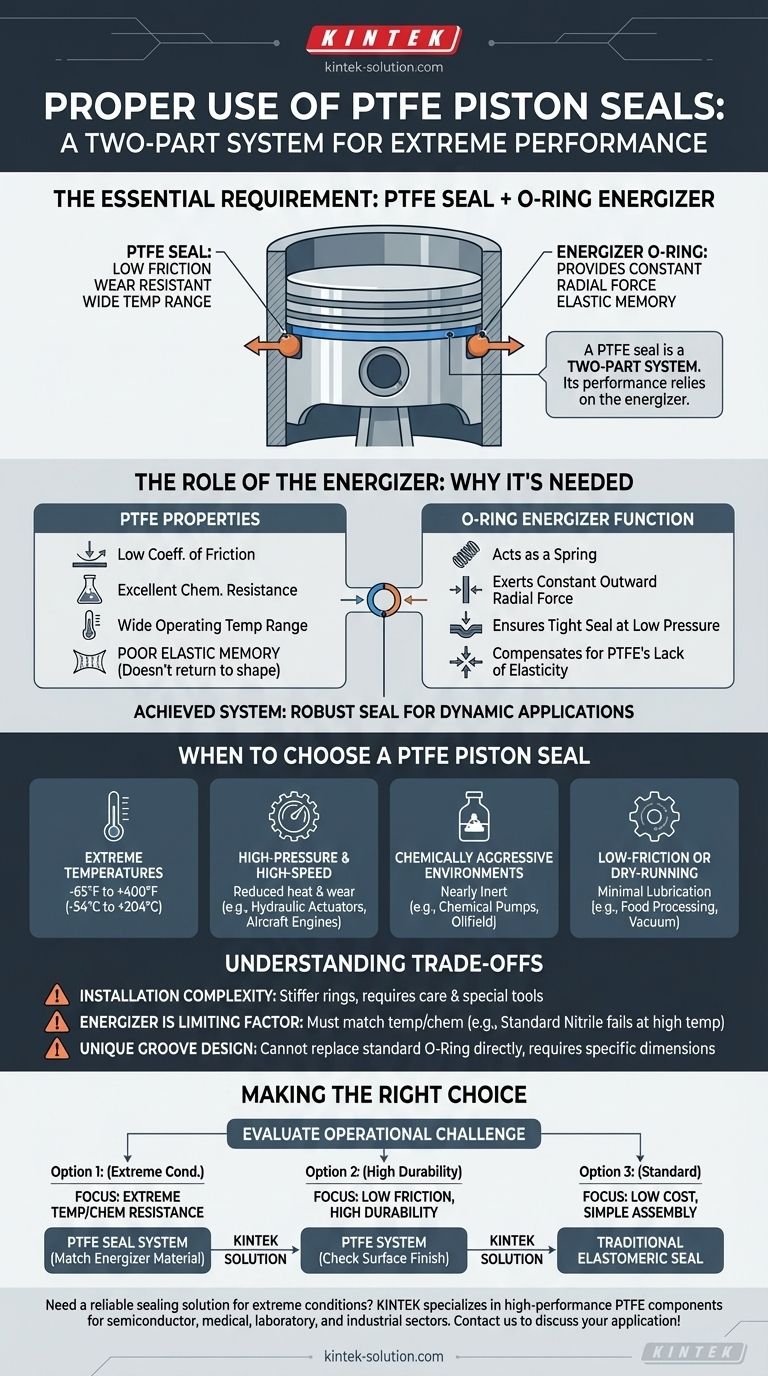
To ensure proper function, a PTFE piston seal must always be used in conjunction with an O-Ring energizer. The PTFE material itself provides the low-friction sealing surface, but it lacks the elasticity to maintain a consistent force against the cylinder wall. The energizer, typically an elastomeric O-Ring, sits behind the PTFE ring and provides the constant radial pressure required to create and maintain a reliable seal.
A PTFE seal is not a standalone component but a two-part system. Its high performance in extreme conditions is entirely dependent on the presence of an energizer to compensate for the material's inherent lack of memory and elasticity.

