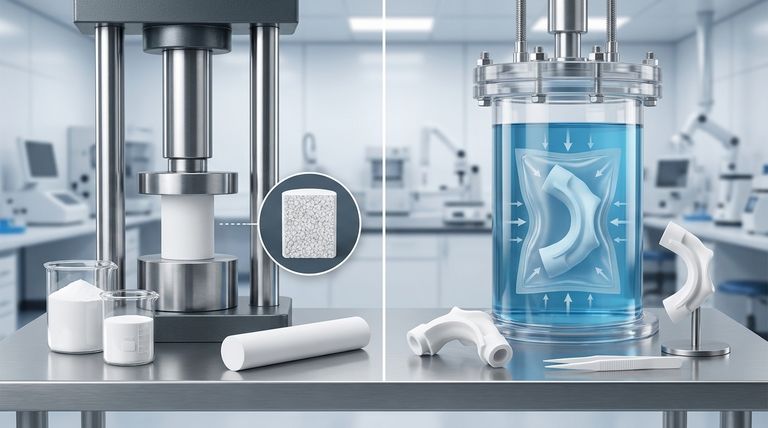
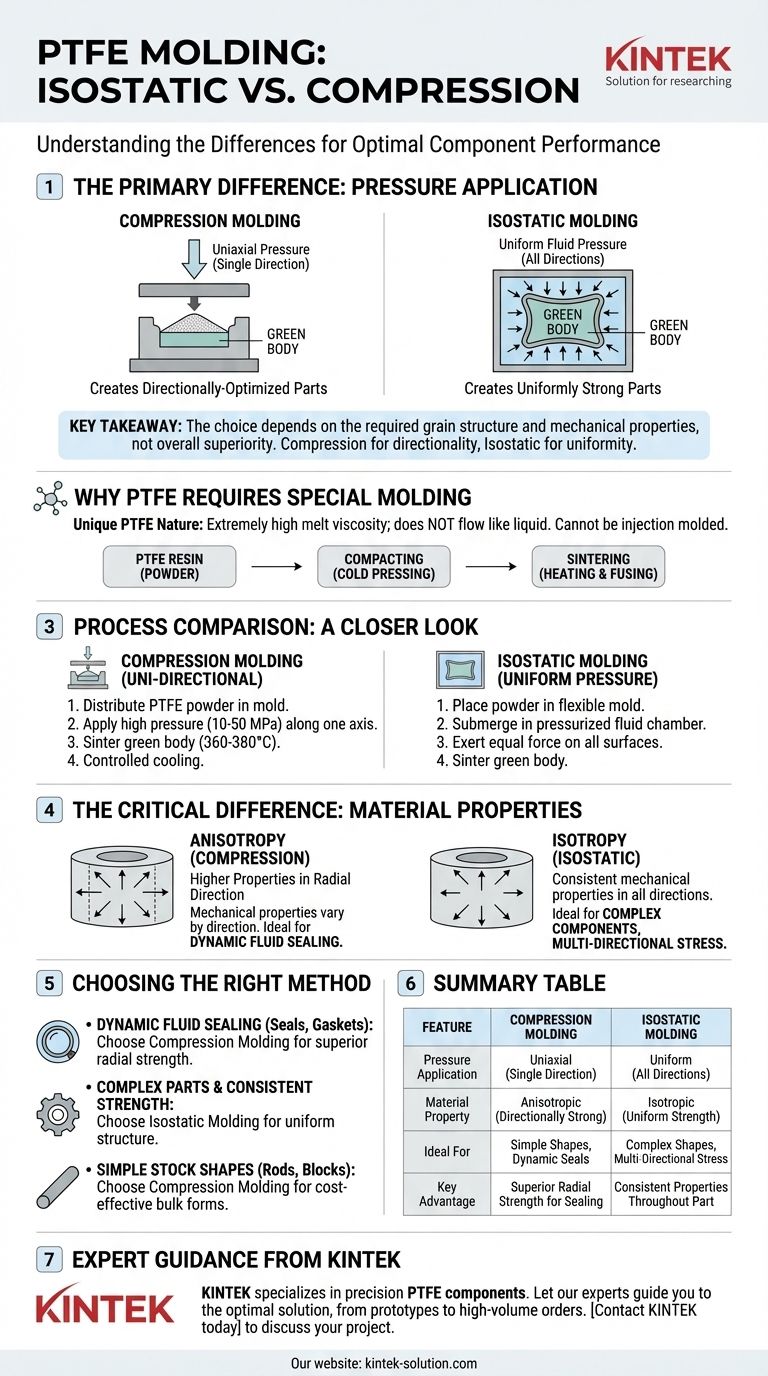
The primary difference between isostatic and compression molding for PTFE lies in how pressure is applied during the initial forming stage. Isostatic molding uses fluid pressure applied uniformly from all directions, creating a part with consistent properties throughout. In contrast, compression molding applies pressure from a single direction (uniaxially), which results in different mechanical properties along different axes of the part.
The choice between isostatic and compression molding is not about which method is superior overall, but which one creates the specific grain structure and mechanical properties required by your final application. Compression molding creates directionally-optimized parts, while isostatic molding creates uniformly strong parts.

