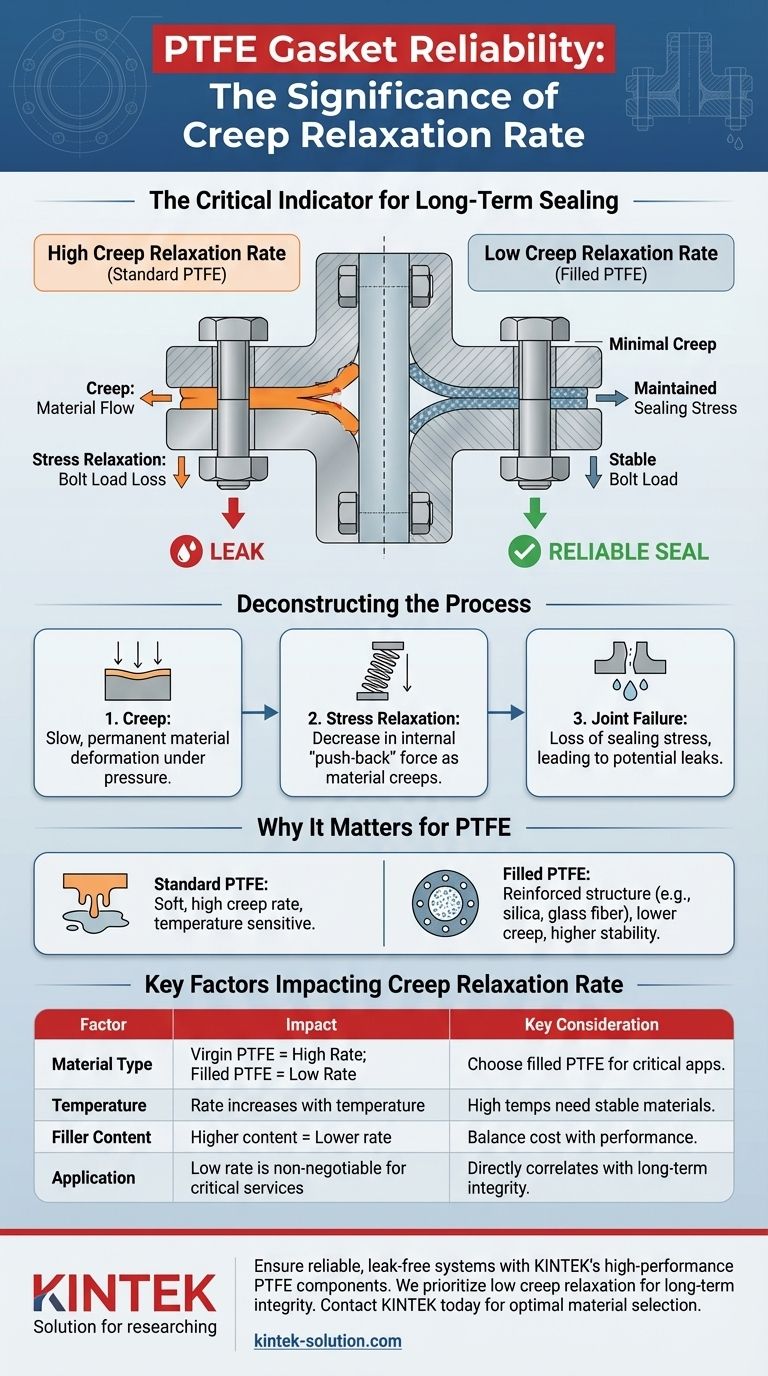
In short, the creep relaxation rate is the single most important indicator of a PTFE gasket's long-term sealing reliability. It measures how well the gasket can maintain the necessary sealing stress under the pressure of bolted flanges over time. A low creep relaxation rate signifies a durable, reliable seal, while a high rate is a direct predictor of future leaks.
The fundamental challenge with any gasketed joint is that the initial bolt load inevitably decreases over time. The creep relaxation rate quantifies how quickly a specific PTFE material loses its "push-back" force, directly determining its ability to maintain a leak-free seal long after installation.
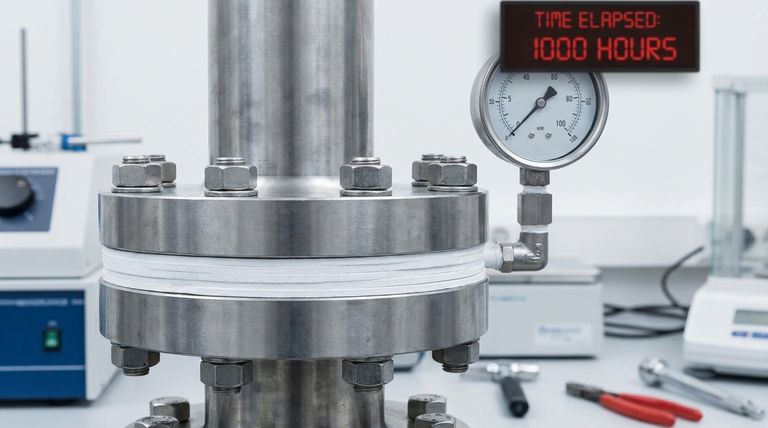

Deconstructing Creep and Stress Relaxation
To grasp the significance of the rate, you must first understand the two forces it measures: creep and stress relaxation. Though related, they describe different aspects of material failure.
