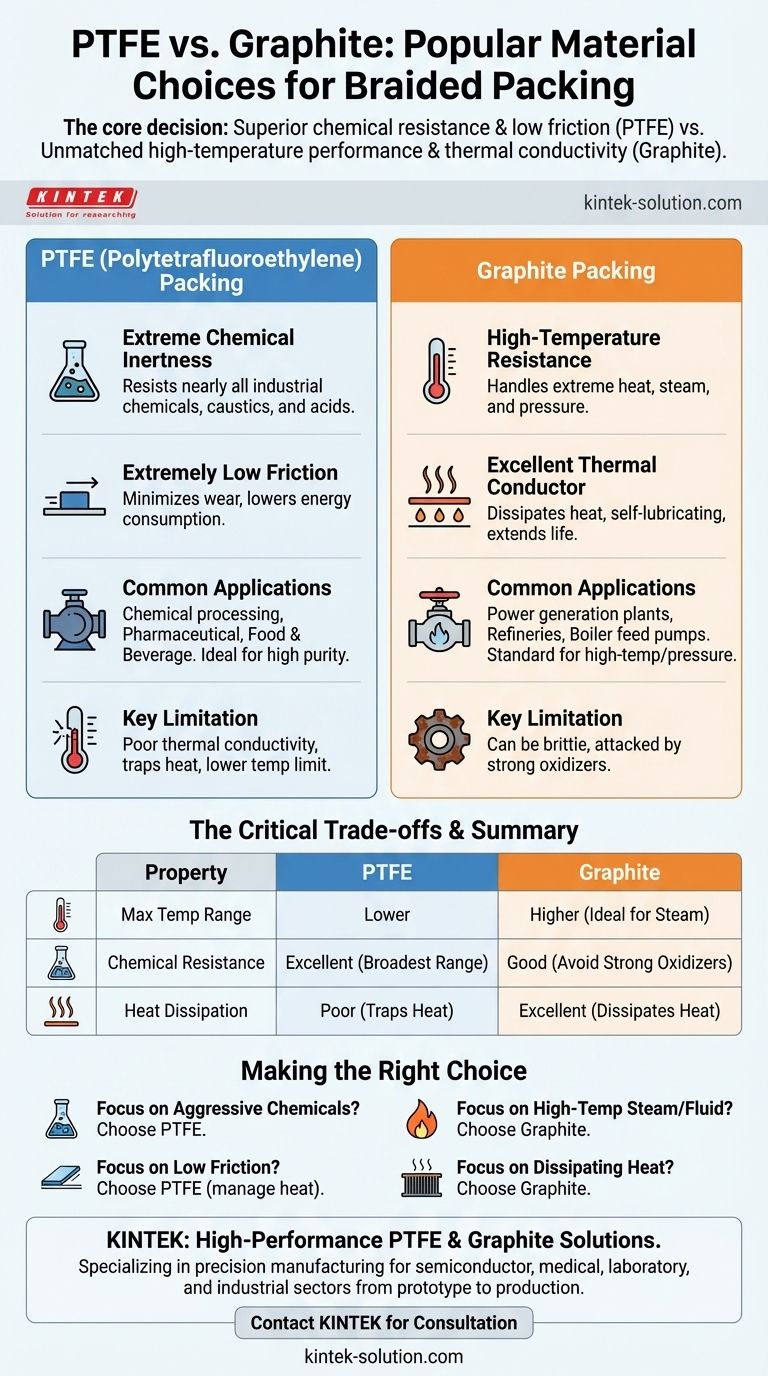
The two most popular material choices for braided packing are PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) and flexible graphite. These materials dominate the market due to their distinct and highly valuable properties, which make them suitable for a wide range of demanding industrial sealing applications.
The core decision between PTFE and graphite comes down to a simple trade-off: PTFE offers superior chemical resistance and low friction, while graphite provides unmatched high-temperature performance and thermal conductivity.

