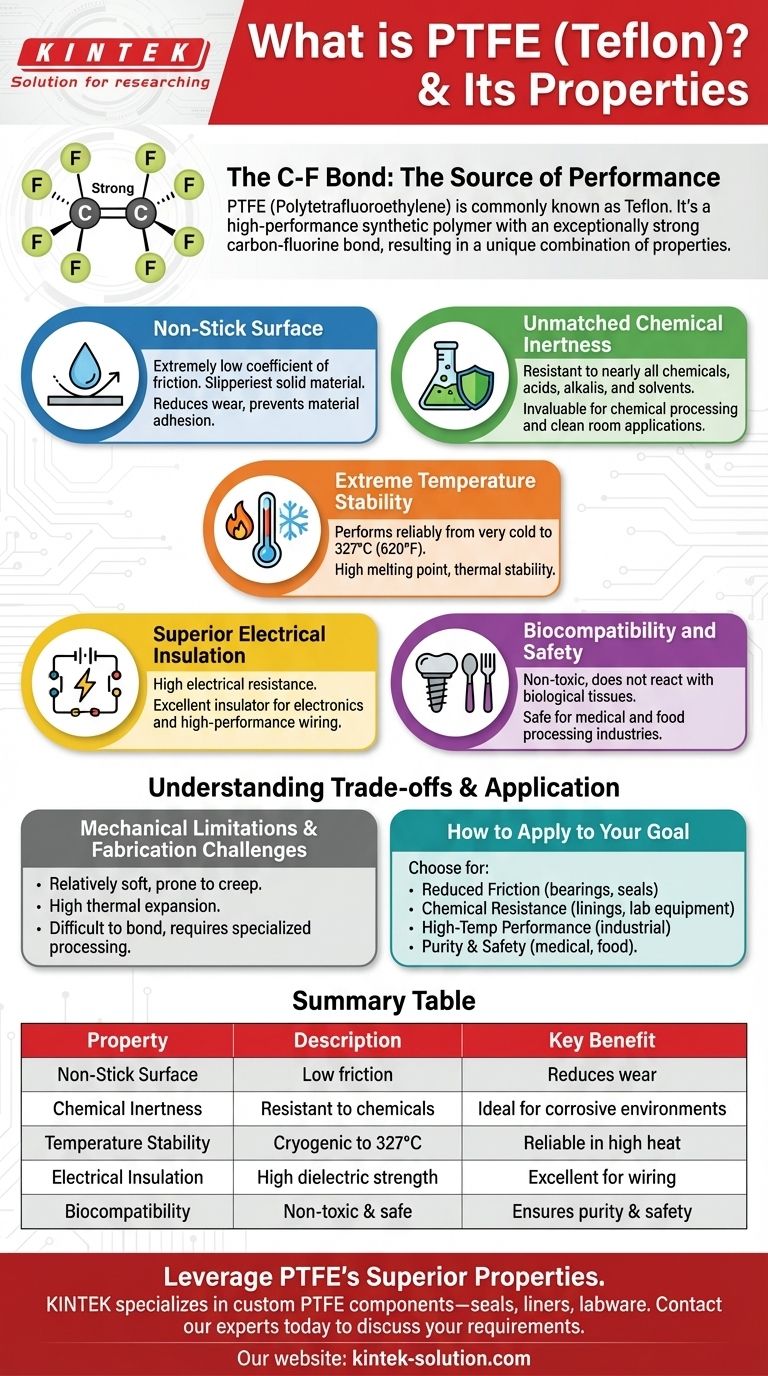
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is most commonly known by its trademarked name, Teflon. It is a high-performance synthetic polymer composed of carbon and fluorine, renowned for a unique combination of properties including an exceptionally non-stick surface, extreme chemical inertness, and high-temperature resistance.
At its core, PTFE's power comes from the incredibly strong bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms. This bond is the source of its famous non-stick quality and makes it one of the most chemically inert and thermally stable materials available for engineering.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE
PTFE's versatility stems from a handful of remarkable properties that are rare to find in a single material. These characteristics are a direct result of its unique molecular structure.
The Famous Non-Stick Surface
The most widely recognized property of PTFE is its extremely low coefficient of friction. It is one of the "slipperiest" solid materials known.
This quality is responsible for its use in non-stick cookware, but also for high-performance industrial applications like self-lubricating bearings and seals. This property also means it has excellent non-adhesion characteristics.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is highly resistant to nearly all chemicals, including powerful acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble.
This makes it an invaluable material for lining pipes, tanks, and vessels in the chemical processing industry. It is also used for laboratory equipment and in clean room applications where purity is essential.
Extreme Temperature Stability
This material performs reliably across an exceptionally wide range of temperatures.
It has a high melting point of around 327°C (620°F), allowing it to be used in high-heat applications without degrading. It also maintains its properties in very cold conditions.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE exhibits high electrical resistance, making it an outstanding electrical insulator.
This property is leveraged in electronics and wiring, especially in applications where high performance and resistance to heat or chemicals are also required.
Biocompatibility and Safety
The material is non-toxic and biocompatible, meaning it does not react with biological tissues.
This allows for its safe use in the medical field for implants and surgical equipment, as well as in the food processing industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material compared to metals. It can be prone to "creep," or deforming slowly over time when a constant load is applied.
It also has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes. This must be accounted for in any precise engineering design.
Fabrication Challenges
The same properties that make PTFE so useful also make it difficult to work with.
Its chemical inertness makes it very difficult to bond to other materials using adhesives. Its high melting point also requires specialized processing techniques.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing a material depends entirely on the problem you need to solve. PTFE is the right choice when its unique properties directly address a specific challenge.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: PTFE's exceptionally low friction coefficient makes it ideal for self-lubricating bearings, seals, and non-stick coatings.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: Its inertness makes it the go-to material for handling corrosive chemicals in lab equipment, pipes, and vessel linings.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: PTFE maintains its properties across a wide temperature range, making it suitable for demanding industrial processes and electrical insulation.
- If your primary focus is purity and safety: Its biocompatibility and non-toxic nature are critical for applications in the medical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's unique molecular structure is the key to leveraging its remarkable capabilities in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Stick Surface | Extremely low coefficient of friction | Reduces wear, prevents material adhesion |
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and solvents | Ideal for corrosive environments |
| Temperature Stability | Performs from cryogenic to 327°C (620°F) | Reliable in high-heat applications |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength | Excellent for wiring and electronics |
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic and safe for medical/food use | Ensures purity and safety |
Leverage PTFE's superior properties for your application. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver the material performance and fabrication expertise your project demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments



















