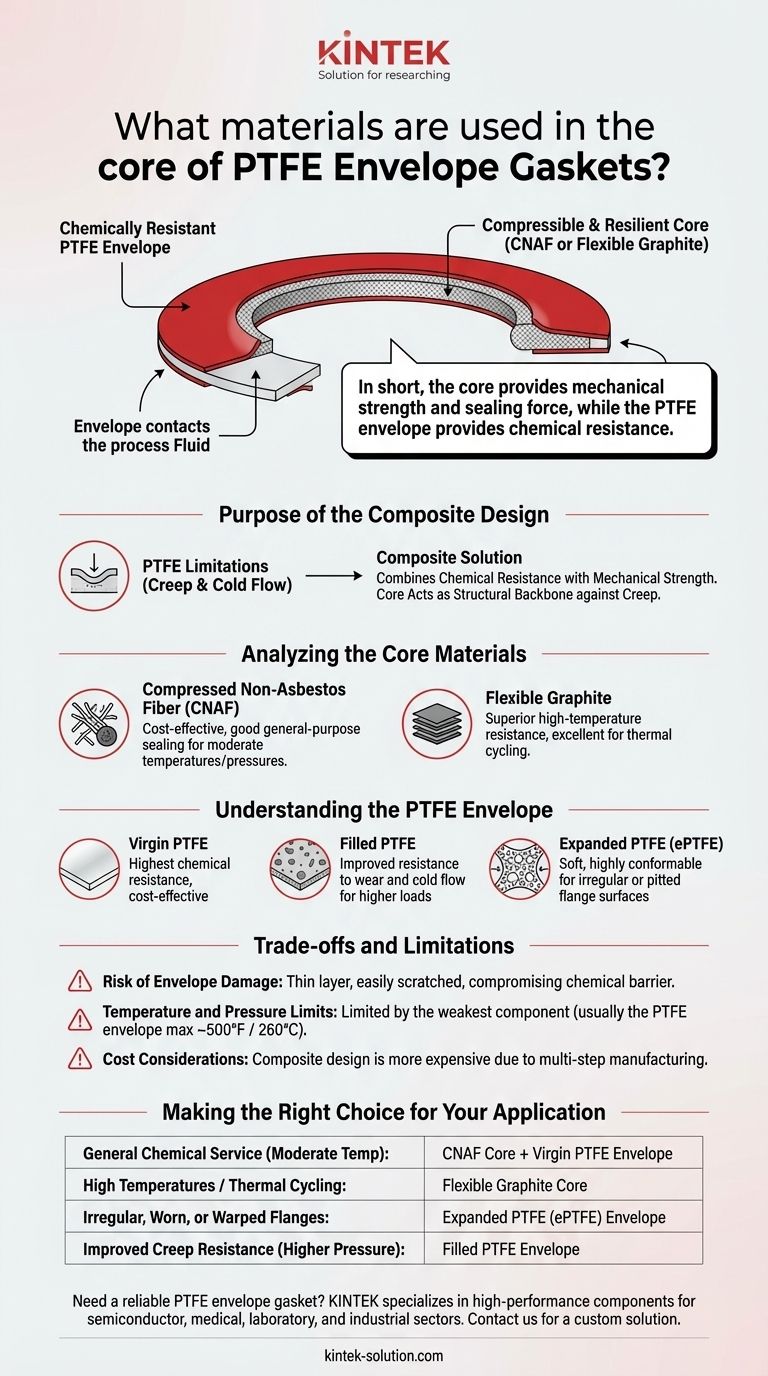
In short, the core of a PTFE envelope gasket is made from a compressible, resilient material, most commonly Compressed Non-Asbestos Fiber (CNAF) or Flexible Graphite. This core provides the mechanical strength and sealing force, while the outer Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) layer, or "envelope," provides the chemical resistance.
The central purpose of a PTFE envelope gasket is to deliver the near-universal chemical inertness of PTFE without suffering from its inherent mechanical weaknesses. By combining a soft, chemically resistant PTFE shell with a strong, resilient inner core, you get a gasket that offers the best of both worlds for demanding applications.
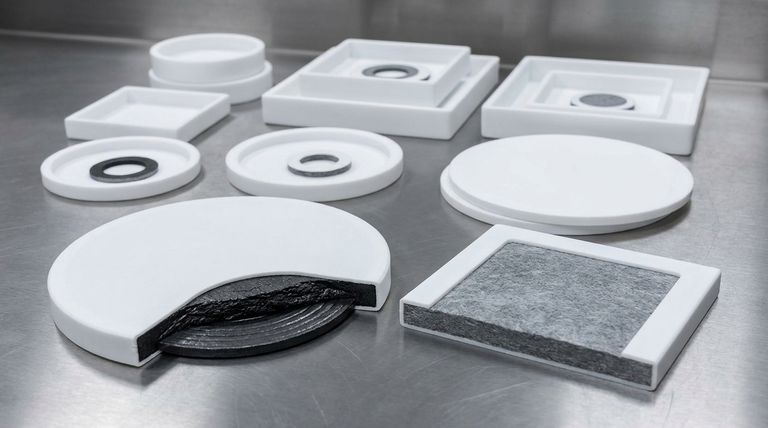

The Purpose of the Composite Design
A standard gasket made of pure PTFE can fail under pressure or temperature changes due to a phenomenon called "creep" or "cold flow," where the material slowly deforms. The envelope design directly solves this problem.
