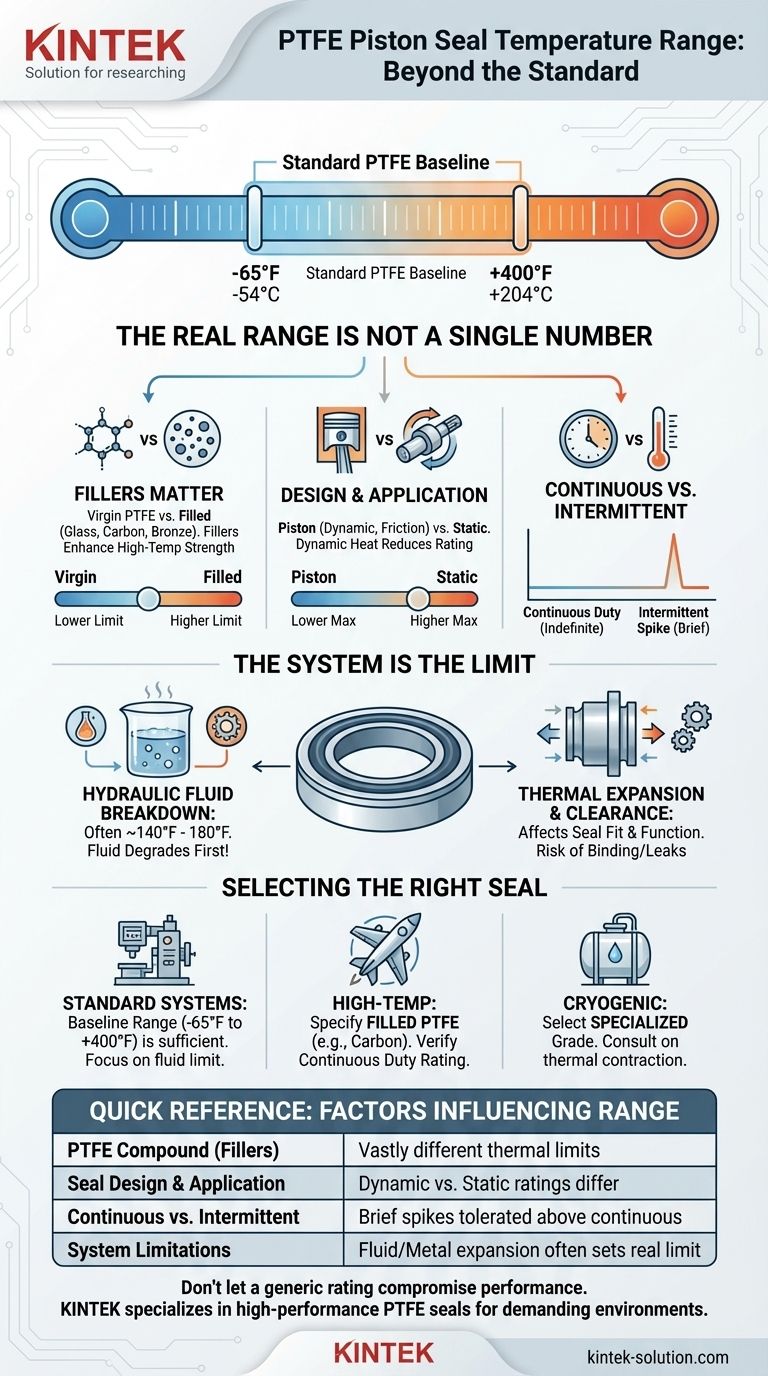
In practice, a standard PTFE piston seal is typically rated for a temperature range of -65°F to +400°F (-54°C to +204°C). However, this figure is only a baseline. The actual operational temperature range of a PTFE seal can vary dramatically based on the specific PTFE compound, the seal's design, and the operational limits of the system it is installed in.
While the base PTFE polymer has an exceptionally wide temperature tolerance, the effective range of a specific seal is ultimately determined by its fillers and the temperature limits of the surrounding components, such as hydraulic fluid.

Why a Single Temperature Range is Misleading
The term "PTFE seal" covers a wide family of products. The idea that they all share one temperature range is a common oversimplification. Several factors determine the true thermal performance.
The Critical Role of Fillers
Pure, or "virgin," PTFE has its own set of properties. However, most industrial seals are made from filled PTFE compounds, where materials are blended in to enhance specific characteristics.
