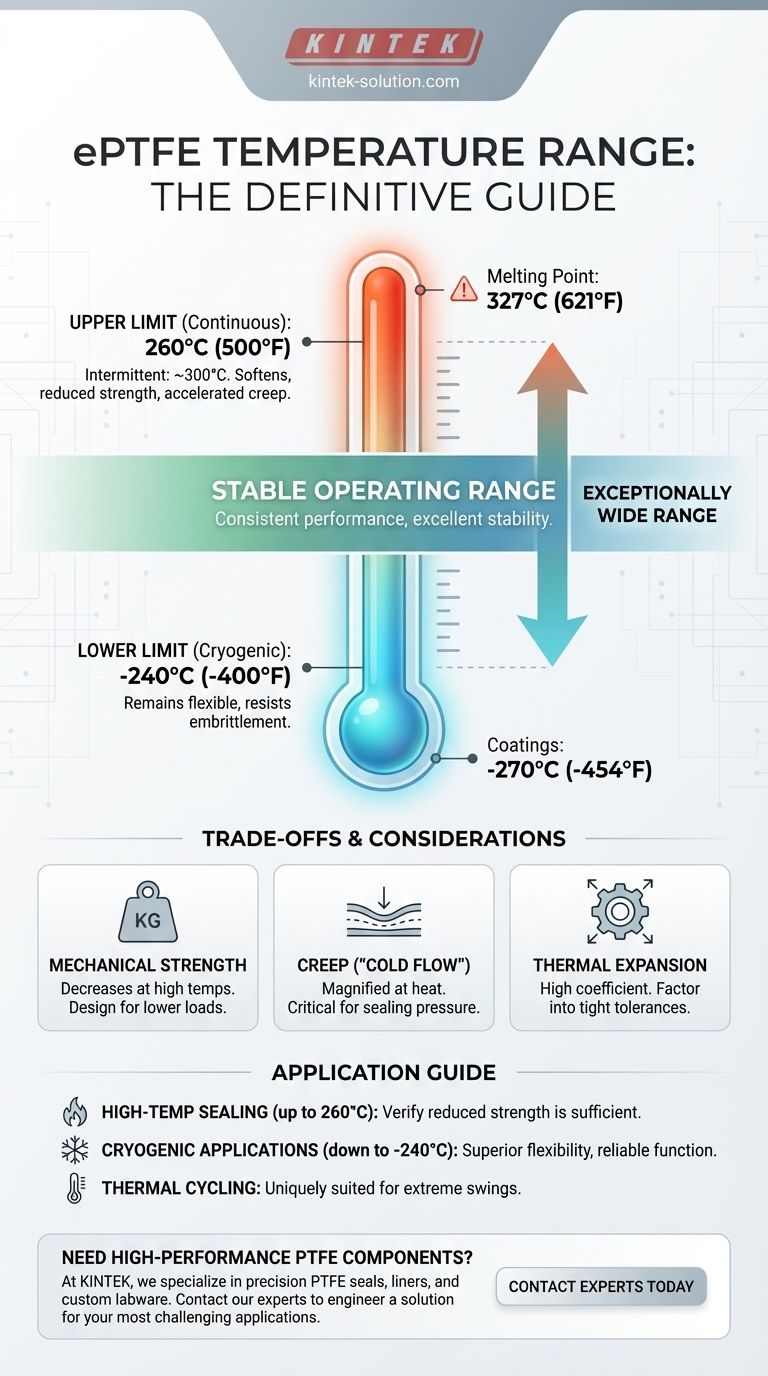
In short, expanded PTFE (ePTFE) has an exceptionally wide service temperature range, making it one of the most versatile polymers for extreme environments. It reliably performs from cryogenic lows of -400°F (-240°C) up to a high continuous service temperature of 500°F (260°C).
The key takeaway is not just the numbers, but the material's stability across this range. Unlike many materials that become brittle in the cold or degrade rapidly in heat, ePTFE maintains its core properties, offering consistent and reliable performance in both cryogenic and high-temperature applications.

Deconstructing the Temperature Range
To properly apply ePTFE, you must understand the nuances of its performance at the upper and lower limits of its operational window.
The Upper Limit: Continuous vs. Intermittent Use
The most cited upper limit for ePTFE is 260°C (500°F). This is the maximum temperature for continuous service, where the material can be expected to perform reliably over long periods without significant degradation.