Why PTFE Requires Special Molding
To understand the molding processes, we must first understand the unique nature of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It is a material that behaves unlike most common plastics.
The Unique Nature of PTFE Resin
PTFE has an extremely high melt viscosity, meaning it does not flow like a liquid when heated. Because of this, it cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding.
Instead, PTFE must be processed more like a powdered metal. This involves compacting the resin powder and then heating it to fuse the particles together in a process called sintering.
From Polymer to Powder
The raw PTFE material is created through polymerization. The resulting resin is processed into granular powders or fine pellets, which become the starting material for the molding process.
A Closer Look at Each Molding Process
Both compression and isostatic molding start with PTFE powder and end with a solid, sintered part. The key distinction is the "cold pressing" step where the powder is initially compacted.
Compression Molding: The Uni-Directional Press
This is the most common method for creating simple, bulk shapes. The process involves distributing PTFE powder evenly into a mold cavity.
A press then applies high pressure (between 10–50 MPa) along a single axis to compact the powder into a "green body."
This pre-formed part is then removed from the mold and sintered in an oven at 360–380°C, where the PTFE particles fuse. A slow, controlled cooling phase prevents cracking from internal stress.
Isostatic Molding: Uniform Pressure, Uniform Properties
In isostatic molding, the PTFE powder is placed in a flexible, deformable mold. This mold is then submerged in a fluid within a high-pressure chamber.
The fluid is pressurized, exerting equal force on all surfaces of the mold simultaneously. This uniform pressure creates a green body with highly consistent density and no internal stress points from the molding process itself.
The Critical Difference: Resulting Material Properties
The direction of applied pressure directly influences the alignment of PTFE particles, which in turn dictates the final part's mechanical characteristics.
Anisotropy in Compression-Molded PTFE
Because pressure is applied in one direction, compression-molded parts are anisotropic. This means their mechanical properties are not the same in all directions.
Specifically, they exhibit higher properties in the radial direction (perpendicular to the pressing force). This characteristic is highly beneficial for applications like dynamic fluid sealing, where radial strength improves seal performance.
Isotropy in Isostatic-Molded PTFE
Because pressure is applied uniformly from all directions, isostatic-molded parts are isotropic, or biaxial. Their mechanical properties are consistent and uniform regardless of which direction you measure.
This is ideal for complex components or parts that will experience stress from multiple, unpredictable directions during operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Choosing the correct method requires evaluating your part's geometry, its end-use application, and any subsequent manufacturing steps.
Part Geometry and Complexity
Compression molding is ideal for producing simple, thick-walled structures and stock shapes like sheets, rods, blocks, and gaskets.
Isostatic molding is better suited for producing more complex pre-forms that are closer to the final part's shape, potentially reducing waste from subsequent machining.
Post-Processing and Machinability
For many applications, the molded part is simply a "blank" that undergoes CNC machining to achieve precise final dimensions.
Compression molding is the standard method for creating these machinable stock shapes. The properties of the PTFE (unfilled or filled with materials like glass or carbon) will dictate the machining parameters more than the molding method itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your decision should be driven by the performance requirements of the finished component.
- If your primary focus is dynamic fluid sealing: Choose compression molding to leverage its superior radial mechanical properties for a tighter, more effective seal.
- If your primary focus is consistent strength in all directions for a complex part: Isostatic molding is the better choice as it produces a more uniform, isotropic material structure.
- If your primary focus is producing simple, cost-effective stock shapes (rods, blocks) for later machining: Compression molding is the standard, highly effective method for creating these bulk forms.
By understanding how the molding process fundamentally shapes the material's internal structure, you can confidently select the method that ensures your component's success.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Compression Molding | Isostatic Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Application | Uniaxial (Single Direction) | Uniform (All Directions) |
| Material Property | Anisotropic (Directionally Strong) | Isotropic (Uniform Strength) |
| Ideal For | Simple Shapes, Dynamic Seals | Complex Shapes, Multi-Directional Stress |
| Key Advantage | Superior Radial Strength for Sealing | Consistent Properties Throughout Part |
Unsure which PTFE molding method is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, from custom seals and liners to complex labware. We understand that the choice between compression and isostatic molding is critical to your part's performance.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution. We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet the exact demands of the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and achieve superior results with the right PTFE molding process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing the thickness of a PTFE gasket? Optimize Your Seal for Flange Condition & Pressure
- Why is CNC machining ideal for manufacturing Teflon parts? Unlock Precision Without Compromising Material Integrity
- How does a Teflon sheet protect materials during heat press applications? Prevent Scorching & Smudging for Professional Results
- What industries benefit from using PTFE gaskets in ball valves? Ensure Purity & Reliability in Critical Processes
- What are the specifications of a high-pressure, low-speed PTFE seal profile? Handle 3,000 psi with Confidence
- Why is machined PTFE popular in the medical field? Unmatched Biocompatibility & Precision
- How do PTFE seals contribute to reducing vehicle emissions? Achieve Cleaner, More Efficient Vehicles
- In what industries or applications are PTFE bellows commonly used? Essential for Purity and Corrosion Resistance



















