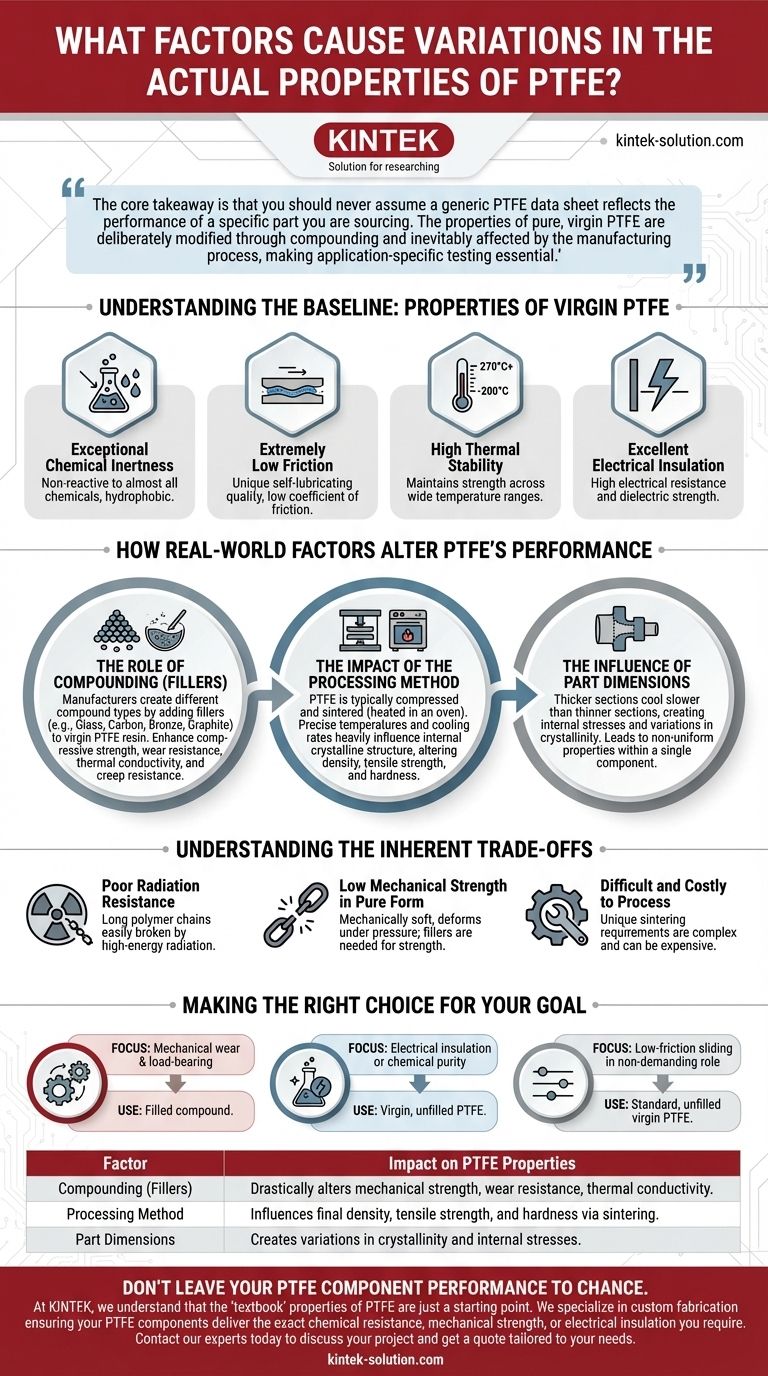
The short answer is that the "textbook" properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) are just a baseline. The actual performance of a finished PTFE component is significantly altered by three primary factors: the processing method used to form the part, the type of compound (i.e., whether fillers have been added), and the final physical dimensions of the product.
The core takeaway is that you should never assume a generic PTFE data sheet reflects the performance of a specific part you are sourcing. The properties of pure, virgin PTFE are deliberately modified through compounding and inevitably affected by the manufacturing process, making application-specific testing essential.