What is Creep?
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. It's a slow, continuous "flowing" process.
Imagine placing a heavy weight on a block of soft material. The initial compression is immediate, but if you leave the weight there, the block will continue to get thinner over hours or days. That slow thinning is creep.
What is Stress Relaxation?
Stress relaxation is the observed decrease in stress in response to strain generated in the structure. In a gasketed joint, this means the gasket loses its internal "push-back" force even though it is held at a constant thickness by the flanges.
As the gasket material creeps and thins, the tension in the bolts holding the joint together slightly decreases. This loss of bolt tension reduces the compressive stress on the gasket, a phenomenon we call stress relaxation.
How They Combine in a Flange Joint
In a real-world bolted flange, creep and stress relaxation are locked in a destructive cycle. The constant pressure from the bolts causes the PTFE gasket to creep. This creep (thinning) causes the bolt load to relax, which in turn reduces the sealing stress on the gasket face, creating a potential leak path.
Why This Rate is So Critical for PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is prized for its exceptional chemical resistance and low-friction surface, but its mechanical properties present a significant challenge for sealing.
The Inherent Nature of PTFE
Standard, unfilled PTFE is a relatively soft polymer. This softness makes it inherently susceptible to creep, especially as service temperatures increase. Without modification, PTFE will deform and lose sealing stress quite rapidly.
Quantifying Performance
The creep relaxation rate provides a standardized, numerical value (often expressed as a percentage of stress loss) that allows engineers to compare different gasket materials objectively.
A low creep relaxation rate indicates that the material is dimensionally stable and will maintain a high percentage of the initial sealing stress for a long time. This is the goal for any critical application.
The Consequence of a High Rate
A gasket with a high creep relaxation rate will lead to a significant loss of bolt load. This forces maintenance teams to retorque the bolts, a process that is often impractical or unsafe. If left unchecked, this stress loss will inevitably result in a leak.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE gasket is not just about chemical compatibility; it's about balancing performance against operational conditions and cost.
Temperature's Amplifying Effect
Creep relaxation is not a linear process; it accelerates dramatically with increasing temperature. A PTFE gasket that performs adequately at ambient temperature may fail quickly at higher temperatures due to a sharply increased creep rate.
The Role of Fillers
To combat PTFE's natural tendency to creep, manufacturers add fillers such as silica, glass fiber, or barium sulfate. These fillers create a reinforced internal structure within the polymer.
This "filled PTFE" has a significantly lower creep relaxation rate and is far more stable at higher temperatures than virgin PTFE. This is the most common solution for demanding services.
The Cost of Reliability
As a rule, gasket materials with lower creep relaxation rates (like highly filled or specially structured PTFE) carry a higher initial cost. The trade-off is between this upfront investment and the long-term cost and safety risks associated with maintenance, downtime, and potential leaks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the demands of the service. The creep relaxation rate is your primary guide for ensuring long-term joint integrity.
- If your primary focus is non-critical, low-temperature service: A standard or minimally filled PTFE may suffice, but you must anticipate potential stress loss over time.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or high-pressure service: A low creep relaxation rate is non-negotiable. You must select a well-designed filled or structured PTFE gasket.
- If your primary focus is maximizing safety and long-term reliability: Always choose the gasket with the lowest documented creep relaxation rate that meets all other service requirements (chemical, temperature, pressure).
Ultimately, understanding creep relaxation transforms gasket selection from a simple material choice into a strategic decision about the long-term integrity and safety of your system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Creep Relaxation Rate | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Virgin PTFE has a high rate; filled PTFE has a lower rate. | Choose filled PTFE for critical applications. |
| Temperature | Rate increases dramatically with temperature. | Higher service temperatures require more stable materials. |
| Filler Content | Higher filler content generally reduces the rate. | Balances cost with performance and reliability needs. |
| Application Criticality | Low rate is non-negotiable for high-pressure/temperature services. | Directly correlates with long-term joint integrity and safety. |
Ensure your sealing systems are reliable and leak-free with KINTEK's high-performance PTFE components.
Our expertise in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, gaskets, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors means we understand the critical importance of a low creep relaxation rate. We prioritize material science and precision production to deliver components that maintain sealing stress over time, preventing costly downtime and safety hazards.
Whether you need custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, KINTEK provides the reliable, durable sealing solutions your applications demand.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts help you select the optimal PTFE material for long-term reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges do elastomeric seals face in oil and gas operations? Ensuring Reliability Under Extreme Conditions
- What happens when using a soft rotary shaft with PTFE seals? Avoid Premature Wear and System Failure
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing? Ensuring Purity and Compliance
- How do PTFE expansion bellows handle thermal expansion in piping systems? Prevent Stress and Failure
- What are the common uses of PTFE Lined Globe Valves? Essential for Corrosive & High-Purity Flow Control
- How can the lifespan and performance of PTFE bars be maintained? A Guide to Proactive Care
- How should PTFE-lined valves be maintained for optimal performance? Ensure Long-Term Reliability & Prevent Costly Downtime
- What are the benefits of PTFE-encapsulated O-rings? Superior Sealing for Harsh Chemical & High-Temp Environments



