Combining Chemical Resistance with Mechanical Strength
The design is a clever division of labor. The thin PTFE envelope is the only material that comes into contact with the process fluid, providing an exceptionally non-stick and chemically inert barrier.
The inner core material, which is protected from the chemicals, provides the robust mechanical properties needed to create and maintain a seal under the compressive load of the bolted flange.
Overcoming PTFE's Limitations
By itself, PTFE is soft and prone to deforming permanently under pressure, especially at elevated temperatures. This makes it a poor choice for high-pressure applications.
The core material acts as a structural backbone, resisting this creep and providing the elastic recovery necessary to maintain a tight seal even as operating conditions fluctuate.
Analyzing the Core Materials
The choice of core material is determined by the application's temperature, pressure, and mechanical demands.
Compressed Non-Asbestos Fiber (CNAF)
This is a common, cost-effective core material made from a blend of fibers and a rubber binder (like NBR or SBR). It offers excellent general-purpose sealing capabilities at moderate temperatures and pressures.
Flexible Graphite
For more demanding services, flexible graphite is the superior choice. It offers excellent resistance to high temperatures and can handle significant thermal cycling without losing its sealing integrity. It is the go-to core material for high-temperature chemical applications.
Understanding the PTFE Envelope
Just as the core material can vary, so can the type of PTFE used for the envelope itself. This choice affects the gasket's performance and suitability for specific flange conditions.
Virgin PTFE
This is pure, unfilled PTFE. It offers the highest chemical resistance and is cost-effective. It's an excellent choice for standard applications where mechanical stress is not extreme and flange surfaces are in good condition.
Filled PTFE
In this type, a substance like glass, carbon, or graphite is added to the virgin PTFE. These fillers significantly improve the material's mechanical properties, such as its resistance to wear and cold flow, making it suitable for higher loads.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is created by stretching virgin PTFE, resulting in a soft, highly conformable material. An ePTFE envelope is exceptional at sealing irregular, pitted, or warped flange surfaces that other gaskets might struggle with.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, envelope gaskets are not without their own set of considerations.
Risk of Envelope Damage
The PTFE envelope is relatively thin. If it is scratched or damaged during storage or installation, its chemical barrier is compromised. This allows the process fluid to attack the less-resistant core material, leading to premature gasket failure.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
The service limits of the gasket are defined by its weakest component. A gasket with a flexible graphite core may have a high-temperature rating, but it is still ultimately limited by the maximum service temperature of the PTFE envelope (typically around 500°F / 260°C).
Cost Considerations
As a composite gasket requiring a multi-step manufacturing process, an envelope gasket is inherently more expensive than a simple CNAF or graphite sheet gasket. Its use is justified when the chemical resistance of PTFE is a non-negotiable requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct core and envelope combination is critical for ensuring a reliable, long-lasting seal.
- If your primary focus is general chemical service at moderate temperatures: A CNAF core with a virgin PTFE envelope is the standard, cost-effective solution.
- If you are dealing with high temperatures or thermal cycling: Select a flexible graphite core for its superior thermal stability.
- If your flange surfaces are irregular, worn, or warped: An expanded PTFE (ePTFE) envelope offers the best conformability to ensure a tight seal.
- If you need improved creep resistance under higher pressure: Consider a filled PTFE envelope, as the filler material enhances its mechanical strength against deformation.
By understanding how the core and envelope materials work together, you can confidently select the precise gasket construction for optimal performance and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Core Material | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Compressed Non-Asbestos Fiber (CNAF) | Cost-effective, good general-purpose sealing, moderate temperature/pressure resistance | Standard chemical service at moderate temperatures |
| Flexible Graphite | Superior high-temperature resistance, excellent thermal cycling stability | High-temperature chemical applications, demanding thermal cycling |
Need a reliable PTFE envelope gasket for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom envelope gaskets with precisely engineered cores (CNAF or Flexible Graphite) and envelopes (Virgin, Filled, or ePTFE). We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, ensuring precision production from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you select the optimal gasket construction for chemical resistance, temperature stability, and mechanical strength. Contact us today for a custom solution that ensures a reliable, long-lasting seal.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