Understanding the Baseline: Properties of Virgin PTFE
Before exploring the variations, it's crucial to understand the inherent characteristics of pure, unmodified PTFE. These properties are derived from the incredibly strong bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry, making PTFE non-reactive to almost all chemicals. It is also hydrophobic, meaning it repels water, absorbing only about 0.01% by weight over 24 hours.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This gives it a unique, self-lubricating quality that is essential for bearing and seal applications.
High Thermal Stability
With a melting point around 327°C, PTFE maintains its strength, toughness, and other key properties across a wide range of temperatures, including cryogenic conditions. It is physiologically harmless up to 270°C.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE possesses high electrical resistance and dielectric strength, making it a premier material for insulating high-voltage cables and electronic components.
Inherent Physical Traits
Pure PTFE is a dense material, with a specific gravity of 2.2 (2200 kg/m³). It is also highly resistant to UV radiation and is generally opaque and rigid.
How Real-World Factors Alter PTFE's Performance
While the baseline properties are impressive, they are almost always modified in practice. The "PTFE" used in a high-load bearing is fundamentally different from the PTFE used in laboratory tubing.
The Role of Compounding (Fillers)
This is the most significant factor in property variation. Manufacturers create different compound types by adding fillers to the virgin PTFE resin.
While pure PTFE has low friction, its mechanical strength and wear resistance are relatively poor. Fillers like glass, carbon, bronze, or graphite are added to dramatically enhance properties such as compressive strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to deformation under load (creep).
The Impact of the Processing Method
PTFE cannot be melt-processed like most plastics. It is typically compressed into a shape and then heated in an oven (a process called sintering).
The precise temperatures and cooling rates used during this process heavily influence the material's internal crystalline structure. Variations in processing can alter final density, tensile strength, and hardness, even for the exact same PTFE compound.
The Influence of Part Dimensions
The final extruded or molded dimensions of a part matter. Thicker sections cool more slowly than thinner sections, which can create internal stresses and variations in crystallinity.
This can lead to non-uniform properties within a single, complex component. A thick flange on a PTFE part may have slightly different mechanical properties than a thin-walled section on the same part.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
Even in its ideal form, PTFE is a material of compromises. Understanding its natural limitations is key to selecting the right variant.
Poor Radiation Resistance
One of PTFE's most notable weaknesses is its poor resistance to high-energy radiation. The material's long polymer chains are easily broken by radiation, causing it to become brittle and lose its mechanical integrity.
Low Mechanical Strength in Pure Form
While tough, virgin PTFE is mechanically soft. It can be easily scratched and will deform under sustained pressure. This is the primary reason filled compounds are so prevalent in mechanical applications.
Difficult and Costly to Process
The unique processing requirements (sintering rather than melting) make manufacturing PTFE parts more complex and often more expensive than for other common engineering plastics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE requires moving beyond the generic and focusing on the specific demands of your application. The right question isn't "Is PTFE suitable?" but rather "Which grade and form of PTFE is suitable?"
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear and load-bearing: You must use a filled compound. Virgin PTFE will likely fail due to its low compressive strength and poor wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or chemical purity: You must use virgin, unfilled PTFE. Additives would compromise its exceptional dielectric properties and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is low-friction sliding in a non-demanding role: Standard, unfilled virgin PTFE is often the most cost-effective and suitable choice.
Ultimately, you must validate the specific grade and form of PTFE against the unique demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on PTFE Properties |
|---|---|
| Compounding (Fillers) | Drastically alters mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity. |
| Processing Method | Influences final density, tensile strength, and hardness via sintering temperatures. |
| Part Dimensions | Creates variations in crystallinity and internal stresses within a single component. |
Don't leave your PTFE component performance to chance.
At KINTEK, we understand that the 'textbook' properties of PTFE are just a starting point. The real-world performance of your seals, liners, or labware depends on precise manufacturing and the right compound for your specific application—whether in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial settings.
We specialize in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your PTFE components deliver the exact chemical resistance, mechanical strength, or electrical insulation you require.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