The Role of the Energizer: Why PTFE Seals Need Help
Understanding why the energizer is non-negotiable requires understanding the properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) itself.
The Material Properties of PTFE
PTFE is renowned for its extremely low coefficient of friction, excellent chemical resistance, and wide operating temperature range.
However, its primary drawback is its poor elastic memory. It does not readily return to its original shape after being compressed or deformed.
How the O-Ring Energizer Works
The O-Ring energizer acts as a spring. It is installed in the groove behind the PTFE ring.
This elastomeric ring constantly exerts an outward, radial force on the PTFE seal. This force pushes the PTFE ring firmly against the sealing surface (e.g., the cylinder bore), ensuring a tight seal even under low-pressure conditions.
What This System Achieves
This dual-component design leverages the strengths of both materials. You get the low friction, wear resistance, and temperature stability of the PTFE seal face.
Simultaneously, you get the reliable, constant sealing force from the elastomeric O-Ring. This combination creates a robust seal ideal for dynamic applications.
When to Choose a PTFE Piston Seal
A PTFE seal system is a superior choice over standard elastomeric seals when the operating conditions are too demanding.
Extreme High or Low Temperatures
PTFE seals function effectively in a very broad temperature range, typically from -65°F to +400°F (-54°C to +204°C). This far exceeds the capabilities of most common elastomers.
High-Pressure and High-Speed Applications
The inherent toughness and low-friction nature of PTFE reduce heat generation and wear in high-speed reciprocating or rotary motion. This makes them ideal for hydraulic actuators, compressors, and aircraft engines.
Chemically Aggressive Environments
PTFE is nearly chemically inert. This makes it the default choice for sealing applications involving aggressive chemicals or abrasive media, such as in chemical pumps or oilfield equipment.
Low-Friction or Dry-Running Needs
Because of its naturally low friction, a PTFE seal requires minimal to no lubrication and can even perform in dry-running conditions without damage. This is a critical advantage in applications like food processing or vacuum service where contamination from lubricants is unacceptable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a PTFE seal system is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on correct implementation.
Installation Complexity
PTFE rings are significantly stiffer than standard O-Rings. They can be more difficult to install and may require specialized tools or techniques to stretch them over a piston head without causing permanent damage or deformation.
The Energizer as a Limiting Factor
The overall performance of the seal assembly is limited by its weakest link. The temperature range and chemical compatibility of the energizer O-Ring must be matched to the application. Using a standard Nitrile energizer in a high-temperature application will lead to failure, even if the PTFE ring can handle the heat.
Groove Design is Different
You cannot simply replace a standard O-Ring with a PTFE seal and energizer. Piston grooves designed for PTFE seal systems have different dimensions to properly accommodate both the seal ring and the energizer, ensuring correct compression and function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct seal requires evaluating your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature or chemical resistance: A PTFE seal is the right choice, but ensure the O-Ring energizer material (e.g., FKM, FFKM) is also rated for those conditions.
- If your primary focus is low friction and high durability: The PTFE system is ideal, but pay close attention to the hardware's surface finish to maximize seal life and prevent premature wear.
- If your primary focus is low cost and simple assembly in a standard environment: A traditional, single-piece elastomeric seal is likely the more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, understanding that a PTFE seal is a two-part system is the key to unlocking its superior performance in demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PTFE Seal Role | Energizer Role |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Low-friction sealing surface | Provides constant radial sealing force |
| Key Property | Chemical resistance, temperature stability | Elasticity, memory |
| Benefit | Handles harsh conditions, low friction | Ensures consistent contact and pressure |
| Application Note | Not a standalone component | Must be chemically/temperature compatible |
Need a reliable sealing solution for extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom piston seal systems for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production ensures your seals are optimized for your specific temperature, pressure, and chemical requirements. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- How do FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings contribute to equipment longevity? Prevent Costly Downtime with Superior Seals
- What makes PTFE stand out among materials used in sealing technology? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key steps for properly installing PTFE seals? Ensure a Leak-Free, Long-Lasting Seal
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance



















