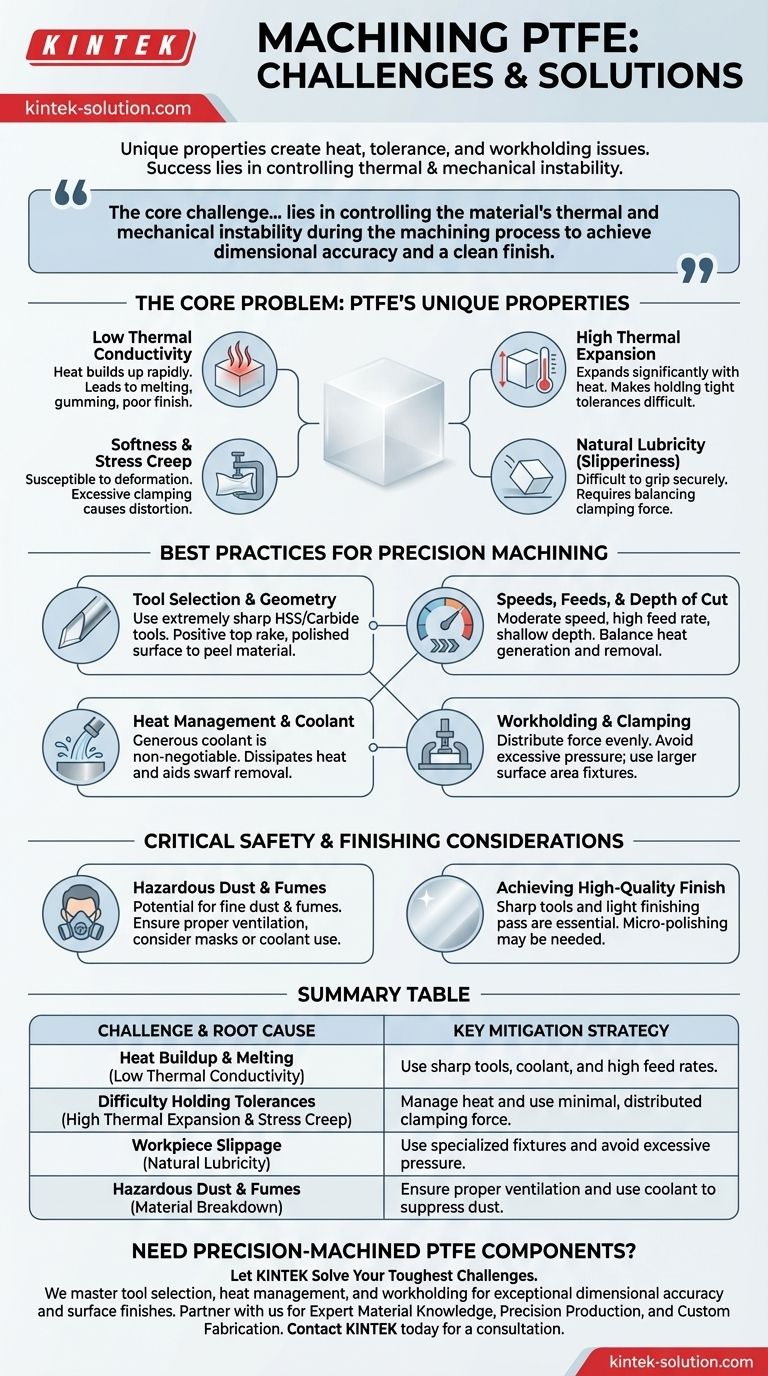
The primary challenges in machining PTFE stem from its unique combination of material properties. Its softness and low melting point create significant heat management issues, while its high thermal expansion and stress creep make holding tight tolerances difficult. Additionally, its natural slipperiness complicates workholding, and the process can release hazardous dust, requiring safety precautions.
The core challenge isn't that PTFE is difficult to cut—it's actually quite soft. The difficulty lies in controlling the material's thermal and mechanical instability during the machining process to achieve dimensional accuracy and a clean finish.
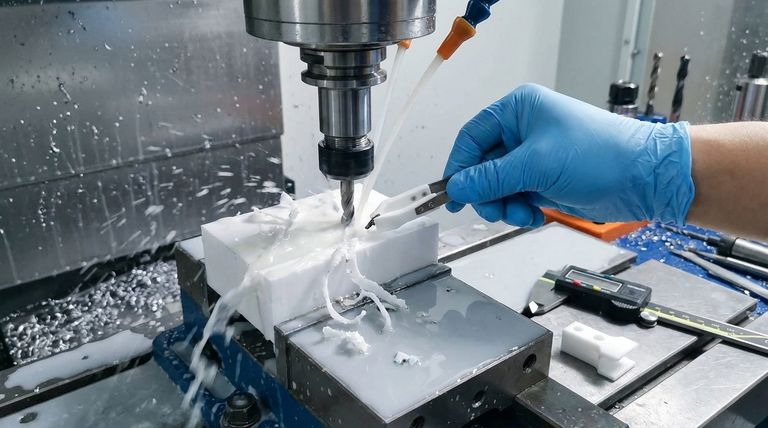

The Core Problem: PTFE's Unique Properties
To successfully machine PTFE, one must first understand the material's inherent characteristics. These properties are the root cause of nearly every challenge you will face.
Low Thermal Conductivity
PTFE is an excellent thermal insulator. This means it doesn't dissipate heat well, causing heat to build up rapidly at the cutting tool's edge.
