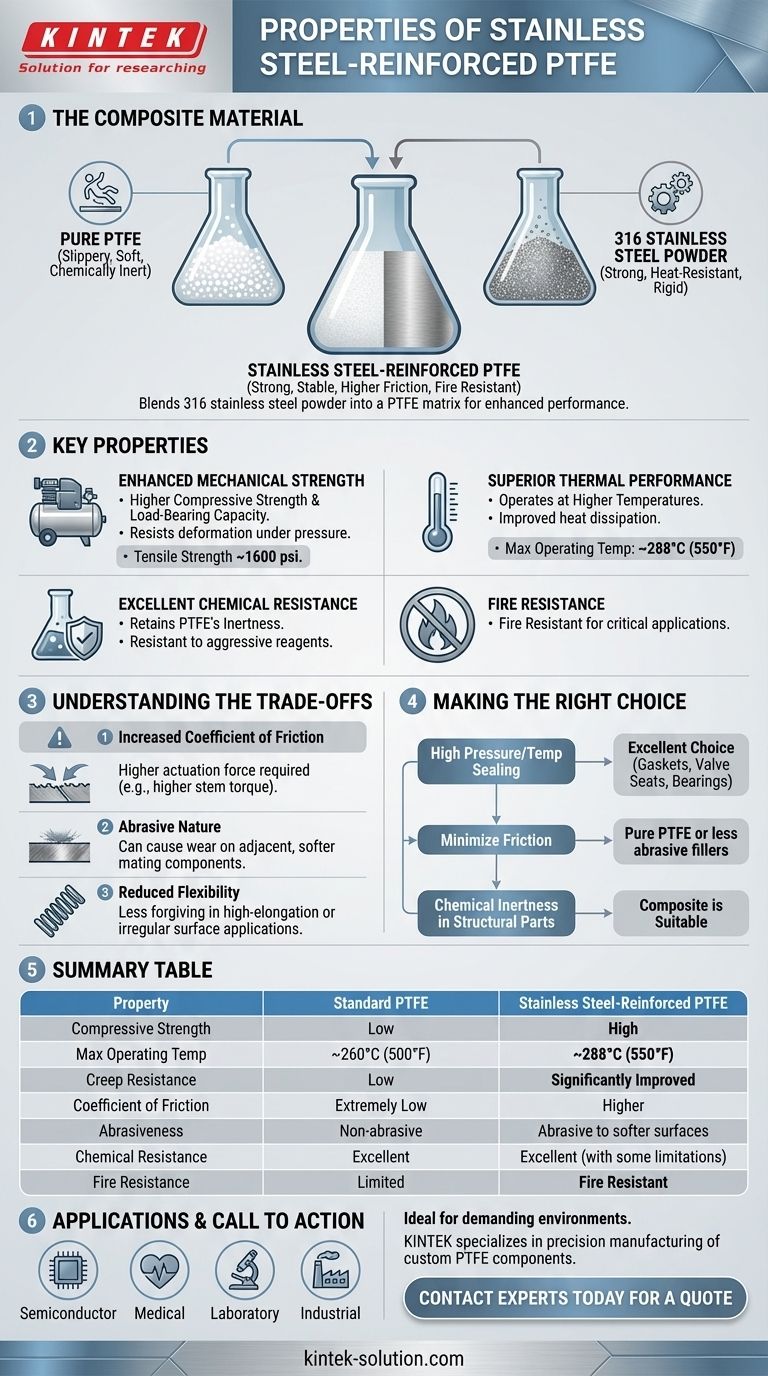
Stainless steel-reinforced PTFE is a composite material engineered for demanding applications. It combines the chemical inertness of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with the strength and thermal stability of 316 stainless steel powder. This blend dramatically enhances the pressure and temperature resistance of standard PTFE, making it suitable for challenging sealing and mechanical roles. However, these benefits come at the cost of a higher coefficient of friction and increased abrasiveness.
By embedding stainless steel powder into a PTFE matrix, you create a material that trades the unparalleled slipperiness of pure PTFE for a dramatic increase in strength, load-bearing capacity, and performance at high temperatures and pressures.

