Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer known for its exceptional resistance to chemicals, extreme temperatures, and friction. Composed entirely of carbon and fluorine, its unique molecular structure gives it a combination of properties that make it invaluable across a wide range of industries, from aerospace to cookware.
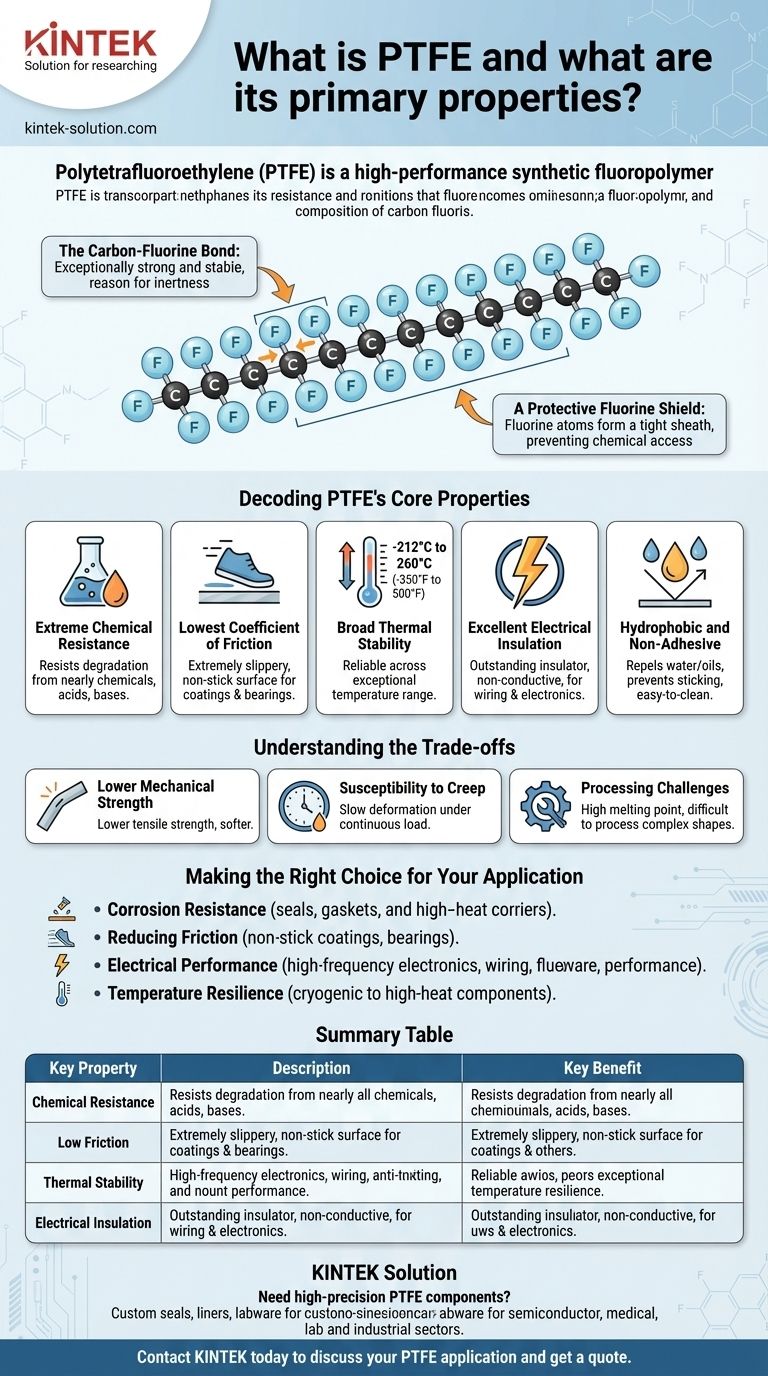
The core of PTFE's power lies in the carbon-fluorine bond, one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This bond creates an incredibly stable and non-reactive molecule, which is the source of nearly all of its sought-after characteristics.

The Molecular Foundation of PTFE
To understand PTFE, you must first understand its simple but powerful chemical structure. This molecular foundation is the origin of its unique performance profile.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon is bonded to two fluorine atoms. The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable.
This chemical stability is the primary reason PTFE does not easily react with other substances, giving it its famous inertness.
A Protective Fluorine Shield
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. They effectively form a tight, protective sheath around the carbon backbone.
This "fluorine shield" prevents other chemicals from accessing and reacting with the carbon chain, further enhancing its durability and resistance.
Decoding PTFE's Core Properties
The unique molecular structure of PTFE directly translates into a set of distinct and highly desirable material properties.
Extreme Chemical Resistance
Because of its stable bonds and protective shield, PTFE is one of the most non-reactive materials known. It resists degradation from nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This gives it an extremely slippery, non-stick surface, which is why it is used for everything from pan coatings to low-friction bearings.
Broad Thermal Stability
This material performs reliably across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from cryogenic lows of -212°C (-350°F) up to 260°C (500°F). It maintains its properties in conditions where most other polymers would fail.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with a very low dielectric constant. It does not conduct electricity, making it a critical material for high-performance wiring, cables, and electronic components.
Hydrophobic and Non-Adhesive
The material is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and oils. This property prevents substances from sticking to its surface, contributing to its non-stick and easy-to-clean nature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. While PTFE's properties are remarkable, it's crucial to understand its limitations to use it effectively.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to metals and some engineering plastics, PTFE has lower tensile strength and is softer. It is not typically used for primary structural components that bear heavy loads.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under a continuous load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE can slowly deform over time. This phenomenon, known as "creep," must be accounted for in engineering designs.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has a very high melting point and high melt viscosity, which can make it more difficult and costly to process into complex shapes compared to more common thermoplastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about leveraging its unique strengths where they matter most.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in extreme chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: It is the go-to material for non-stick coatings, self-lubricating bearings, and other low-drag surfaces.
- If your primary focus is electrical performance: Its insulating properties make it essential for high-frequency electronics, aerospace wiring, and critical connectors.
- If your primary focus is temperature resilience: It excels in components that must function reliably in both cryogenic and high-heat conditions.
Ultimately, PTFE is a powerful problem-solving material designed for conditions where conventional materials would quickly fail.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and bases. | Unmatched durability in corrosive environments. |
| Low Friction | One of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. | Excellent for non-stick and low-wear applications. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from -212°C to 260°C (-350°F to 500°F). | Reliability across extreme temperature ranges. |
| Electrical Insulation | Outstanding insulator with a low dielectric constant. | Critical for high-performance electronics and wiring. |
Need high-precision PTFE components that leverage these properties?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and more for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine material expertise with precision production to deliver components—from prototypes to high-volume orders—that meet your exact specifications for performance and reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE application and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of carbon-filled PTFE? A High-Performance Composite for Demanding Applications
- What are the characteristics and uses of bronze-filled PTFE? A Guide to High-Strength PTFE Composites
- How does PTFE perform with different hydraulic fluids and environmental exposures? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resilience
- What certifications does the manufacturer of PTFE products hold? The ISO 9001 Assurance for Quality
- How does material selection impact PCB manufacturing and cost? Optimize Performance and Budget
- What makes PTFE chemically inert? Discover the Molecular Secrets of its Unmatched Resistance
- What are the temperature limits for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Thermal Range from -200°C to +260°C
- What is PTFE's resistance to chemicals? Discover the Ultimate Chemical-Resistant Polymer



















