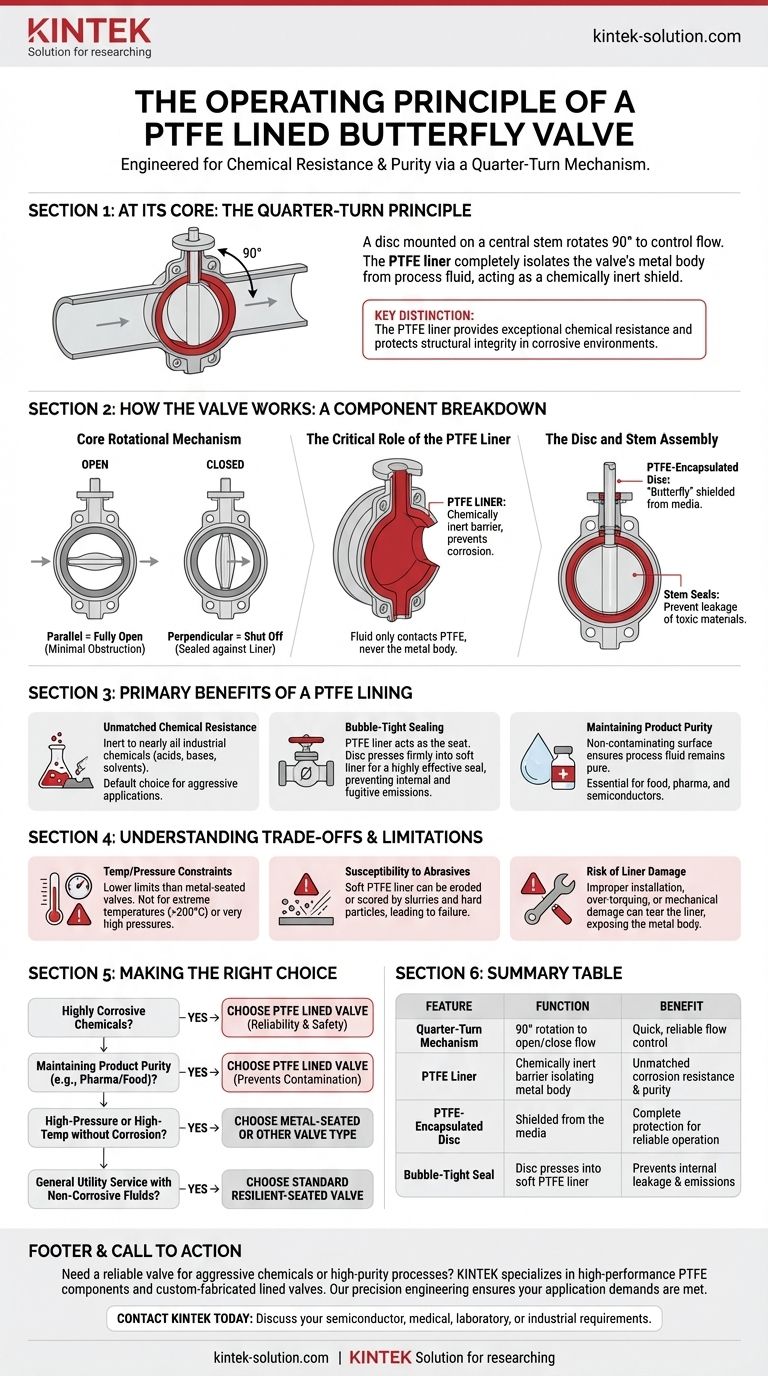
At its core, a PTFE lined butterfly valve operates on a simple quarter-turn principle. A disc, mounted on a central stem within a pipe, rotates 90 degrees to control flow. The key distinction of this valve is the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) liner, which completely isolates the valve's metal body from the process fluid, providing exceptional chemical resistance.
The fundamental purpose of a PTFE lined butterfly valve is not just to control flow, but to do so safely and reliably within highly corrosive or high-purity environments. The PTFE acts as a chemically inert shield, protecting the valve's structural integrity from aggressive media.

