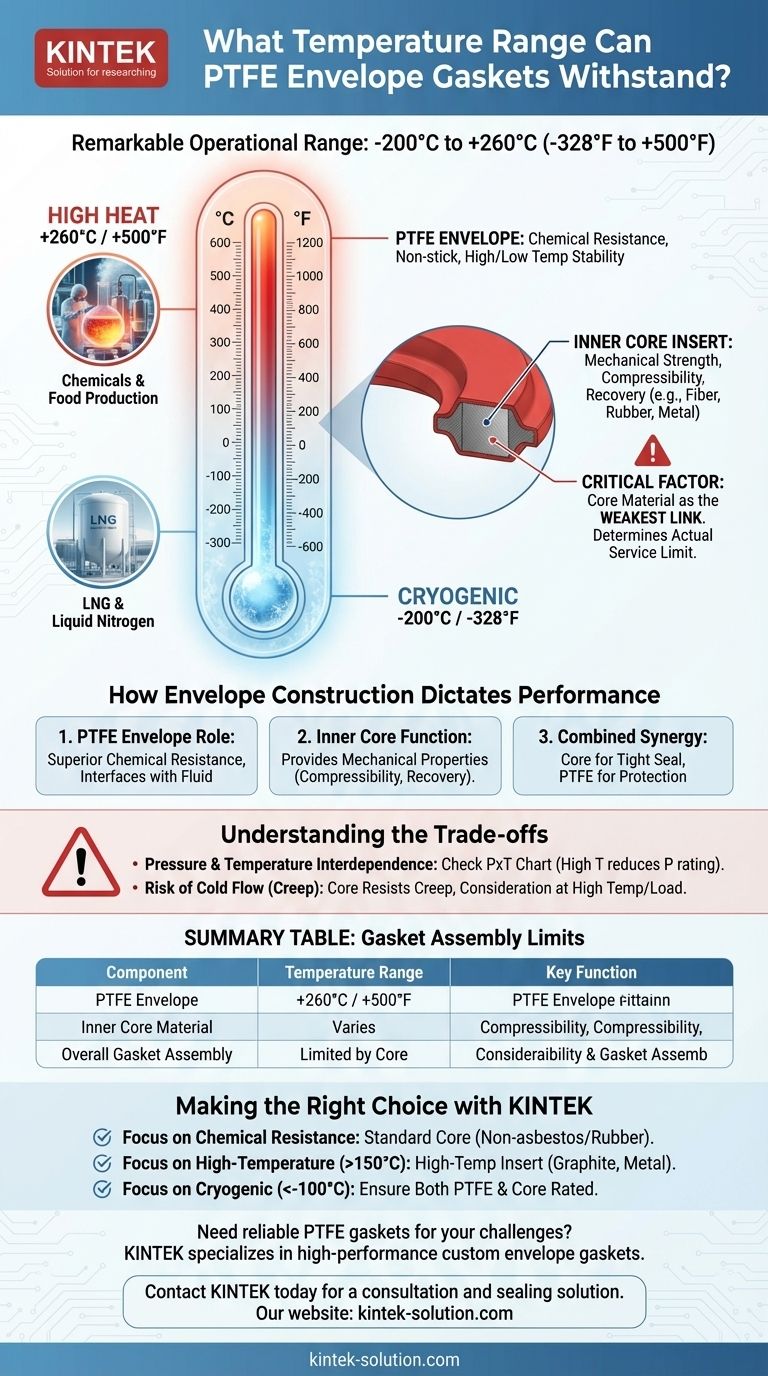
In short, PTFE envelope gaskets offer a remarkable operational temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). This wide spectrum makes them a default choice for applications involving both extreme high heat and cryogenic lows, especially in chemically aggressive environments.
While the PTFE material itself defines these impressive temperature boundaries, the gasket's true performance limit is often dictated by the less-visible core material. Understanding this interaction is the key to selecting a reliable seal.
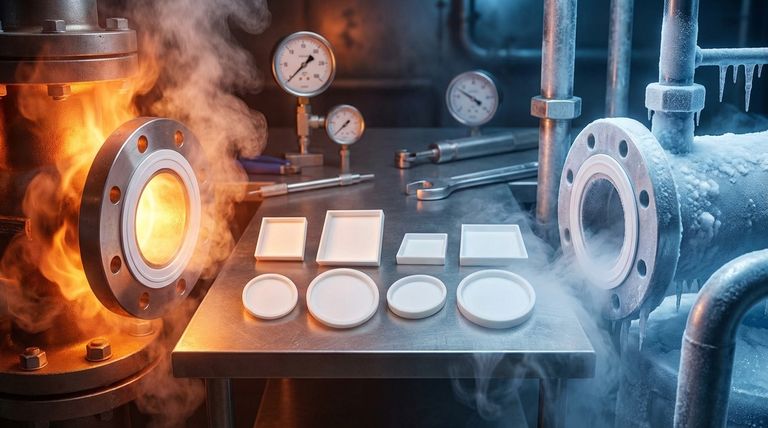

How Envelope Construction Dictates Performance
A PTFE envelope gasket is a composite design, engineered to leverage the strengths of two different materials. This construction is what gives it such unique versatility.