For short, intermittent periods, PTFE can withstand slightly higher temperatures, with some sources indicating a tolerance up to 290-300°C (554-572°F). Exceeding the continuous rating for extended periods will accelerate the decline of its mechanical properties.
The Cryogenic Limit: Performance in Extreme Cold
The lower service limit for ePTFE is approximately -240°C (-400°F). In some forms, like coatings, PTFE can reach even lower temperatures of -270°C (-454°F).
Its performance in cryogenic conditions is a defining feature. While many polymers become extremely brittle and fail at such low temperatures, ePTFE retains a significant degree of its flexibility and resilience.
Understanding the Melting Point
It is critical to distinguish the service temperature from the melting point. PTFE's melting point is much higher, around 327°C (621°F).
The 260°C service limit represents the point where the material begins to lose significant mechanical strength, even though it is not yet melting. This provides a crucial safety margin in high-heat applications.
What Happens at the Temperature Extremes?
A material's temperature rating is only useful when you understand how it behaves at those boundaries.
Approaching the Upper Limit
As ePTFE approaches its 260°C continuous limit, its physical properties change. The material softens, leading to a decrease in tensile strength, wear resistance, and compressive strength.
This is a critical design consideration for any application involving mechanical load at high temperatures.
At Cryogenic Temperatures
The primary advantage of ePTFE in the cold is its resistance to embrittlement. It remains a tough, flexible material, making it an ideal choice for seals, gaskets, and components in cryogenic systems like those used for Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) or in aerospace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging the trade-offs associated with ePTFE's thermal performance.
Mechanical Strength Degradation
Thermal stability is not the same as mechanical stability. While ePTFE survives high temperatures, its strength is compromised. A part designed for a load at room temperature may fail under the same load at 250°C.
Creep or "Cold Flow"
PTFE is known for its tendency to "creep," or slowly deform under a sustained load. This effect is significantly magnified at higher temperatures. In gasket or sealing applications, this must be accounted for to prevent a loss of sealing pressure over time.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals. In assemblies with tight tolerances that experience wide temperature swings, this expansion and contraction must be factored into the design to avoid component failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if ePTFE is the correct material for your specific thermal challenge.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sealing (up to 260°C): ePTFE is an excellent candidate, but you must verify that its reduced mechanical strength at your target temperature is sufficient for the load and pressure requirements.
- If your primary focus is a cryogenic application (down to -240°C): ePTFE is a superior choice due to its ability to remain flexible and not become brittle, ensuring a reliable seal or component function.
- If your primary focus is thermal cycling across a wide range: ePTFE's ability to handle both extreme heat and cold makes it uniquely suited for environments that experience significant temperature swings.
Ultimately, ePTFE's value lies in its predictable performance across one of the widest temperature ranges of any polymer.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Limit: 260°C (500°F) | Stable for continuous service. | Mechanical strength decreases; creep is accelerated. |
| Lower Limit: -240°C (-400°F) | Remains flexible; resists embrittlement. | Ideal for cryogenic seals and components. |
| Melting Point: 327°C (621°F) | Service limit provides a safety margin. | Not a recommended operating temperature. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and custom labware that deliver reliable performance from cryogenic conditions to high-heat environments. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures your components are optimized for your specific thermal and mechanical requirements, whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector.
Let's engineer a solution for your most challenging applications. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs, from prototypes to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What alternative material is gaining popularity for hydrogenerator thrust bearings? PTFE for Superior Performance & Reliability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between PTFE and conventional oil seals? Optimize Performance and Cost
- How can designers balance aesthetics and functionality in PTFE machining? Master Material Properties for Superior Results
- How does PTFE's chemical resistance benefit industrial applications? Boost Equipment Lifespan & Safety
- What are the advantages of using PTFE in plain bearings? Achieve Maintenance-Free, High-Performance Operation
- How can the properties of PTFE sheets be enhanced? Improve Wear, Strength, and Performance with Fillers
- How does the structure of ePTFE gaskets improve upon standard PTFE? Solve Creep and Cold Flow for Superior Seals
- How does Teflon lining on the internal wall of valves improve performance? Enhance Valve Life and Purity



