Understanding PTFE Packing
Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE, is a synthetic fluoropolymer renowned for its exceptional properties. When used in braided packing, it creates a reliable and versatile seal.
Core Properties of PTFE
The primary advantage of PTFE is its extreme chemical inertness. It can withstand nearly all industrial chemicals, caustics, and acids, making it a default choice for aggressive media.
It also boasts an extremely low coefficient of friction. This slick surface reduces drag on rotating shafts and valve stems, minimizing wear and lowering energy consumption.
Common Applications
PTFE packing is widely used in pumps, valves, and mixers within the chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage industries. Its non-contaminating nature makes it ideal for applications requiring high purity.
Key Limitations
The main drawback of PTFE is its poor thermal conductivity. Heat generated from friction can become trapped, potentially damaging the packing and the equipment shaft if not managed with sufficient flush water. Its temperature resistance is also lower than that of graphite.
Understanding Graphite Packing
Flexible graphite is produced by exfoliating natural graphite flake. This process creates a material that can be compressed into yarn and braided, offering a robust seal under extreme conditions.
Core Properties of Graphite
Graphite's signature strength is its high-temperature resistance. It can handle extreme heat and pressure, particularly in applications involving steam or hot liquids, far exceeding the limits of PTFE.
It is also an excellent thermal conductor. This property allows it to dissipate frictional heat away from the shaft, reducing the risk of overheating and extending the life of both the packing and the equipment. Graphite is also self-lubricating.
Common Applications
Graphite packing is the standard for high-temperature, high-pressure services. It is essential in power generation plants for steam valves, in refineries, and for boiler feed pumps where other materials would quickly fail.
Key Limitations
While chemically resistant to many substances, graphite can be attacked by strong oxidizing agents. It can also be more brittle than PTFE, making it less forgiving in applications with significant shaft run-out or abrasive media.
The Critical Trade-offs: PTFE vs. Graphite
Choosing the correct material requires a clear understanding of the specific demands of your application. Neither material is universally superior; their value is context-dependent.
Temperature Resistance
Graphite is the undisputed winner for high-temperature applications. It maintains its integrity and sealing capability in conditions where PTFE would rapidly degrade.
Chemical Compatibility
PTFE offers the broadest range of chemical resistance. For sealing highly aggressive or corrosive chemicals, especially strong oxidizers, PTFE is the safer and more reliable choice.
Heat Dissipation
Graphite's ability to conduct heat away from the shaft is a critical performance advantage. In high-speed pump applications, this prevents overheating and scoring, reducing the need for external cooling. PTFE, by contrast, acts as an insulator, trapping heat.
Cost and Handling
Material costs can vary, but the true cost is determined by performance and service life. A packing that fails prematurely leads to downtime and expensive repairs, far outweighing any initial material savings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your operational environment and performance goals will dictate the best material. Use these guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals: Choose PTFE for its near-universal chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature steam or fluid service: Graphite is the only suitable choice for reliable, long-term performance.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction on a pump shaft: PTFE's low coefficient of friction is a significant advantage, but heat must be managed.
- If your primary focus is dissipating heat in a high-speed application: Graphite's thermal conductivity is essential to protect your equipment.
Ultimately, selecting the right packing material is fundamental to ensuring equipment reliability and operational safety.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE Packing | Graphite Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Chemical Resistance, Low Friction | High Temperature, Heat Dissipation |
| Max Temp Range | Lower | Higher (Ideal for Steam) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Broadest Range) | Good (Avoid Strong Oxidizers) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Poor (Traps Heat) | Excellent (Dissipates Heat) |
| Key Feature | Non-Stick, Low Friction | Self-Lubricating, Robust |
Still Unsure Which Packing Material is Right for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and graphite components, including custom braided packing solutions. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, prioritizing precision and reliability from prototype to high-volume production.
Let our experts help you select the optimal material to enhance your equipment's reliability, safety, and efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and get the perfect seal for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Adjustable Height Flower Basket
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection



