The Core Principle: Enhancing PTFE's Limitations
The PTFE Foundation
Pure PTFE is renowned for two primary characteristics: it has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid, and it is almost completely inert, resisting attack from nearly all chemicals.
However, pure PTFE is mechanically soft. It can deform under load (a process known as "creep") and has a limited operating temperature range, which restricts its use in high-stress applications.
The Role of Stainless Steel Reinforcement
Adding 50% powdered 316 stainless steel into the PTFE matrix fundamentally changes the material's behavior. The steel particles act as a reinforcing filler, providing a rigid internal structure.
This reinforcement directly counteracts PTFE's softness, creating a composite with significantly improved mechanical and thermal properties.
Key Properties of the Composite Material
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
The stainless steel filler drastically increases the material's compressive strength and load-bearing capabilities. This makes it highly resistant to deformation under pressure.
It exhibits significantly less creep relaxation than pure PTFE, ensuring a more stable and reliable seal over time, especially in high-pressure systems. Its tensile strength is often in the range of 1600 psi.
Superior Thermal Performance
Stainless steel-reinforced PTFE can operate at higher temperatures, with a typical upper limit around 550°F (288°C).
The metal content also improves thermal conductivity, allowing the material to dissipate heat more effectively than pure PTFE, which is an insulator.
Excellent Chemical Resistance
The composite retains the majority of PTFE's legendary chemical inertness. It remains stable when exposed to aggressive reagents like concentrated acids.
The primary chemical vulnerability comes from the 316 stainless steel, but given that the PTFE matrix encapsulates it, the material is suitable for a vast range of chemical environments.
Fire Resistance
A key advantage in critical applications is its fire resistance. This property makes it a specified material for use in industries where fire safety is a primary concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Increased Coefficient of Friction
This is the most critical compromise. While pure PTFE is exceptionally slippery, adding abrasive steel particles significantly increases friction.
This results in the need for higher actuation force in components like valve seats, often referred to as higher "stem torque."
Abrasive Nature
The hardness of the stainless steel particles can cause wear on adjacent, softer surfaces.
When designing with this material, the hardness of mating components (like valve stems or shafts) must be considered to prevent premature failure of the system.
Reduced Flexibility
The addition of a rigid filler makes the composite less flexible than pure PTFE. While this is desirable for structural integrity and creep resistance, it means the material is less forgiving in applications requiring high elongation or conformity to irregular surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting this material depends entirely on whether its strengths outweigh its compromises for your specific use case.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure and high-temperature sealing: This material is an excellent choice for gaskets, valve seats, and bearings where pure PTFE would fail due to creep or extrusion.
- If your primary focus is minimizing friction and protecting mating surfaces: Pure PTFE or variants filled with less abrasive materials (like glass or carbon) may be a better choice to prevent wear on softer components.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness in a structural part: The composite retains PTFE's chemical resistance while adding the mechanical strength needed for self-supporting components in corrosive environments.
Ultimately, stainless steel-reinforced PTFE is a problem-solving material for when mechanical and thermal demands exceed the capabilities of standard polymers.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | Stainless Steel-Reinforced PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Low | High |
| Max Operating Temp | ~260°C (500°F) | ~288°C (550°F) |
| Creep Resistance | Low | Significantly Improved |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely Low | Higher |
| Abrasiveness | Non-abrasive | Abrasive to softer surfaces |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent (with some limitations) |
| Fire Resistance | Limited | Fire Resistant |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Component for Your Application?
Stainless steel-reinforced PTFE is ideal for demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors where strength and temperature resistance are critical.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, we deliver parts that meet your exact specifications for performance and durability.
Let us help you solve your toughest sealing and mechanical challenges. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency
- Why is dimensional stability a concern when machining PTFE? Ensure Accurate, Stable PTFE Components
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What are some applications of CNC machined PTFE parts? Critical Components for Medical, Electrical & Food Industries



















