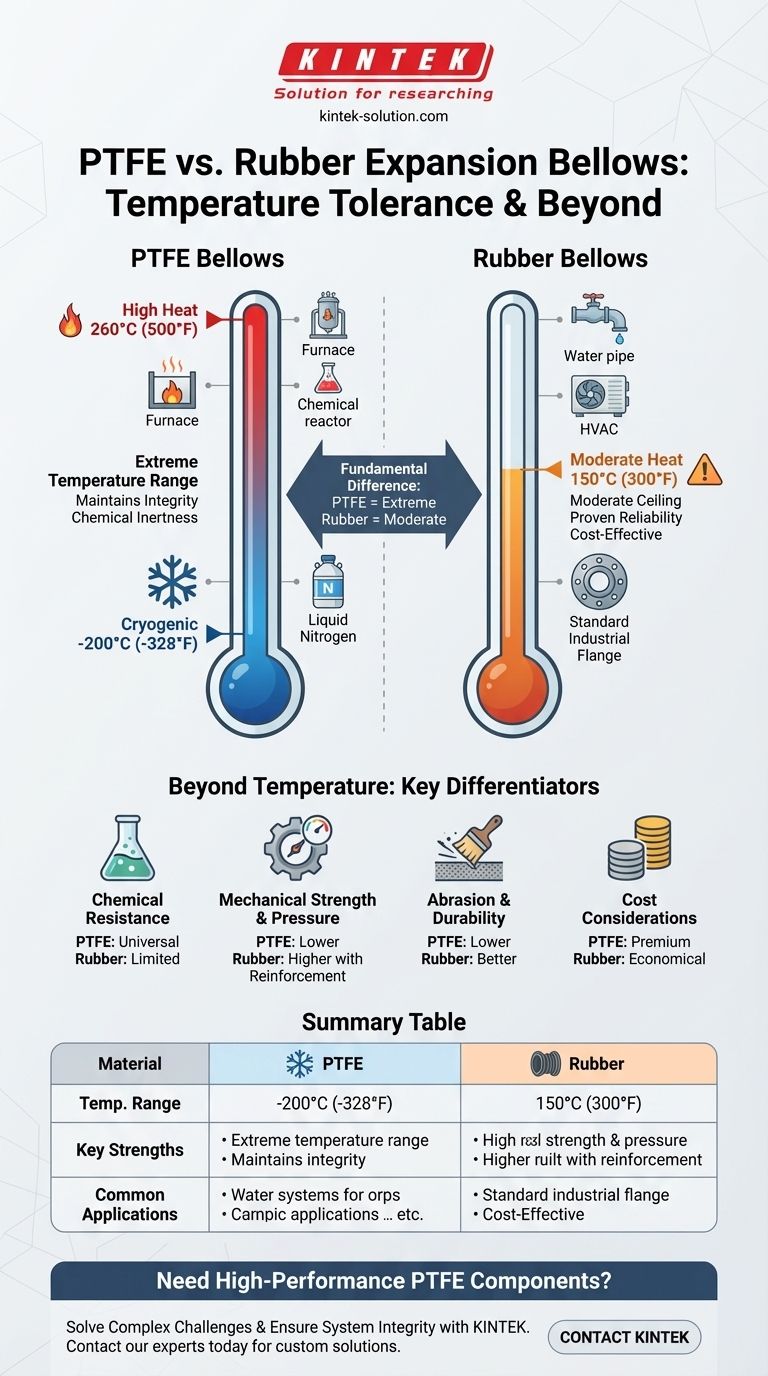
The fundamental difference is that PTFE expansion bellows are engineered for extreme temperature ranges, while rubber bellows are suited for more moderate industrial conditions. PTFE can reliably operate from cryogenic lows of -200°C up to high-heat environments of 260°C, whereas rubber bellows typically have a maximum service temperature of around 150°C.
The choice between PTFE and rubber is not just about heat tolerance; it's a decision based on the total operational environment. PTFE offers superior performance in extreme temperatures and harsh chemical settings, while rubber provides a practical, cost-effective solution for less demanding applications.
Why PTFE Excels in Extreme Temperatures
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance fluoropolymer, which gives it properties that commodity elastomers like rubber cannot match. Its stability under thermal stress is a primary reason for its use in demanding industries.
