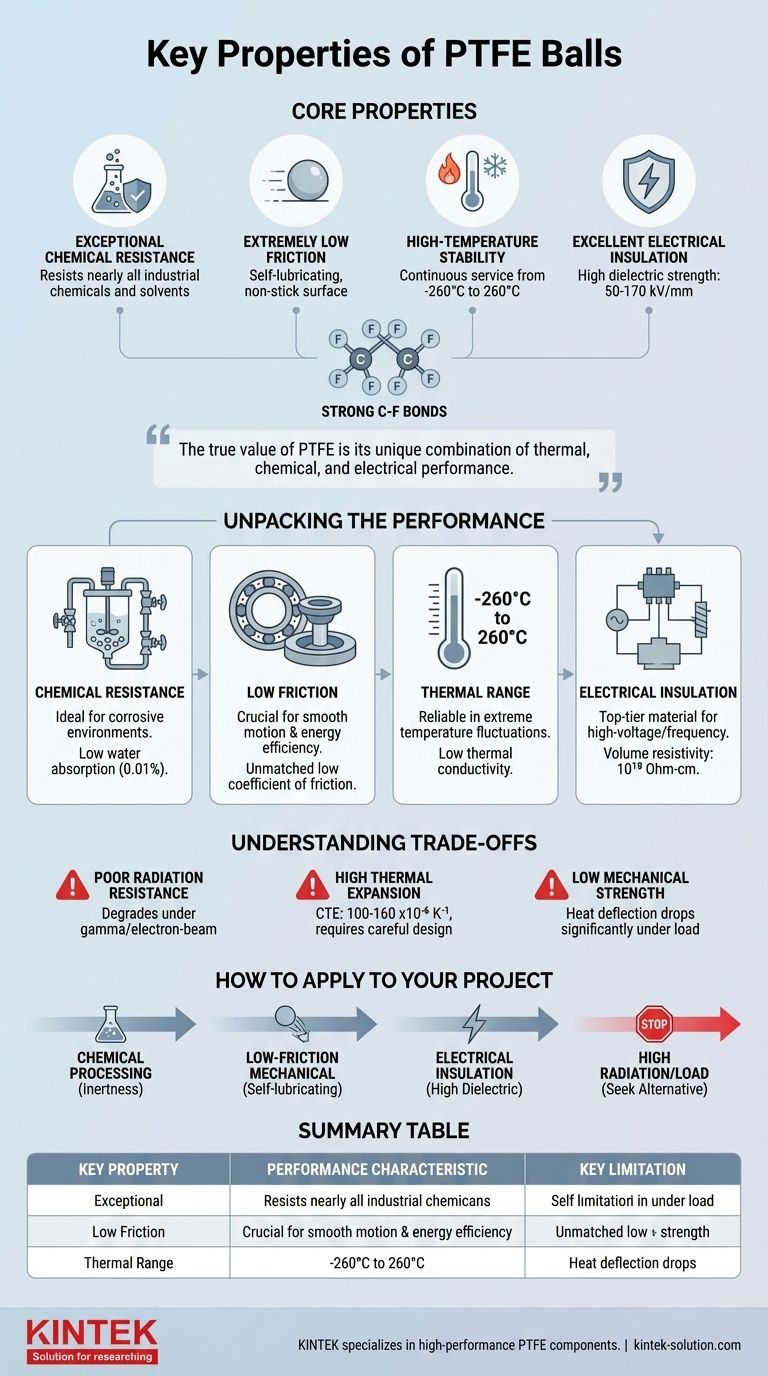
The core properties of PTFE balls are defined by four standout characteristics: exceptional chemical resistance, an extremely low coefficient of friction, high-temperature stability, and excellent electrical insulation. These traits stem directly from the strong carbon-fluorine bonds in its polytetrafluoroethylene molecular structure, making it a highly specialized material for demanding applications.
The true value of PTFE is its unique combination of thermal, chemical, and electrical performance in a single material. However, success in any application requires understanding not only these strengths but also its critical limitations, such as poor radiation resistance and high thermal expansion.

Unpacking the Performance Characteristics
To understand if PTFE is the correct material for your needs, we must examine the specific data behind its primary attributes.
Extreme Chemical Resistance
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert polymers known. It resists nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents, even at elevated temperatures.
This property makes it an ideal choice for components in chemical processing, such as check valves, bearings, and mixing beads that will be exposed to corrosive substances.
Unmatched Low Friction
With an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, PTFE provides a self-lubricating, non-stick surface. This is why it is used in everything from non-stick cookware to low-friction bearings.
This characteristic is crucial for applications requiring smooth, repeatable motion with minimal energy loss, such as in ball bearings and valve seats.
Broad Thermal Operating Range
PTFE maintains its properties across an impressively wide temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows of -260°C up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C.
Its thermal conductivity is low (0.25 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹), meaning it also acts as a thermal insulator. This stability makes it reliable in environments with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator, characterized by a high dielectric strength of 50-170 kV/mm and an extremely high volume resistivity of 10¹⁸ Ohm-cm.
These properties make it a top-tier material for electrical components, especially in high-voltage or high-frequency applications where preventing electrical arcing and signal loss is critical.
Key Physical Data
Beyond the main performance categories, several other physical properties are important for design considerations.
PTFE has very low water absorption (0.01% over 24 hours), is highly resistant to UV radiation, and is inherently flame retardant with a limiting oxygen index of 95%.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. Acknowledging the limitations of PTFE is essential for proper engineering and application design.
Poor Radiation Resistance
This is a critical weakness. PTFE is highly susceptible to degradation from high-energy radiation, such as gamma or electron-beam radiation. The molecular structure breaks down, causing the material to become brittle and lose its mechanical properties.
High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes, with a coefficient of thermal expansion between 100-160 x10⁻⁶ K⁻¹. This must be accounted for in any design where tight tolerances are critical across a range of operating temperatures.
Low Mechanical Strength
While durable in many ways, PTFE is a relatively soft material. Its performance under mechanical load is limited, as shown by its heat deflection temperature, which drops from 120°C at 0.45 MPa of pressure to just 54°C at 1.8 MPa. It is not suitable for high-load structural components.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice should be dictated by the most critical demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is chemical processing: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for its inertness against nearly all corrosive materials.
- If your primary focus is low-friction mechanical systems: Its self-lubricating nature makes it ideal for components like check valves or light-duty bearings.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Its high dielectric strength and resistivity make it a top-tier material for high-voltage or high-frequency insulators.
- If your application involves high radiation or high mechanical loads: You must seek an alternative material better suited for those specific stresses.
By understanding both its remarkable strengths and its specific weaknesses, you can confidently leverage PTFE for demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Performance Characteristic | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all chemicals and solvents | Not suitable for high radiation environments |
| Coefficient of Friction | Extremely low, self-lubricating | Low mechanical strength under high load |
| Temperature Range | Stable from -260°C to 260°C | High coefficient of thermal expansion |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength (50-170 kV/mm) | - |
Ready to leverage PTFE's unique properties for your project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, labware, and custom balls. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we provide solutions that meet your exact specifications—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Our expertise ensures your components deliver on PTFE's promise of chemical inertness, low friction, and thermal stability. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your application requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- In which industries are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits
- Why are PTFE balls particularly suitable for high-performance applications? Key Properties & Selection Guide
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What factors determine the different grades of PTFE balls available? Select the Right Grade for Your Application
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency



















