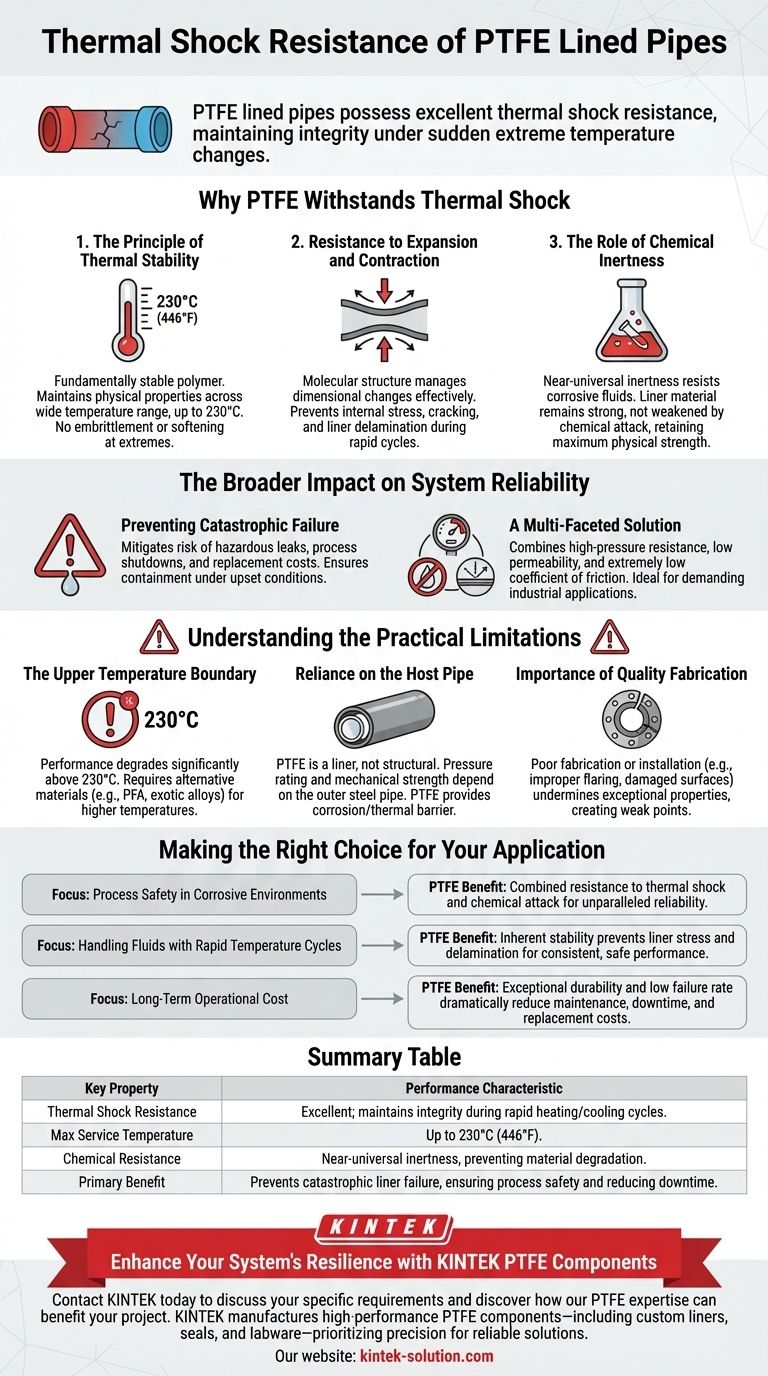
PTFE lined pipes possess excellent thermal shock resistance. This means they are engineered to maintain their structural integrity and dimensional stability without cracking, warping, or failing when subjected to sudden and extreme temperature changes.
The core reason for this resilience lies in PTFE's inherent thermal stability and low reactivity. This combination prevents the material from degrading or developing stress fractures during rapid heating or cooling cycles, ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of the pipeline.

Why PTFE Withstands Thermal Shock
The Principle of Thermal Stability
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a fundamentally stable polymer across a wide operational temperature range, often up to 230°C (446°F).
Unlike many materials that become brittle or soft at temperature extremes, PTFE maintains its key physical properties, providing a consistent and reliable barrier.
Resistance to Expansion and Contraction
Thermal shock failure often occurs when a material expands or contracts too quickly, creating internal stresses that lead to cracks.
PTFE's molecular structure allows it to manage these dimensional changes effectively without compromising its integrity, preventing the liner from pulling away from the host pipe or developing fissures.
The Role of Chemical Inertness
The performance of a pipe liner is not just about thermal stress; it's also about its condition. PTFE is almost universally inert, resisting attack from the vast majority of corrosive fluids.
Because the liner material is not being weakened or degraded by chemical attack, it retains its maximum physical strength to resist the mechanical stresses of thermal shock.
The Broader Impact on System Reliability
Preventing Catastrophic Failure
A liner failure is more than an inconvenience; it can be a catastrophic event leading to hazardous leaks, process shutdowns, and significant replacement costs.
The thermal shock resistance of PTFE directly mitigates this risk, ensuring containment of corrosive or high-temperature media even under upset conditions.
A Multi-Faceted Solution
While thermal shock resistance is a critical feature, PTFE is specified because it solves multiple problems simultaneously.
It offers a combination of high-pressure resistance, low permeability, and an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it an ideal choice for the most demanding industrial applications.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
The Upper Temperature Boundary
While robust, PTFE is not without its limits. Its performance degrades significantly above its maximum recommended service temperature of approximately 230°C. For applications beyond this point, alternative materials like PFA or exotic metal alloys must be considered.
Reliance on the Host Pipe
It is critical to remember that PTFE is a liner, not a structural component. The overall pressure rating and mechanical strength of the system are determined by the outer carbon steel or stainless steel pipe. The PTFE provides the corrosion and thermal barrier.
Importance of Quality Fabrication
The exceptional properties of PTFE can be undermined by poor fabrication or installation. Improperly flared ends or damaged surfaces can create weak points that are susceptible to failure under thermal or mechanical stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct material is about matching its capabilities to your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is process safety in corrosive environments: PTFE's combined resistance to thermal shock and near-universal chemical attack provides unparalleled reliability.
- If your primary focus is handling fluids with rapid temperature cycles: PTFE's inherent stability prevents liner stress and delamination, ensuring consistent and safe performance.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational cost: The exceptional durability and low failure rate of PTFE lining dramatically reduce maintenance, downtime, and replacement costs over the asset's lifespan.
Ultimately, specifying PTFE lined pipe is a strategic decision to engineer resilience directly into your critical fluid handling systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Performance Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent; maintains integrity during rapid heating/cooling cycles. |
| Max Service Temperature | Up to 230°C (446°F). |
| Chemical Resistance | Near-universal inertness, preventing material degradation. |
| Primary Benefit | Prevents catastrophic liner failure, ensuring process safety and reducing downtime. |
Enhance Your System's Resilience with KINTEK PTFE Components
Does your application involve corrosive fluids and rapid temperature swings? The exceptional thermal shock resistance of PTFE is critical for preventing costly failures and ensuring long-term operational safety.
KINTEK manufactures high-performance PTFE components—including custom liners, seals, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production to deliver reliable solutions, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you engineer resilience into your critical systems. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our PTFE expertise can benefit your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