A Vast Operational Range
PTFE expansion bellows can function effectively in temperatures ranging from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
This incredibly wide range makes PTFE uniquely suitable for applications involving both cryogenic processes and high-heat systems, such as those found in power plants or chemical reactors.
Maintaining Material Integrity
At temperatures that would cause rubber to degrade, melt, or become brittle, PTFE maintains its structural integrity and chemical stability.
This reliability prevents system failure in critical applications where a breach could have significant consequences.
The Role of Rubber Bellows
Rubber expansion bellows are a common and highly effective solution for a wide variety of industrial systems. Their limitations in temperature do not detract from their utility within their specified operational window.
A Moderate Temperature Ceiling
Rubber bellows are typically rated for service temperatures up to 150°C (300°F).
While this is significantly lower than PTFE, it is more than sufficient for a vast number of applications, including HVAC systems, water lines, and general industrial piping.
Proven Reliability in Standard Conditions
Within their designed temperature and pressure ranges, rubber bellows offer excellent performance in absorbing vibration, reducing noise, and compensating for minor pipe misalignment.
They represent a dependable and economical choice for systems that do not involve extreme thermal or chemical stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs Beyond Temperature
Temperature tolerance is only one part of the equation. A comprehensive decision requires evaluating other critical performance factors where these materials differ significantly.
Chemical Resistance
PTFE exhibits near-universal chemical resistance, making it inert to most acids, bases, and solvents. This makes it essential for aggressive chemical processing lines where rubber would quickly corrode.
Mechanical Strength and Pressure
PTFE's primary weakness can be its lower mechanical strength compared to reinforced rubber composites. For high-pressure applications, specialized rubber or metallic bellows are often a better choice.
Abrasion and Durability
Rubber generally offers better abrasion resistance than PTFE. In systems transporting abrasive slurries or materials, a durable rubber lining is often preferred.
Cost Considerations
PTFE is a premium material, and its manufacturing process is more complex. Consequently, PTFE bellows are typically more expensive than their rubber counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your System
Selecting the correct material is critical for ensuring system safety, reliability, and longevity. Base your decision on a clear understanding of your specific operational demands.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability (hot or cold): PTFE is the definitive choice for its unmatched operational range from -200°C to 260°C.
- If your primary focus is a standard application with moderate heat: Rubber provides a reliable and cost-effective solution for systems operating at or below 150°C.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical transport: PTFE's chemical inertness often makes it the only viable option, protecting your system from corrosive media.
Ultimately, choosing the right expansion bellow requires matching the material's capabilities to the precise demands of your environment.
Summary Table:
| Material | Temperature Range | Key Strengths | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | -200°C to 260°C | Extreme temperature stability, superior chemical resistance | Chemical processing, semiconductor, power generation, cryogenics |
| Rubber | Up to 150°C | Cost-effective, good abrasion resistance, vibration absorption | HVAC, water lines, general industrial piping |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
Choosing the right material is critical for the safety and reliability of your system. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom expansion bellows—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We help you:
- Solve complex challenges with components that withstand extreme temperatures (-200°C to 260°C) and aggressive chemicals.
- Ensure system integrity with custom-fabricated parts, from prototypes to high-volume production.
- Gain a reliable partner committed to precision and quality in every order.
Let's discuss your specific application requirements. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of 55% Bronze + 5% MoS2-filled PTFE bushings? Achieve Superior Performance in High-Load Applications
- How can counter rotation failure be avoided in rotary seals? Prevent Costly Seal Failure and Downtime
- What are the limitations of PTFE coated fasteners regarding abrasion resistance? The Trade-Off for Superior Chemical Protection
- Why is biocompatibility important in Medical Grade PTFE Liners? Ensuring Patient Safety and Device Success
- What are FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings? Superior Seals for Harsh Chemical & Thermal Environments
- Why is chemical compatibility important for diaphragm valves in pharmaceutical applications? Ensure Product Purity & Patient Safety
- What is the purpose of PTFE gasket sealing material in mechanical equipment? Enhance Reliability and Efficiency
- How do NBR and PTFE seat materials impact valve performance? Choose the Right Butterfly Valve for Your System



