How the Valve Works: A Component Breakdown
A standard butterfly valve is simple, but the PTFE-lined variant adds a critical layer of protection. Understanding how these components interact reveals its unique value.
The Core Rotational Mechanism
The valve operates via a quick, 90-degree rotation. When the handle or actuator is turned, the stem rotates the internal disc.
When the disc is parallel to the flow, the valve is fully open, offering minimal obstruction. When the disc is rotated to be perpendicular to the flow, it presses against the liner (or seat) to create a seal, shutting off the flow completely.
The Critical Role of the PTFE Liner
The PTFE liner is the most important feature. It is a thick, continuous layer of chemically inert plastic molded to the interior of the valve's metal body.
This liner serves as an impenetrable barrier. The fluid passing through the valve only ever touches the PTFE, never the structural carbon steel or stainless steel of the body. This prevents corrosion that would otherwise destroy a standard valve.
The Disc and Stem Assembly
The disc, often a metal casting encapsulated in PTFE, is the "butterfly" that moves to block the flow. Encapsulating the disc ensures that it, too, is protected from the corrosive media.
The stem penetrates the valve body to connect to the disc. A series of seals where the stem exits the body prevents the process fluid from leaking out, a critical feature for containing toxic or hazardous materials.
The Primary Benefits of a PTFE Lining
The choice to use a PTFE lined valve is driven by the need to solve specific, challenging problems that standard valves cannot handle.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE, also known by the brand name Teflon®, is inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and solvents. This makes the valve the default choice for aggressive chemical processing applications.
Bubble-Tight Sealing
The resilient PTFE liner also functions as the valve seat. When the disc closes, it presses firmly into the soft liner, creating a highly effective, "bubble-tight" seal. This prevents both internal leakage down the pipeline and fugitive emissions into the atmosphere.
Maintaining Product Purity
Because PTFE is a non-contaminating material, these valves are essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and semiconductors. The inert surface ensures the process fluid remains pure and is not tainted by metal ions or corrosion byproducts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE lined valves are not a universal solution. Their design involves specific trade-offs that are important to recognize.
Temperature and Pressure Constraints
PTFE is a polymer, and as such, it has a lower operating temperature and pressure limit than a metal-seated valve. In services with extreme temperatures (above approximately 400°F / 200°C) or very high pressures, a different valve design may be required.
Susceptibility to Abrasives
The softness that makes PTFE an excellent sealing material also makes it susceptible to damage from abrasive media. Slurries containing hard particles can erode or score the liner, eventually leading to valve failure.
Risk of Liner Damage
The integrity of the valve depends entirely on the integrity of the liner. Improper installation, over-torquing flange bolts, or mechanical damage can create a tear or a "hot spot" in the liner, exposing the metal body to the corrosive fluid and leading to rapid failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve is about matching its capabilities to the demands of the service environment.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: The PTFE liner provides the essential protection needed for long-term reliability and safety.
- If your primary focus is maintaining product purity (e.g., food, pharma): The inert PTFE flow path prevents contamination and ensures the quality of the end product.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure or high-temperature service without corrosion: A metal-seated butterfly valve or a different valve type would be a more suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is general utility service with non-corrosive fluids: A standard, unlined resilient-seated butterfly valve is often the more cost-effective and appropriate solution.
By understanding this principle of engineered isolation, you can confidently specify the right valve for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Quarter-Turn Mechanism | 90° rotation of a disc to open/close flow | Quick, reliable flow control |
| PTFE Liner | Chemically inert barrier isolating metal body | Unmatched corrosion resistance and product purity |
| PTFE-Encapsulated Disc | The 'butterfly' is shielded from the media | Complete protection for reliable operation in harsh environments |
| Bubble-Tight Seal | Disc presses into soft PTFE liner upon closing | Prevents internal leakage and fugitive emissions |
Need a reliable valve for aggressive chemicals or high-purity processes?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom-fabricated lined valves. Our precision engineering ensures your valves deliver the chemical resistance and sealing integrity your application demands, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the main applications of PTFE type Teflon? Unlock Its Versatility for Your Industry
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















