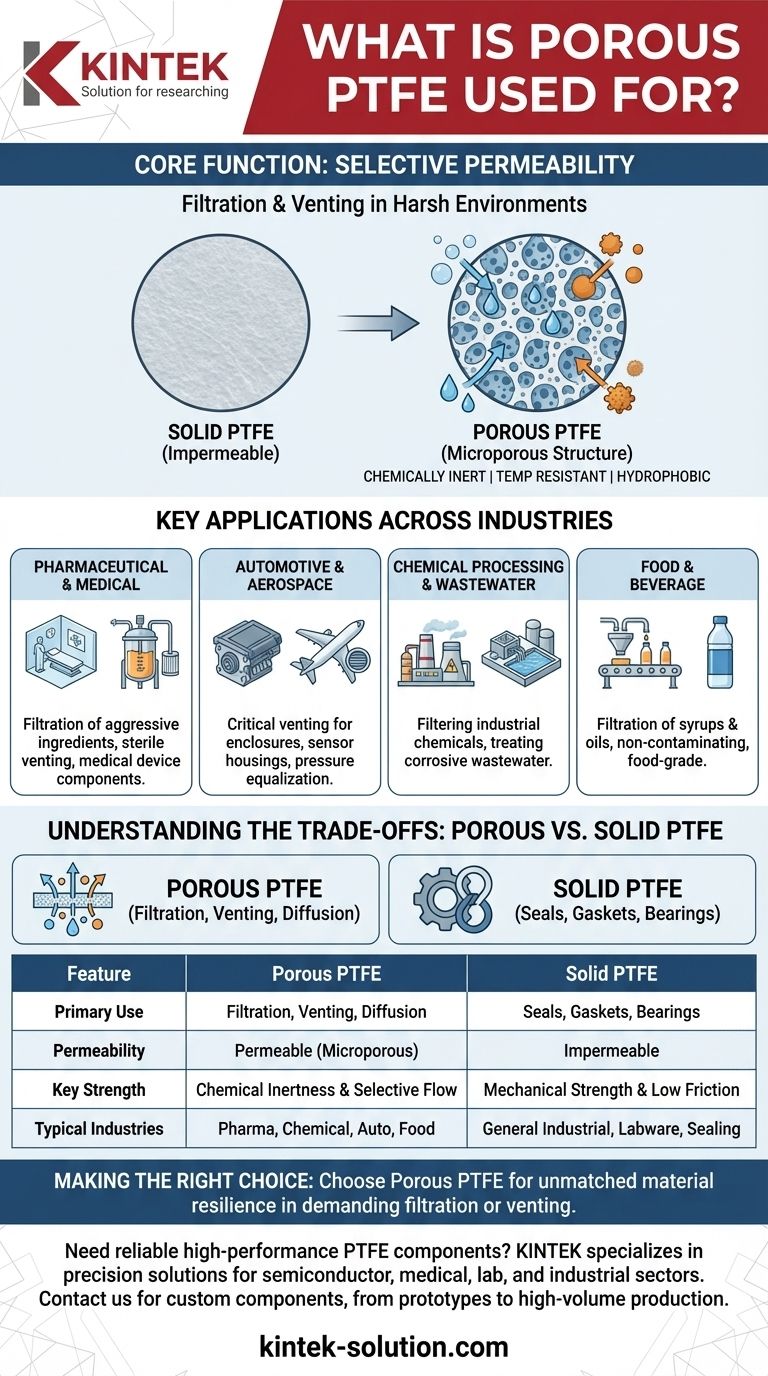
In short, porous PTFE is primarily used for advanced filtration and venting in chemically aggressive and high-temperature environments. It is engineered into components like filter membranes, vents, and diffusers that must allow fluids to pass through while resisting degradation from acids, solvents, or extreme heat.
The core value of porous PTFE is that it combines the exceptional chemical inertness and temperature resistance of solid PTFE with a microporous structure. This unique combination allows it to filter or vent substances in applications where nearly any other polymer would fail.

The Core Function: Selective Permeability
The utility of porous PTFE stems from its unique physical structure, which builds upon the inherent strengths of the base Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material.
What is Porous PTFE?
Porous PTFE is a form of standard PTFE that has been processed to create a network of microscopic, interconnected pores. This transforms the solid, impermeable plastic into a material that acts like a highly durable, chemically inert sponge or membrane.
