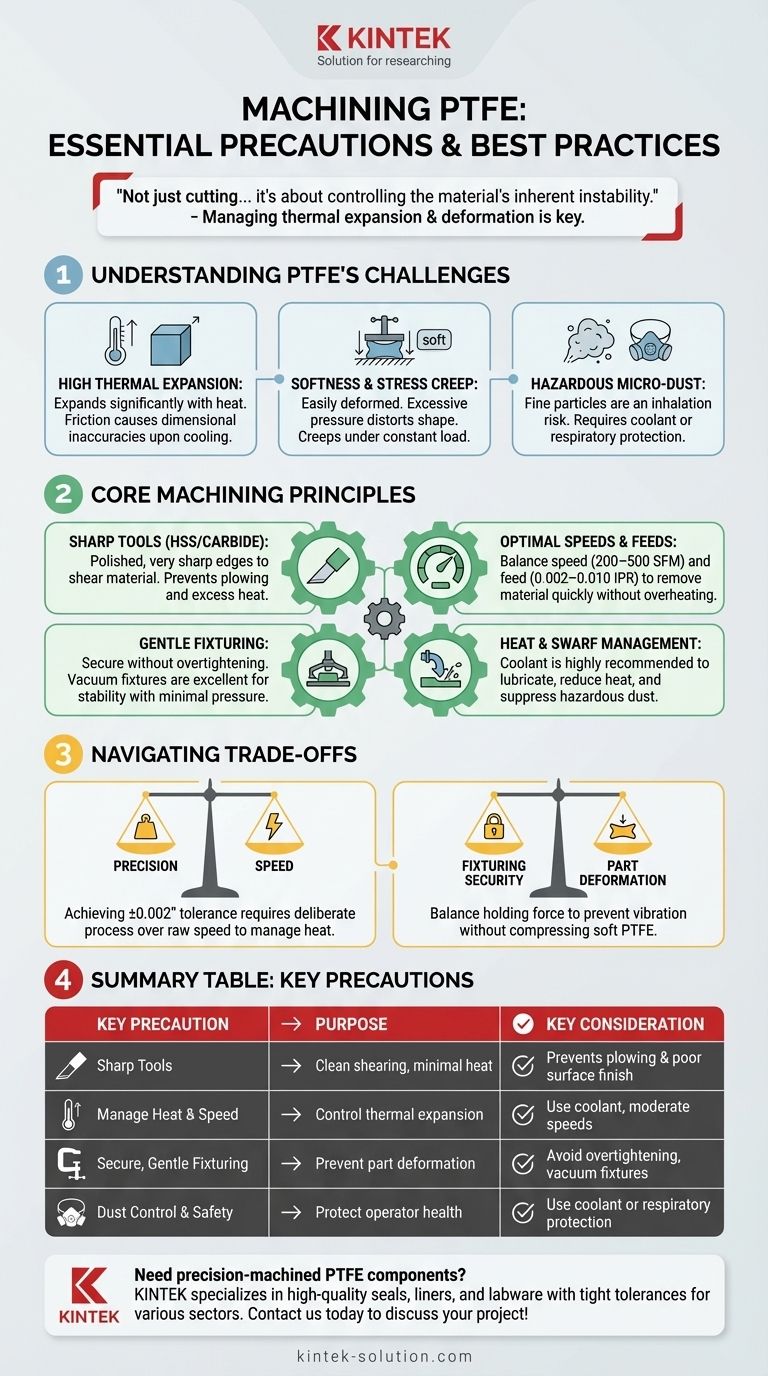
The primary precautions for machining PTFE involve using extremely sharp tools, managing heat buildup with appropriate speeds and coolants, and mitigating the inhalation risk from hazardous micro-dust. Because PTFE is soft and has a high rate of thermal expansion, you must also use precise clamping pressure to avoid deforming the part and ensure dimensional accuracy.
While PTFE's softness makes it seem easy to cut, successful machining is not about cutting the material—it's about controlling the material's inherent instability. The real challenge lies in managing thermal expansion and mechanical deformation to achieve tight tolerances.

Understanding PTFE's Unique Machining Challenges
To machine PTFE effectively, you must first respect its core properties. Its characteristics are fundamentally different from metals or even other plastics, and these differences dictate every necessary precaution.
