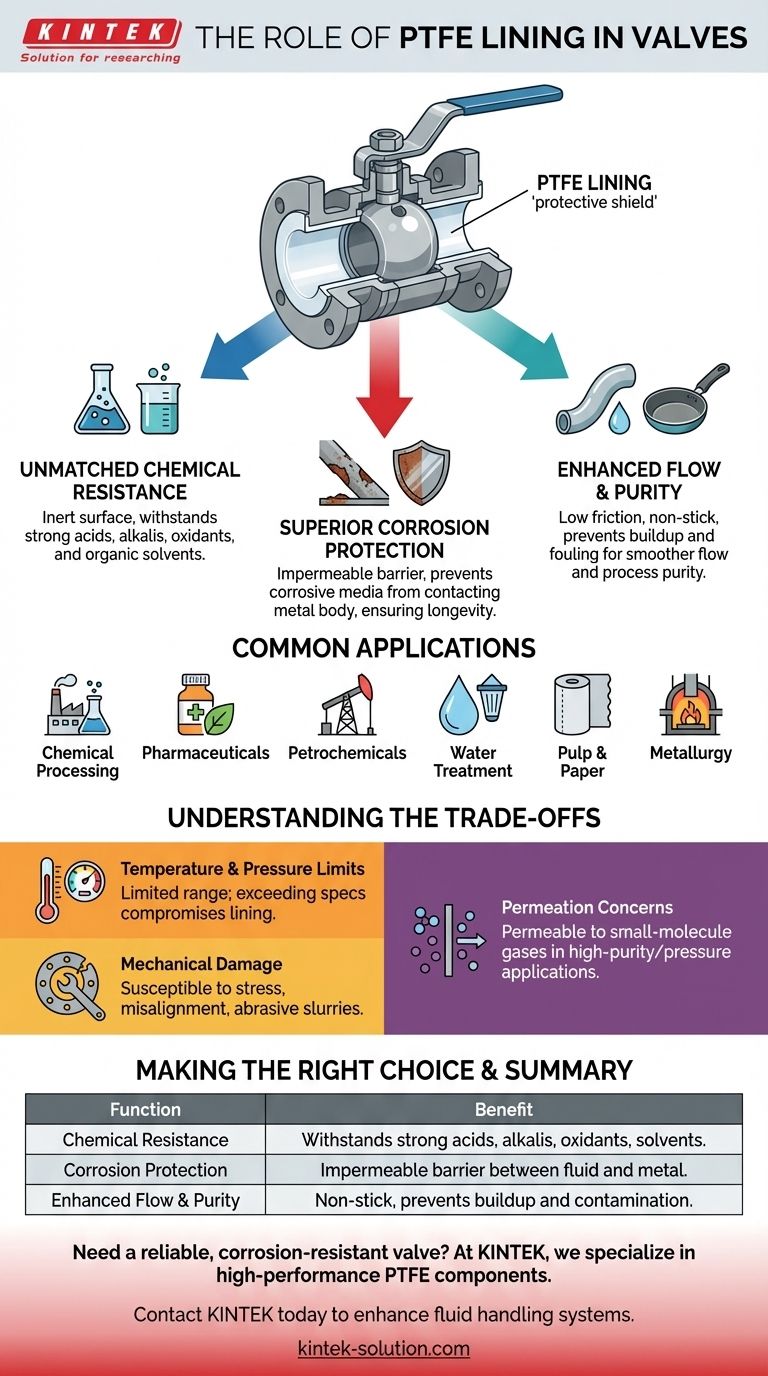
At its core, the PTFE lining in a valve serves as a protective shield. This non-reactive barrier isolates the valve's internal metal components from the process fluid, providing exceptional chemical resistance, preventing corrosion, and ensuring a smooth, non-stick surface for efficient flow.
The fundamental purpose of a PTFE lining is to enable the use of cost-effective valve materials in highly aggressive chemical applications. It imparts the near-universal chemical inertness of solid PTFE to a valve without the prohibitive cost and mechanical limitations of constructing the entire valve from it.

The Core Functions of a PTFE Lining
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer, and its unique properties make it an ideal lining material for industrial valves handling aggressive or sensitive media. Its role can be broken down into three primary functions.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The most critical role of the PTFE lining is to provide a chemically inert surface. It is virtually unaffected by the most aggressive chemicals used in industry.
This includes resistance to strong acids, strong alkalis, strong oxidants, and all organic solvents. Its capabilities are so extensive that it can even withstand exposure to aqua regia, a mixture capable of dissolving noble metals like gold and platinum.
Superior Corrosion Protection
The PTFE lining creates a continuous, impermeable barrier between the process fluid and the valve's structural body, which is typically made of carbon steel or stainless steel.
This barrier prevents corrosive media from ever making contact with the metal components, completely eliminating the risk of chemical corrosion and degradation. This function is the key to the valve's durability and longevity in harsh environments.
Enhanced Flow and Purity
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction and low surface energy, giving it powerful non-stick properties.
This prevents process media, especially sticky or viscous fluids, from adhering to the valve's internal surfaces. The result is smoother, more consistent flow control, reduced wear on components, and a minimized risk of process contamination from buildup or fouling.
Common Applications Across Industries
The combination of these properties makes PTFE-lined valves essential components in a wide range of demanding industrial settings.
Where They Are Used
You will find these valves widely deployed in industries where media is corrosive or purity is paramount.
This includes chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, petrochemical plants, fertilizer production, pulp and paper manufacturing, water treatment, and metallurgical operations. In these sectors, equipment reliability and safety are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, a lined valve represents a specific engineering choice with inherent trade-offs compared to valves made from solid, high-grade alloys.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
PTFE has a more limited operating temperature and pressure range compared to solid metal. Exceeding these specifications can compromise the integrity of the lining.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Damage
The lining can be damaged by improper installation, pipeline stress (pipe-flange misalignment), or highly abrasive slurries if the valve is not specified for such service. Careful handling is essential.
Permeation Concerns
While excellent for liquids, PTFE linings can be susceptible to permeation by certain small-molecule gases over time, which can be a consideration in very specific high-purity or high-pressure gas applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE-lined valve is a strategic decision based on the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive media: The near-universal chemical inertness of a PTFE lining offers the most reliable and cost-effective protection for your equipment.
- If your primary focus is maintaining process purity: The non-stick, non-reactive surface of PTFE is critical for preventing contamination in pharmaceutical, food, or semiconductor applications.
- If your primary focus is maximizing equipment longevity: Using a PTFE lining is a proven strategy to significantly extend the service life of valves in aggressive chemical environments, reducing downtime and replacement costs.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the PTFE lining empowers you to design a safer, more durable, and more efficient fluid handling system.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Withstands strong acids, alkalis, oxidants, and solvents. |
| Corrosion Protection | Creates an impermeable barrier between fluid and metal body. |
| Enhanced Flow & Purity | Non-stick surface prevents buildup and contamination. |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom-fabricated liners and seals for industrial valves. Our precision production ensures your equipment delivers unmatched chemical resistance, superior corrosion protection, and maintains process purity.
Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, pharmaceutical, or chemical processing industry, we provide solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE expertise can enhance the durability and efficiency of your fluid handling systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