These fillers fundamentally alter thermal performance. For example, adding glass fiber or carbon significantly increases the seal's resistance to deformation under load at high temperatures compared to virgin PTFE.
Seal Design and Application
The design of the seal is engineered for its specific task, which influences its temperature rating.
A piston seal experiences linear movement and pressure, while a rotary shaft seal contends with constant friction in one area. These different stress profiles mean that a PTFE compound rated for 500°F as a static seal might have a lower rating in a high-speed dynamic application due to friction-generated heat.
Continuous vs. Intermittent Temperature
Manufacturers often provide two temperature ratings: continuous and intermittent.
- Continuous Temperature: The maximum temperature the seal can withstand indefinitely without degrading.
- Intermittent Temperature: A higher temperature the seal can tolerate for brief spikes. Exceeding the continuous rating for extended periods will shorten the seal's life.
The System is the True Limiting Factor
A seal does not operate in a vacuum. Its performance is directly tied to the system it serves. Focusing only on the seal's maximum temperature rating is a frequent cause of system failure.
Mismatch with System Fluids
The most common limitation is the operating fluid. A PTFE seal may be rated to +400°F, but standard hydraulic fluid begins to break down and oxidize rapidly above 180°F, with optimal performance often below 140°F.
Running the system at a temperature that the seal can handle but the fluid cannot will lead to fluid degradation, sludge formation, and eventual system failure.
Thermal Expansion and Clearance
Extreme temperatures—both hot and cold—cause materials to change size. At high temperatures, the seal and the metal housing will expand. At cryogenic temperatures, they contract.
These dimensional changes affect the precise clearances required for the seal to function. If not accounted for in the design, expansion can cause the seal to bind, while contraction can lead to leaks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a seal for a specific temperature range involves balancing performance, longevity, and cost.
Performance at Extreme Cold
At the cryogenic end of the spectrum (below -300°F), PTFE becomes stiffer and less flexible. While specialized PTFE compounds can operate at these temperatures without fracturing, their ability to provide a dynamic, responsive seal may be reduced. This can be a critical factor in applications requiring consistent sealing pressure during temperature fluctuations.
Performance at Extreme Heat
As PTFE approaches its upper temperature limit, it begins to soften, and its rate of wear accelerates. For filled grades, temperatures nearing 500°F can compromise the bond between the PTFE and the filler material, degrading its enhanced properties. Exceeding the absolute maximum temperature will cause permanent decomposition.
The Cost of Specialization
Seals designed for extreme temperature ranges, such as those with specialized carbon or polymer fillers, are significantly more expensive than standard glass-filled or bronze-filled PTFE compounds. Using a standard seal in an extreme environment is a false economy that will lead to premature failure.
Selecting the Right Seal for Your Application
To make the right choice, you must match the seal's capabilities to your system's specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is standard hydraulic or pneumatic systems: A seal rated for -65°F to +400°F is typically more than sufficient, as system fluid is the limiting factor.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature environment (e.g., aerospace, down-hole drilling): You must specify a filled PTFE (such as carbon or specialized polymer) and verify its continuous duty rating matches your system's operating temperature.
- If your primary focus is a cryogenic or extreme cold application: Select a specialized cryogenic-grade PTFE compound designed to maintain some flexibility at low temperatures and consult with the manufacturer on thermal contraction.
Always consult the manufacturer’s specific data sheet for the exact seal compound you intend to use.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| PTFE Compound (Fillers) | Virgin PTFE vs. filled (glass, carbon) compounds have vastly different thermal limits. |
| Seal Design & Application | Dynamic (piston) vs. static seals have different ratings due to friction and stress. |
| Continuous vs. Intermittent Use | Brief temperature spikes can be tolerated above the continuous duty rating. |
| System Limitations | Hydraulic fluid breakdown or thermal expansion of metal parts often sets the real limit. |
Don't let a generic temperature rating compromise your system's performance.
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise lies in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to ensure your seals are perfectly matched to your application's specific temperature, pressure, and chemical requirements.
Get a seal engineered for your exact needs. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the overall operating temperature range for PTFE seals, gaskets, and O-rings? Achieve Sealing Integrity from -200°C to +260°C
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance
- How do PTFE seals perform under pressurized conditions? Achieving Reliable Sealing in Demanding Environments
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals in demanding industries? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions



















