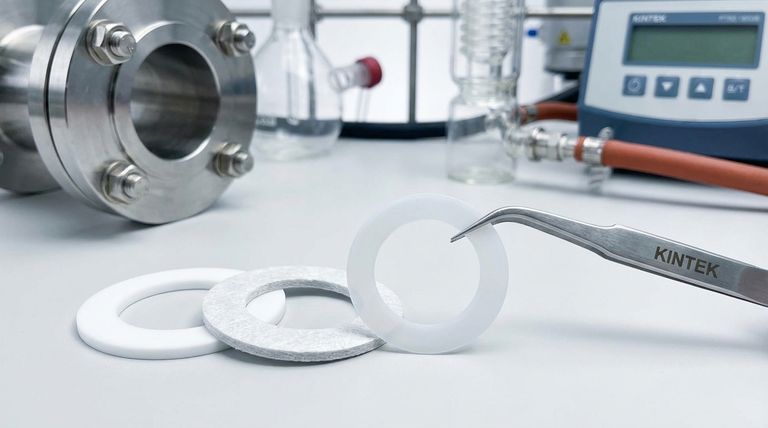
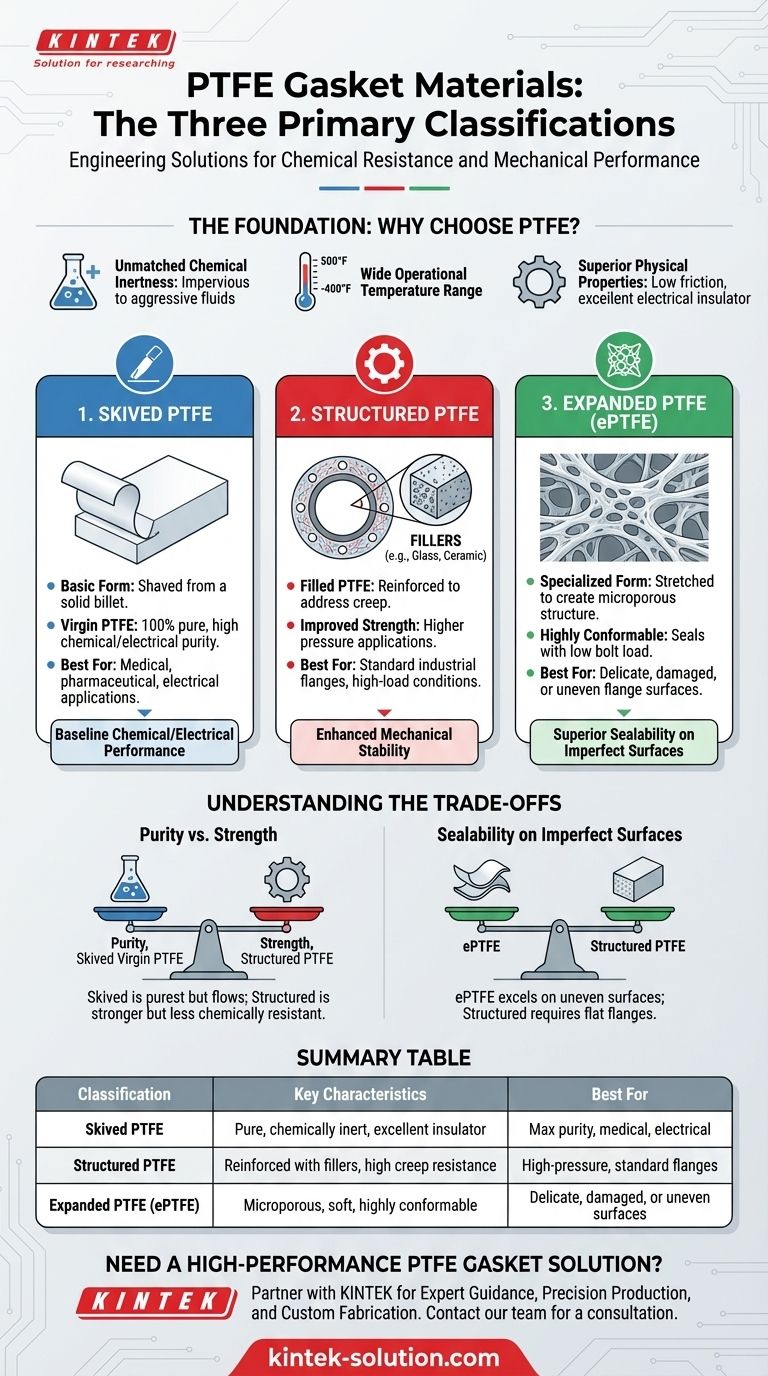
In short, the three primary classifications of PTFE gasket materials are skived, structured, and expanded. These variations are engineered to leverage the exceptional chemical resistance of pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) while addressing its mechanical limitations for specific industrial sealing applications.
The core difference between PTFE gasket types lies in how they are manufactured to solve a fundamental problem: pure PTFE is chemically inert but mechanically soft. The classifications—skived, structured, and expanded—represent different strategies for enhancing its strength and sealability for demanding environments.