The Role of the PTFE Envelope
The outer "envelope" is made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This layer is what interfaces directly with the process fluid and the flange faces.
Its primary function is to provide superior chemical resistance. PTFE is inert to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents, making it invaluable in corrosive service. It also creates a non-stick, low-friction surface.
The Function of the Inner Core
Inside the PTFE jacket is a core insert. This core provides the mechanical properties that PTFE lacks, such as compressibility and recovery.
This insert is what allows the gasket to conform to flange imperfections and maintain a resilient sealing force under bolt load. Common core materials include non-asbestos fiber, rubber, or corrugated metal.
Combining Chemical and Mechanical Resistance
The envelope design creates a synergy: the core provides the mechanical strength and elasticity needed for a tight seal, while the PTFE envelope protects the core from chemical attack and temperature extremes.
Deconstructing the Temperature Limits
The advertised temperature range is impressive, but a technical understanding requires looking at both the high and low ends, as well as the components responsible for them.
The High-Temperature Limit (Up to +260°C / +500°F)
The upper limit of +260°C (+500°F) is a function of the PTFE material's stability. It will not break down or degrade when exposed to this level of heat.
This makes it highly suitable for high-temperature processes in industries like chemical processing, metallurgy, and food production where aggressive fluids are common.
The Cryogenic Limit (Down to -200°C / -328°F)
At the other end of the spectrum, PTFE maintains its integrity and avoids the embrittlement that causes many other polymers to fail in cryogenic applications.
This resilience makes it a reliable choice for sealing liquid nitrogen, LNG, and other low-temperature systems.
The Critical Factor: The Insert Material
The performance of the entire gasket assembly is only as good as its most vulnerable component. While the PTFE can handle the full -200°C to +260°C range, the inner core material often cannot.
For example, a standard EPDM rubber insert may have an upper temperature limit of only 150°C (300°F). In that assembly, the gasket's service limit is 150°C, not 260°C, because the core would fail long before the PTFE.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specifying these gaskets requires acknowledging that their composite nature creates critical dependencies. Ignoring these can lead to premature seal failure.
Core Material as the Weakest Link
You must always verify the service temperature of the entire gasket assembly, not just the PTFE. The manufacturer's data sheet will list the rating for the specific combination of envelope and core material you are considering. Assume the gasket's limit is determined by its most restrictive component.
Pressure and Temperature Interdependence
A gasket's maximum temperature rating is rarely achievable at its maximum pressure rating. These two factors work against each other. High temperature softens materials, reducing their ability to withstand pressure. Always check the manufacturer's PxT (Pressure x Temperature) chart to ensure the gasket is suitable for your specific operating conditions.
Risk of Cold Flow (Creep)
PTFE, especially in its pure form, has a tendency to "creep" or cold flow under a constant compressive load. The core insert material provides resistance to this phenomenon, but it remains a consideration, particularly in high-load flanges at elevated temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct gasket, match the specific construction to your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance at moderate temperatures: An envelope gasket with a standard non-asbestos or rubber insert is a cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature service (above 150°C / 300°F): You must specify a gasket with a high-temperature insert, such as graphite, specialized fiber, or corrugated metal, to support the PTFE envelope.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic service (below -100°C / -150°F): Ensure both the PTFE and the selected core material are explicitly rated for cryogenic use to prevent thermal contraction and embrittlement.
Always verify the manufacturer's data sheet for the specific gasket assembly to ensure its capabilities align with your system's operational demands.
Summary Table:
| Component | Temperature Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| PTFE Envelope | -200°C to +260°C | Chemical resistance, non-stick surface |
| Inner Core Material | Varies (e.g., EPDM: ~150°C, Graphite: >260°C) | Mechanical strength, compressibility |
| Overall Gasket Assembly | Limited by the core material | Determines actual service limit |
Need a PTFE gasket that reliably handles your specific temperature and chemical challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom envelope gaskets. We understand that the core material is critical to performance. Our experts will help you select or design a gasket with the right insert—whether for extreme high heat, cryogenic service, or aggressive chemicals—ensuring a perfect seal for your application in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and durability.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let us provide a sealing solution built for your exact conditions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What advantages do Graphite packings offer when treated with PTFE? Achieve Superior Sealing Performance
- What is the role of PTFE backup rings in sealing applications? Prevent Seal Extrusion Under High Pressure
- How are PTFE diaphragms manufactured? Achieve Optimal Performance for Your Application
- What makes Teflon valuable for electrical applications? Leverage its High-Performance Insulating Properties
- Why is the integrity of seals and gaskets important in PTFE butterfly valves? Ensure System Safety and Efficiency
- Which industries benefit the most from PTFE-lined diaphragm valves? Essential for Corrosive & High-Purity Processes
- How should Teflon O-rings be maintained? A Proactive Guide to Prevent Seal Failure
- What are the tolerance specifications for the thickness of PTFE disks? Why ±20% is the Industry Standard



















