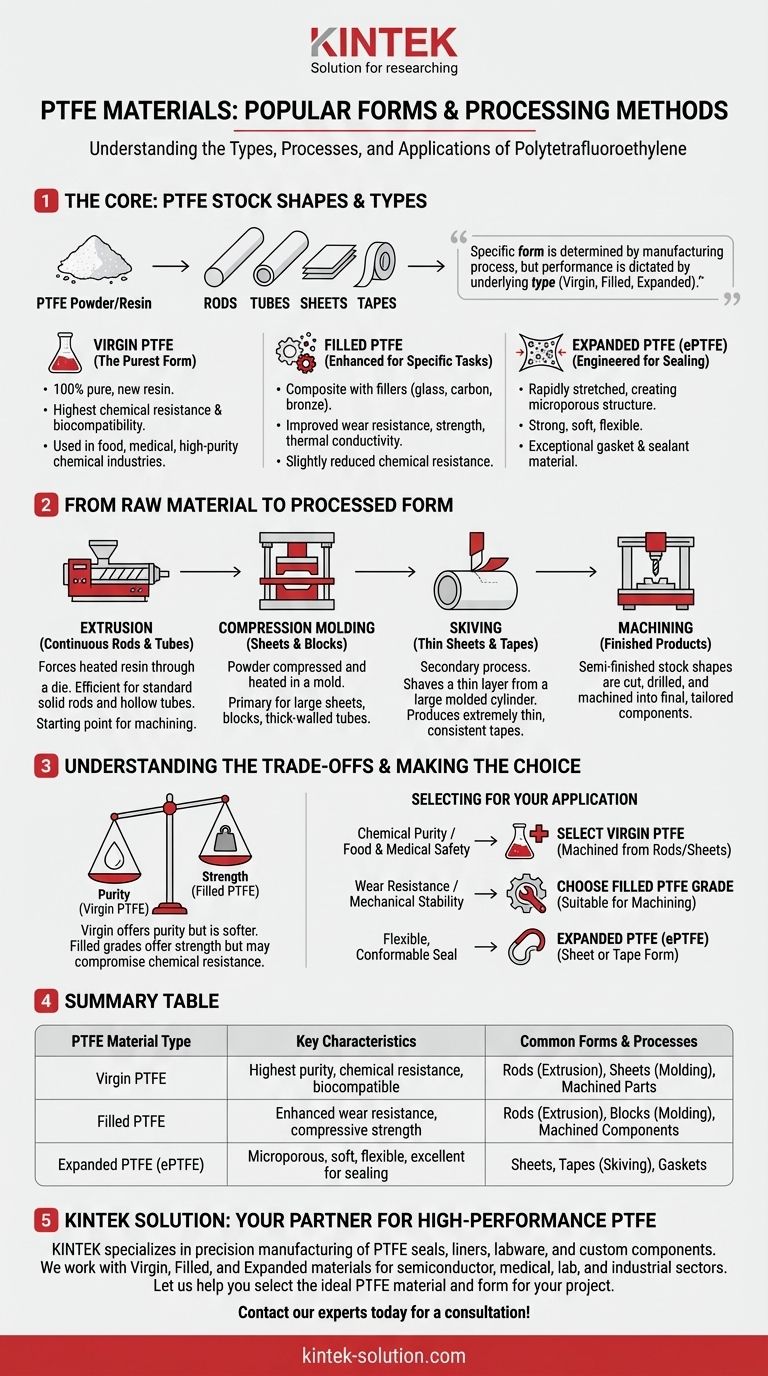
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is processed into several common stock shapes ready for industrial use. The most popular forms are rods, tubes, sheets, and thin tapes, which are created through methods like extrusion, molding, and skiving. These shapes serve as the foundational materials for creating a vast array of finished components.
The specific form of a PTFE product (like a rod or sheet) is determined by its manufacturing process, but its performance characteristics are dictated by the underlying type of PTFE material used—primarily Virgin, Filled, or Expanded. Understanding both is essential for proper material selection.
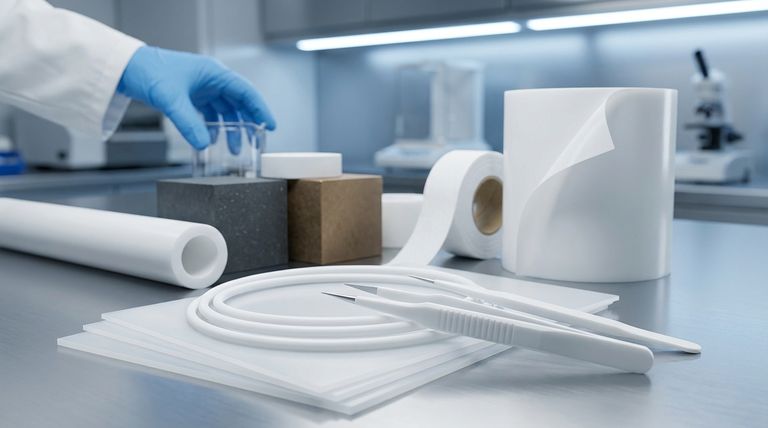

The Foundational Types of PTFE
Before a final shape is created, the raw PTFE material itself comes in distinct types. The choice of which type to use is the single most important factor influencing the final product's properties.
