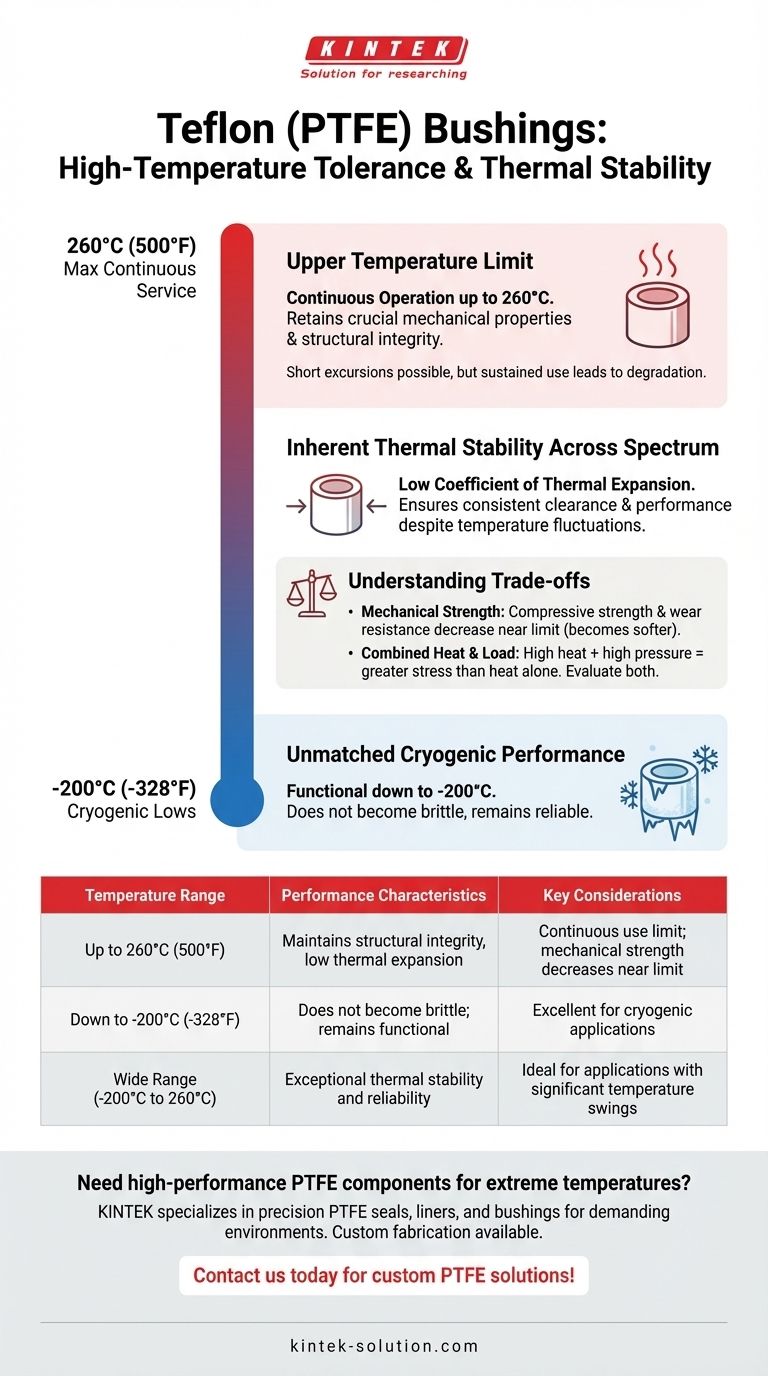
In short, Teflon (PTFE) bushings have a maximum continuous service temperature of approximately 260°C (500°F). This high tolerance allows them to maintain their structural integrity and key performance characteristics in demanding industrial, automotive, and manufacturing environments without degrading.
The true value of Teflon isn't just its ability to withstand high heat, but its exceptional thermal stability across an incredibly wide temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows to high-temperature industrial processes.

Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
The performance of a material is defined by its stability under stress. For PTFE, its molecular structure gives it an inherent resistance to thermal energy, making it a reliable choice for applications with significant temperature variations.
The Upper Temperature Limit
Teflon bushings can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). At this temperature, the material retains its crucial mechanical properties and does not lose its structural integrity, which is essential for components under load.
Unmatched Cryogenic Performance
Equally impressive is PTFE's performance in extreme cold. It remains functional and does not become brittle at temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F). This makes it one of the few materials suitable for both high-heat and cryogenic applications.
Inherent Thermal Stability
A critical feature of Teflon is its very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means the bushing will not significantly change its size or shape when subjected to temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent clearance and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While Teflon's temperature range is impressive, selecting it requires understanding its behavior near its operational limits, especially when other forces are at play.
The Impact on Mechanical Strength
As PTFE approaches its maximum temperature limit, its compressive strength and wear resistance naturally decrease. It becomes softer, which can be a critical factor in high-load applications.
The Combined Effect of Heat and Load
The performance of a Teflon bushing depends on the interplay of temperature, load, and speed. An application with high heat and high pressure will stress the material far more than an application with high heat alone. Both factors must be evaluated together.
"Continuous Use" is a Key Qualifier
The 260°C (500°F) rating is for continuous operation. While brief excursions above this temperature may be tolerated, sustained use beyond this limit will lead to accelerated degradation and eventual failure of the component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to the specific demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is high heat under moderate load: Teflon is an excellent candidate, offering reliable performance and dimensional stability up to 260°C (500°F).
- If your primary focus is performance across extreme temperature swings: Teflon's stability from cryogenic conditions to high heat makes it a uniquely dependable choice.
- If your primary focus is a high-load environment near the temperature limit: You must carefully analyze the combined stresses to ensure the bushing's mechanical strength remains sufficient for your needs.
Ultimately, choosing Teflon for its thermal properties provides a solution known for its stability, reliability, and unparalleled operational range.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 260°C (500°F) | Maintains structural integrity, low thermal expansion | Continuous use limit; mechanical strength decreases near limit |
| Down to -200°C (-328°F) | Does not become brittle; remains functional | Excellent for cryogenic applications |
| Wide Range (-200°C to 260°C) | Exceptional thermal stability and reliability | Ideal for applications with significant temperature swings |
Need high-performance PTFE components for extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components like seals, liners, and bushings for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your components deliver reliable thermal stability and structural integrity.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific temperature, load, and speed requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a quote for custom PTFE solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why are non-stick properties important in PTFE washers? Prevent Adhesion and Ensure Reliability
- What types of parts can be fabricated using PTFE machining? Seals, Bushings, Insulators & More
- How do PTFE gaskets contribute to electrical insulation? Ensuring Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What are the advantages of using PTFE Expansion Bellows? Maximize System Integrity & Uptime
- What are the advantages of PTFE gaskets in terms of chemical resistance? Achieve Unmatched Sealing in Corrosive Environments
- What are the key properties of PTFE/Teflon? Why It's the Ideal Choice for Demanding Machined Parts
- What are the key benefits of PTFE expansion bellows in terms of chemical resistance? Achieve Unmatched System Integrity
- Are Teflon backup rings suitable for food processing applications? Ensure Safety and Reliability



