It is manufactured in various forms, including sheets, tubes, rolls, and discs, to suit different industrial needs.
The PTFE Advantage
The base material, PTFE, is renowned for its properties:
- Chemical Inertness: It is virtually immune to attack from acids, alkalis, and solvents.
- Temperature Resistance: It maintains its integrity in both cryogenic conditions and high-heat applications.
- Hydrophobicity: It naturally repels water.
By making this material porous, it becomes a perfect medium for separating particles from aggressive fluids or for allowing air to vent without letting in water or contaminants.
Key Applications Across Industries
Porous PTFE's unique characteristics make it indispensable in sectors that demand high performance and reliability under challenging conditions.
Pharmaceutical & Medical
In sterile environments, porous PTFE is used for the filtration of aggressive pharmaceutical ingredients, venting on fermentation tanks, and components in medical devices like injectors where purity is paramount.
Automotive & Aerospace
It serves as a critical venting medium for sensitive electronic enclosures and sensor housings. It allows pressure to equalize with the atmosphere while providing a durable barrier against water, oils, and other contaminants.
Chemical Processing & Wastewater
Its ability to withstand harsh chemicals makes it ideal for filtering industrial chemicals and treating wastewater streams containing heavy metals or other corrosive agents that would destroy conventional filters.
Food & Beverage
Porous PTFE is used to filter food products like syrups and oils. Its non-stick, non-contaminating nature ensures it meets strict food-grade standards.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Porous vs. Solid PTFE
A common point of confusion is differentiating between the applications for porous and standard (solid) PTFE. The choice depends entirely on whether you need a barrier or a passageway.
When to Choose Porous PTFE
Choose porous PTFE for applications centered on filtration, venting, or diffusion. Its defining feature is its controlled permeability. However, this porous structure means it has lower mechanical strength than its solid counterpart.
When to Choose Solid PTFE
Choose solid PTFE for applications requiring a low-friction surface, a robust seal, or a durable bearing. Its non-permeable nature is essential for creating gaskets, valve components, pump parts, and non-stick coatings.
The Cost Factor
Porous PTFE is an engineered, value-added material. It is typically more expensive than standard solid PTFE stock, so its use is justified by extreme performance requirements that less expensive materials cannot satisfy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct form of PTFE is critical to the success of your application. Your decision should be guided by the primary function the material needs to serve.
- If your primary focus is filtering aggressive fluids or venting a sensitive enclosure: Porous PTFE is the correct material due to its unique combination of chemical resistance and permeability.
- If your primary focus is creating a seal, a gasket, or a low-friction bearing surface: Solid (non-porous) PTFE is the industry standard for these mechanical and sealing applications.
- If your primary focus is filtration in a less demanding environment: Other porous polymers may be a more cost-effective solution, but PTFE remains the definitive choice for extreme chemical and thermal conditions.
Ultimately, choosing porous PTFE is a decision to prioritize unmatched material resilience in a demanding filtration or venting application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Porous PTFE | Solid PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Filtration, Venting, Diffusion | Seals, Gaskets, Bearings |
| Permeability | Permeable (Microporous) | Impermeable |
| Key Strength | Chemical Inertness & Selective Flow | Mechanical Strength & Low Friction |
| Typical Industries | Pharmaceutical, Chemical, Automotive, Food & Beverage | General Industrial, Labware, Sealing Applications |
Need a reliable partner for high-performance PTFE components?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision porous and solid PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, filter membranes, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, we deliver chemically inert, temperature-resistant solutions tailored to your exact needs.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE bushings? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- What are some common automotive applications of PTFE seals? Solve High-Temp, High-Speed Sealing Challenges
- What are the advantages of MoS2-filled PTFE? Enhance Wear Resistance & Lubricity
- What is the basic structure and working principle of PTFE O-ring seals? Unlock Superior Sealing Performance
- What industries commonly use Teflon CNC machined parts? Critical Solutions for Aerospace, Medical & More
- What are the color differences between PTFE and graphite packing? Select the Right Material for Your Application
- How are PTFE lip seals used in industrial applications? Solving Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What are the key differences between PTFE lip seals and elastomer rubber lip seals? A Guide for Extreme Conditions



