The Impact of High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a very high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts significantly with even minor changes in temperature.
Friction from the cutting tool generates heat, which can cause the workpiece to expand during machining. This leads to inaccurate dimensions once the part cools down to ambient temperature.
The Problem of Softness and Stress Creep
PTFE is a very soft material that can easily be compressed or deformed. Excessive clamping pressure in a vise or fixture will distort the part's shape.
Furthermore, the material is subject to stress creep, meaning it will slowly deform over time when held under constant pressure. This makes secure, non-damaging workholding a critical challenge.
The Hazard of Micro-Dust
Machining PTFE, especially in dry conditions, produces fine, lightweight dust particles. This micro-dust can remain suspended in the air and is hazardous if inhaled.
Therefore, safety precautions are not optional. You must either machine under coolant to suppress the dust or use appropriate respiratory protection like a mask.
Core Machining Principles for Success
With a clear understanding of the material's behavior, you can implement a strategy that works with PTFE's properties instead of against them.
Tool Selection and Geometry
The single most important factor is tool sharpness. A dull tool will plow through the material rather than shear it, generating excess heat and a poor surface finish.
Use High-Speed Steel (HSS) or carbide-tipped tools that are ground to a very sharp, polished cutting edge. Proper tool clearance is also essential to prevent rubbing, which generates friction and heat.
Speeds and Feed Rates
Your goal is to achieve a clean cut without overheating the workpiece. This requires balancing cutting speed and feed rate.
General guidelines suggest cutting speeds of 200–500 surface feet per minute and high feed rates of 0.002–0.010 inches per revolution. A high feed rate helps produce a continuous chip and removes material quickly before significant heat can build up.
Workpiece Fixturing
Secure the workpiece without deforming it. Avoid overtightening vises or clamps.
For delicate or complex geometries, vacuum fixtures are an excellent solution as they provide stable support with minimal clamping pressure.
Heat and Swarf Management
Effective removal of chips (swarf) is critical to prevent them from rubbing against the workpiece and generating heat.
For heat-intensive operations, the application of a coolant is highly recommended. Coolant serves three purposes: it lubricates the cut, reduces thermal expansion, and suppresses hazardous dust.
Navigating the Inherent Trade-offs
Machining PTFE involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is key to troubleshooting and achieving consistent results.
Precision vs. Speed
Pushing for faster cycle times by increasing cutting speed can introduce excessive heat, ruining dimensional tolerances. Achieving a tolerance of ±0.002 inches requires a deliberate, controlled process where heat management is prioritized over raw speed.
Fixturing Security vs. Part Deformation
You need to hold the workpiece securely to prevent vibration and chatter, which destroy surface finish. However, the clamping force required for security can easily compress and deform the soft PTFE, leading to inaccuracies. This balance requires careful fixture design and operator skill.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your machining strategy should adapt to the specific requirements of the final part.
- If your primary focus is achieving the tightest possible tolerances: Prioritize thermal stability above all. Use sharp, polished tools, moderate speeds, and a steady supply of coolant.
- If your primary focus is a high-quality surface finish: Ensure your tool has a very sharp cutting edge and avoid any vibration by using secure, well-designed fixtures.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Never machine PTFE dry without proper ventilation and respiratory protection. Using coolant is the most effective way to control the hazardous dust.
Ultimately, mastering PTFE machining comes from treating it as a unique material that demands a specific and thoughtful approach.
Summary Table:
| Key Precaution | Purpose | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Sharp Tools (HSS/Carbide) | Clean shearing, minimal heat | Prevents plowing and poor surface finish |
| Manage Heat & Speed | Control thermal expansion | Use coolant, moderate speeds (200-500 SFM) |
| Secure, Gentle Fixturing | Prevent part deformation | Avoid overtightening; consider vacuum fixtures |
| Dust Control & Safety | Protect operator health | Use coolant or respiratory protection |
Need precision-machined PTFE components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in machining PTFE for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between tool sharpness, heat management, and safe handling required to produce high-quality seals, liners, and labware with tight tolerances.
Whether you need custom prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your parts are manufactured correctly from the start.
Contact us today to discuss your PTFE project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















