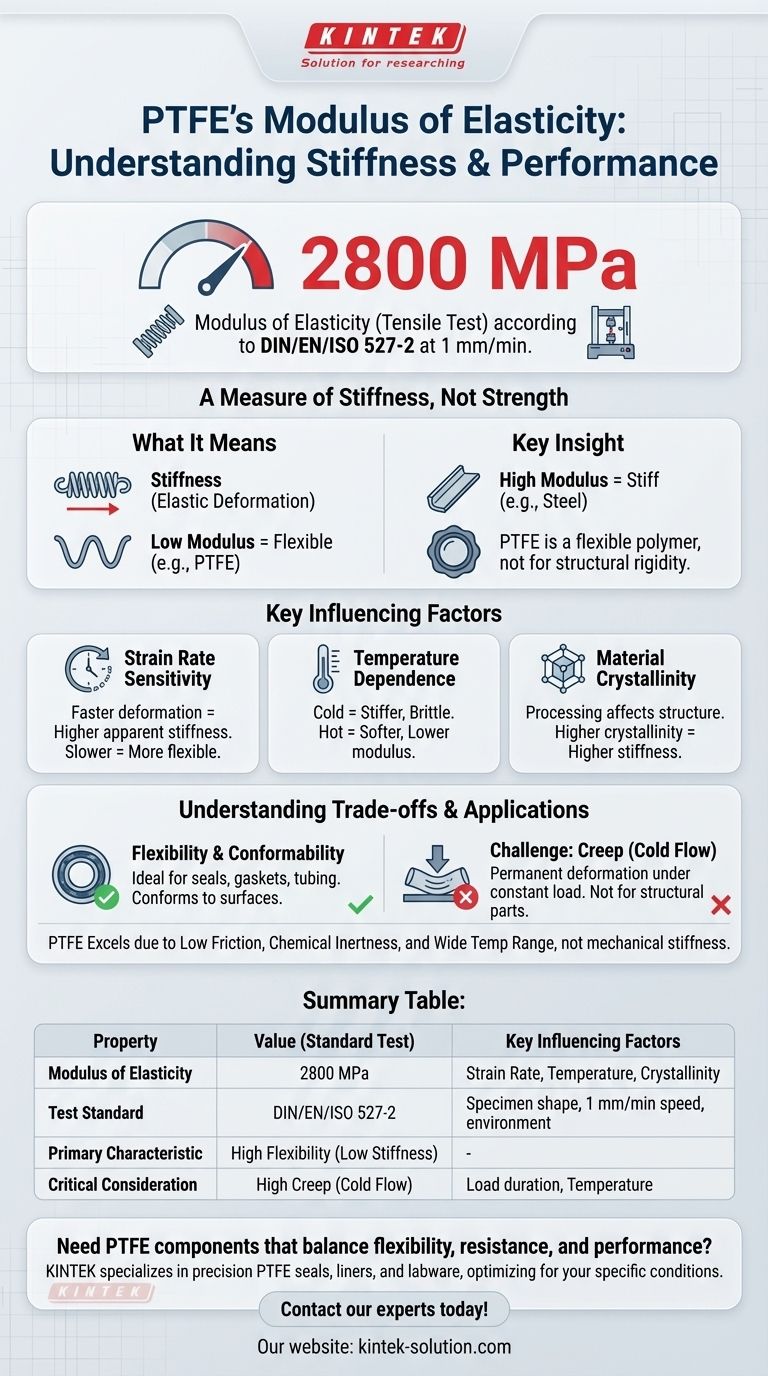
For PTFE, the modulus of elasticity from tensile tests is 2800 MPa. This value is determined according to the DIN/EN/ISO 527-2 standard when the material is tested at a specific speed of 1 mm/min. This standard ensures that the result is consistent and comparable across different labs and material batches.
While the number 2800 MPa provides a direct answer, the true takeaway is that this value represents a single point under ideal lab conditions. For a material like PTFE, its real-world performance is critically dependent on temperature, load duration, and the rate at which it is stressed.

What the Modulus of Elasticity Reveals
The modulus of elasticity, also known as Young's Modulus, is a fundamental measure of a material's stiffness. It describes the relationship between stress (force per unit area) and strain (proportional deformation) in the material's elastic region.
A Measure of Stiffness, Not Strength
A high modulus indicates a stiff material that resists elastic deformation, like steel (~200,000 MPa). A low modulus indicates a flexible material that deforms easily under load.
PTFE's modulus of 2800 MPa places it firmly in the category of flexible polymers. It is not designed for applications requiring high structural rigidity.