Virgin PTFE: The Purest Form
Virgin PTFE is made from 100% pure, new PTFE resin without any recycled or filler material. This purity makes it the most chemically resistant and biocompatible option.
It is prized for applications in food, medical, and high-purity chemical industries where contamination is a primary concern.
Filled PTFE: Enhanced for Specific Tasks
Filled PTFE is a composite material where fillers are added to the virgin resin to enhance specific properties. Common fillers include glass, carbon, graphite, or bronze.
This process improves characteristics like wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity, but it may slightly reduce the material's chemical resistance compared to its virgin counterpart.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE): Engineered for Sealing
Expanded PTFE is created by rapidly stretching virgin PTFE under specific conditions. This process creates a microporous structure that is strong yet soft and flexible.
This unique structure makes ePTFE an exceptional gasket and sealant material, capable of conforming to irregular surfaces and maintaining a tight seal under pressure.
From Raw Material to Processed Form
The raw PTFE types are transformed into usable shapes through several key manufacturing processes. Each process is suited to creating a different final form.
Extrusion: For Continuous Rods and Tubes
Extrusion forces heated PTFE resin through a die to create long, continuous profiles. This method is highly efficient for producing standard-sized solid rods and hollow tubes.
These extruded shapes are often the starting point for CNC machining into smaller, more complex components like bearings, insulators, or rollers.
Compression Molding: For Sheets and Blocks
In compression molding, a pre-measured amount of PTFE powder is placed into a mold, heated, and compressed into a solid form. This is the primary method for creating large sheets, blocks, and thick-walled tubes.
Molded sheets provide a large surface area ideal for cutting gaskets or fabricating larger structural parts.
Skiving: For Thin Sheets and Tapes
Skiving is a secondary process, not a primary one. It involves shaving a very thin layer from a large, molded PTFE cylinder, much like peeling a vegetable.
This is the only way to produce extremely thin and consistent PTFE sheets or tapes, often used for electrical insulation, non-stick surface linings, or thread seal tape.
Machining: For Finished Products
The rods, tubes, and sheets created by the processes above are rarely the final product. They are "semi-finished" stock shapes that are subsequently cut, drilled, and machined into finished components tailored to a specific application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right PTFE material involves balancing performance requirements against other factors. There is no single "best" option.
Purity vs. Mechanical Strength
Virgin PTFE offers the highest purity and chemical inertness, making it essential for sanitary or highly corrosive environments. However, it is softer and more prone to "creep" (deformation under load).
Filled PTFE grades provide significantly better mechanical strength and wear resistance, but the fillers can compromise its universal chemical resistance and may not be suitable for food or medical use.
Form Factor vs. Application
The required shape dictates the process. If you need a simple seal washer, a machined part from an extruded rod is efficient. If you need a large, complex gasket, it may be cut from a molded sheet.
For thin, flexible insulation or lining applications, only a skived tape or film will provide the necessary thickness and consistency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your end goal will determine the ideal combination of PTFE type and form.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or food/medical safety: Select Virgin PTFE, typically in a machined form from extruded rods or molded sheets.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and mechanical stability: Choose a Filled PTFE grade (like glass or carbon-filled) in a form that is suitable for machining your component.
- If your primary focus is creating a flexible, conformable seal: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) in sheet or tape form is the definitive choice.
By aligning the material's fundamental type and its processed form with your specific needs, you can leverage the remarkable properties of PTFE effectively.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Material Type | Key Characteristics | Common Forms & Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Highest purity, chemical resistance, biocompatible | Rods (Extrusion), Sheets (Molding), Machined Parts |
| Filled PTFE | Enhanced wear resistance, compressive strength | Rods (Extrusion), Blocks (Molding), Machined Components |
| Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Microporous, soft, flexible, excellent for sealing | Sheets, Tapes (Skiving), Gaskets |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components from prototypes to high-volume orders. We work with Virgin, Filled, and Expanded PTFE materials to meet the demanding requirements of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Let us help you select the ideal PTFE material and form for your project. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the installation advantages of PTFE lined butterfly valves? Simplify Setup & Save on Costs
- What are the steps for installing PTFE seals? A Guide to Leak-Free, Long-Lasting Performance
- Are PTFE V-Rings customizable? Engineer a Perfect Seal for Your Unique Application
- How do expanded PTFE gaskets prevent leakage in industrial applications? Achieve a Superior, Leak-Proof Seal
- Why is the manufacturing cost of PTFE processing machines high? The Engineering Behind High-Performance Polymer Processing
- How are Teflon rods utilized in the chemical processing industry? For Seals, Liners & Valves That Resist Corrosion
- What are PTFE bellows and diaphragms, and why are they important in critical systems?
- What are PTFE gaskets and how are they made? A Guide to High-Performance Sealing Solutions



