This localized heat can cause the PTFE to exceed its low melting point, leading to a gummy or melted surface, gumming up the tool, and resulting in a poor finish.
High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
In response to the heat generated during cutting, PTFE expands significantly—far more than metals or other plastics.
This thermal expansion makes holding tight tolerances a primary challenge. A part measured as accurate while warm from machining may become out of spec once it cools to ambient temperature.
Softness and Stress Creep
While its softness makes PTFE easy to cut with minimal force, it also makes it susceptible to deformation.
Excessive clamping pressure can easily compress or distort the material, a phenomenon known as stress creep. This distortion can ruin the part's dimensional accuracy before a single cut is made.
Natural Lubricity (Slipperiness)
PTFE's extremely low coefficient of friction makes it difficult to grip securely in a chuck or vise.
This requires a delicate balance: applying enough clamping force to hold the slick material without applying so much that you cause deformation or stress creep.
Best Practices for Precision Machining
Overcoming PTFE's challenges requires a specific approach to tooling, speeds, and heat management. The goal is to minimize friction, heat generation, and cutting forces.
Tool Selection and Geometry
The right tool is critical for a clean cut. Use extremely sharp cutting tools, preferably made from high-speed steel (HSS), Stellite, or carbide.
Tools should have a positive top rake (between 0 and 15 degrees) and be polished or smooth. This geometry reduces cutting forces, minimizes friction, and helps peel the material away rather than pushing through it.
Speeds, Feeds, and Depth of Cut
The key is to balance heat generation with efficient material removal.
Use moderate cutting speeds (typically 200 to 500 surface feet per minute) to avoid overheating. This should be paired with a high feed rate (0.002 to 0.010 inches per revolution) to keep the tool moving and prevent it from dwelling and melting the material.
To further reduce heat and tool pressure, always use a shallow depth of cut.
Heat Management and Coolant
Aggressive heat management is non-negotiable for precision work.
Using a generous supply of coolant or lubricant is highly recommended. This serves two purposes: it dissipates heat from the cutting zone and aids in swarf removal, preventing chips from melting onto the tool or workpiece.
Workholding and Clamping
Secure the workpiece without deforming it.
Avoid excessive clamping pressure. If possible, use fixtures or chuck jaws with a larger surface area to distribute the clamping force more evenly. For slick parts, additional securing measures may be necessary.
Critical Safety and Finishing Considerations
Beyond the cutting process itself, operators must be aware of potential hazards and finishing requirements to ensure a successful and safe outcome.
The Hazard of PTFE Dust and Fumes
Machining PTFE can generate fine dust particles and, if overheated, hazardous fumes.
Inhaling this micro-dust can be dangerous. Always ensure proper ventilation, and consider wearing a mask or performing operations under coolant to suppress dust creation entirely.
Achieving a High-Quality Surface Finish
Because of its softness, PTFE can sometimes result in a "fuzzy" or burred surface finish.
Extremely sharp tools and a light finishing pass are essential. For applications requiring a very smooth surface, post-processing methods like micro-polishing may be necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your machining strategy should be dictated by your project's most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is achieving tight tolerances: You must prioritize aggressive heat management with coolant and carefully control clamping pressure to prevent material expansion and deformation.
- If your primary focus is a smooth surface finish: Your priority must be using extremely sharp, polished tools with a positive rake and maintaining a high feed rate to avoid melting.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: You must ensure excellent ventilation and use a coolant system to suppress the creation of hazardous airborne dust.
Ultimately, mastering PTFE machining comes from respecting its properties and adapting your techniques accordingly.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Root Cause | Key Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Buildup & Melting | Low thermal conductivity | Use sharp tools, coolant, and high feed rates |
| Difficulty Holding Tolerances | High thermal expansion & stress creep | Manage heat and use minimal, distributed clamping force |
| Workpiece Slippage | Natural lubricity (low friction) | Use specialized fixtures and avoid excessive pressure |
| Hazardous Dust & Fumes | Material breakdown during machining | Ensure proper ventilation and use coolant to suppress dust |
Need Precision-Machined PTFE Components? Let KINTEK Solve Your Toughest Challenges.
Machining PTFE to exact specifications requires specialized expertise to overcome its unique properties. At KINTEK, we manufacture high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We master the delicate balance of tool selection, heat management, and workholding to deliver parts with exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface finishes, from prototypes to high-volume production runs.
Partner with us to benefit from:
- Expert Material Knowledge: We understand PTFE's behavior inside and out.
- Precision Production: We hold tight tolerances by controlling heat and stress creep.
- Custom Fabrication: We tailor solutions to your specific application requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and let us deliver the reliable PTFE components your project demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE rotary seals becoming a preferred choice for engineers and OEMs? Solve Critical Performance Failures
- What are the key properties of Teflon plastic sheets? Unlocking Performance in Extreme Environments
- Why are Teflon sheets important for sublimation printing? Protect Your Press & Ensure Perfect Prints
- What are some common applications of PTFE seals? Engineered for Extreme Chemical, Temperature, and Pressure Challenges
- What other fields can PTFE gaskets be used in? Beyond Chemical Plants to Electronics & Pharma
- What are some common applications of machined Teflon? Critical Components for Harsh Environments
- What are the common issues hindering the adoption of PTFE wear plates? Overcome These 4 Key Barriers
- What are the optimal load and speed conditions for PTFE performance? Master the PV Limit for Longevity



