The Foundation: Why Choose PTFE?
Before diving into the classifications, it's essential to understand why PTFE is such a sought-after gasket material. Its unique combination of properties makes it a default choice for many critical applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant materials known. It is virtually impervious to aggressive fluids, vapors, and gases, making it ideal for the pharmaceutical, chemical, and food and beverage industries.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
This material performs reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature spectrum. PTFE gaskets can operate effectively from cryogenic temperatures as low as -400°F (-240°C) up to 500°F (260°C).
Superior Physical Properties
PTFE exhibits a very low coefficient of friction, creating a non-stick surface that is easy to clean. It also possesses excellent dielectric properties, making it a superb electrical insulator.
Understanding the Three Core Classifications
While all PTFE gaskets share the core benefits above, their physical structure is modified to enhance performance under pressure and in different flange conditions. This is where the classifications become critical.
1. Skived PTFE
Skived PTFE is the most basic form, created by shaving a thin sheet from a solid billet of pure PTFE. This category includes virgin PTFE, which is 100% pure and specified for medical, pharmaceutical, or electrical applications.
It also includes mechanical grade PTFE, which contains a small amount of reprocessed material but is functionally similar for general industrial use. Skived PTFE represents the baseline of chemical and electrical performance.
2. Structured PTFE
Structured PTFE, often called filled PTFE, addresses the primary weakness of pure PTFE: its tendency to deform or "creep" under load.
In this type, fillers and reinforcing agents are blended into the PTFE matrix. Glass fibers improve strength and stability, while materials like ceramic or metal fillers can modify thermal and electrical properties. This creates a much more robust gasket for higher pressure applications.
3. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
Expanded PTFE is a specialized form created by stretching PTFE under specific conditions. This process creates a microporous, fibrous structure that is both incredibly strong and highly conformable.
Because of this unique structure, ePTFE gaskets can create a tight seal with very low bolt load. This makes them exceptionally effective for sealing delicate, damaged, or irregular flange surfaces where standard gaskets might fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a PTFE gasket material is a matter of balancing competing priorities. Modifying pure PTFE to enhance one property can have an impact on others.
Purity vs. Mechanical Strength
The primary trade-off is between chemical purity and mechanical performance. Skived virgin PTFE offers the highest purity and chemical resistance but is the most susceptible to cold flow.
Adding fillers to create structured PTFE dramatically improves creep resistance but may slightly reduce the gasket's overall chemical compatibility, depending on the filler used.
Sealability on Imperfect Surfaces
While structured PTFE is excellent for high-pressure applications with flat, rigid flanges, it can struggle to seal warped or uneven surfaces.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) excels in these situations. Its soft, conformable nature fills in imperfections to create a reliable seal where more rigid materials would leak.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the specific demands of your sealing environment. Consider the primary goal of your application to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity or electrical insulation: Choose skived virgin PTFE for its unadulterated composition.
- If your primary focus is resisting high pressure and creep in standard industrial flanges: Select a structured (filled) PTFE designed for your temperature and media.
- If your primary focus is sealing delicate, damaged, or uneven flanges with low bolt force: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is the definitive choice for its superior conformability.
Ultimately, choosing the correct PTFE classification ensures you leverage the material's benefits without being compromised by its inherent limitations.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Skived PTFE | Pure, chemically inert, excellent electrical insulator | Maximum chemical purity, medical, pharmaceutical, electrical applications |
| Structured PTFE | Reinforced with fillers (e.g., glass, ceramic), high creep resistance | High-pressure applications, standard industrial flanges |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Microporous, soft, highly conformable, seals with low bolt load | Delicate, damaged, or uneven flange surfaces |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Gasket Solution?
Choosing the right PTFE material is critical for the safety and efficiency of your operations. The experts at KINTEK are here to help.
We manufacture precision PTFE components—including seals, gaskets, liners, and custom labware—for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Partner with KINTEK to get:
- Expert Guidance: Our team will help you select the ideal PTFE classification (Skived, Structured, or ePTFE) for your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical requirements.
- Precision Production: We ensure every component meets exact specifications for a reliable, leak-free seal.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver custom solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Don't leave your sealing performance to chance. Contact our team today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What advantages do 40% bronze-filled PTFE bushings provide? Boost Load Capacity, Wear Resistance & Heat Dissipation
- How do PTFE slide bearings compare in load capacity to traditional bearings? Superior Support for High-Load, Low-Speed Applications
- What are the characteristics of unfilled PTFE sheets made from virgin PTFE resin? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Performance
- What are the key advantages of PTFE bushings for high-speed and high-temperature applications? Unlock Maintenance-Free Performance
- What types of fluids can PTFE control valves handle? Master Corrosive Chemicals with Confidence
- What speed capability do PTFE oil seals have? Handle High-Speeds up to 30 m/s
- How does the built-in spring compensate for wear in PTFE shaft seals? Ensure Long-Term Sealing Reliability
- Why is a thin element design preferred for PTFE seals from a cost standpoint? Minimize Initial Cost & Maximize Long-Term Value



