The Critical Role of Test Standards
The mention of DIN/EN/ISO 527-2 is not just a technical detail; it is essential for context. Polymer properties are highly sensitive to testing methods.
This standard specifies the exact shape of the test specimen, the testing speed, and the environmental conditions. Without it, reported values for the same material could vary significantly, making engineering comparisons impossible.
Key Factors That Influence PTFE's Modulus
The single value of 2800 MPa is a baseline. In any real-world application, you must consider several variables that can dramatically alter PTFE's mechanical response.
Strain Rate Sensitivity
Polymers like PTFE are viscoelastic, meaning their properties depend on the speed of deformation. The specified 1 mm/min test speed is very slow.
If a force is applied more rapidly in your application, the apparent stiffness and modulus of the PTFE will be higher. Conversely, under very slow, prolonged stress, it will behave as if it's even more flexible.
Temperature Dependence
The mechanical properties of PTFE are highly dependent on temperature. The 2800 MPa value is valid at ambient room temperature (typically ~23°C).
At lower temperatures, PTFE becomes stiffer and more brittle, increasing its modulus. At higher temperatures, it becomes significantly softer, and its modulus drops substantially.
Material Processing and Crystallinity
How PTFE is processed—from the raw powder into a final shape via methods like compression molding or sintering—affects its internal molecular structure.
This processing determines the material's crystallinity, or the degree of structural order. Higher crystallinity generally leads to a higher modulus and greater stiffness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PTFE's low modulus is not inherently a weakness; it is a characteristic that must be understood in the context of its other unique properties. Its value comes from a balance of trade-offs.
Flexibility vs. Load-Bearing Capacity
PTFE's flexibility is an asset in applications like seals, gaskets, and flexible tubing, where it needs to conform to a surface.
However, this same property makes it unsuitable for components that must resist bending or maintain a precise shape under load.
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
A significant consequence of PTFE's molecular structure is its tendency to creep, or "cold flow." This is a slow, permanent deformation that occurs when the material is subjected to a continuous stress, even if that stress is well below its yield strength.
For any application involving constant pressure, such as a valve seat or a long-term structural insulator, creep must be a primary design consideration.
Where PTFE Excels
Engineers choose PTFE not for its mechanical stiffness, but for its unparalleled combination of other properties: an extremely low coefficient of friction, near-universal chemical inertness, and a very wide operating temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use the standard value as a starting point, but always evaluate it against the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction surface or a chemical-resistant seal: PTFE's flexibility (low modulus) is a key advantage, allowing it to conform perfectly to mating surfaces.
- If your primary focus is a load-bearing structural part: The low modulus and high potential for creep make pure PTFE unsuitable. You should consider filled PTFE grades (e.g., glass- or carbon-filled) or a different high-performance polymer.
- If your primary focus is precise engineering calculations: Always refer to the specific datasheet from your material supplier for the exact grade you are using, and if possible, test under conditions that mimic your application's environment.
Ultimately, understanding these material characteristics is the key to leveraging PTFE's unique strengths while avoiding its inherent limitations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value (Standard Test) | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Modulus of Elasticity (Young's Modulus) | 2800 MPa | Strain Rate, Temperature, Material Crystallinity |
| Test Standard | DIN/EN/ISO 527-2 | Specimen shape, testing speed (1 mm/min), environment |
| Primary Characteristic | High Flexibility (Low Stiffness) | - |
| Critical Consideration | High Creep (Cold Flow) under continuous load | Load duration, temperature |
Need PTFE components that balance flexibility, chemical resistance, and performance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, and custom labware. We understand that the true performance of PTFE depends on your specific application's temperature, load, and environmental conditions. Our expertise ensures your components are fabricated to meet exact requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors.
Let's discuss your project requirements and optimize your PTFE solution. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- In what types of media is the PTFE seat butterfly valve widely used? Essential for Corrosive & High-Purity Applications
- How do Teflon bellow mechanical seals contribute to environmental protection in pulp and paper mills? Prevent Hazardous Leaks
- Which acids show high resistance with Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings? Ensure Leak-Free Performance in Aggressive Chemical Environments
- What materials are used to overcome the limitations of standard PTFE in ball valve seats? Upgrade to High-Performance Polymers
- What are some common applications of PTFE coatings? Explore Their Versatile Uses
- What are the different forms of PTFE used for manufacturing gaskets and seals? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What makes Teflon suitable for use in bearings and similar applications? Discover Its Low-Friction, Chemical-Resistant Advantages
- Are PTFE V-Rings customizable? Engineer a Perfect Seal for Your Unique Application



















