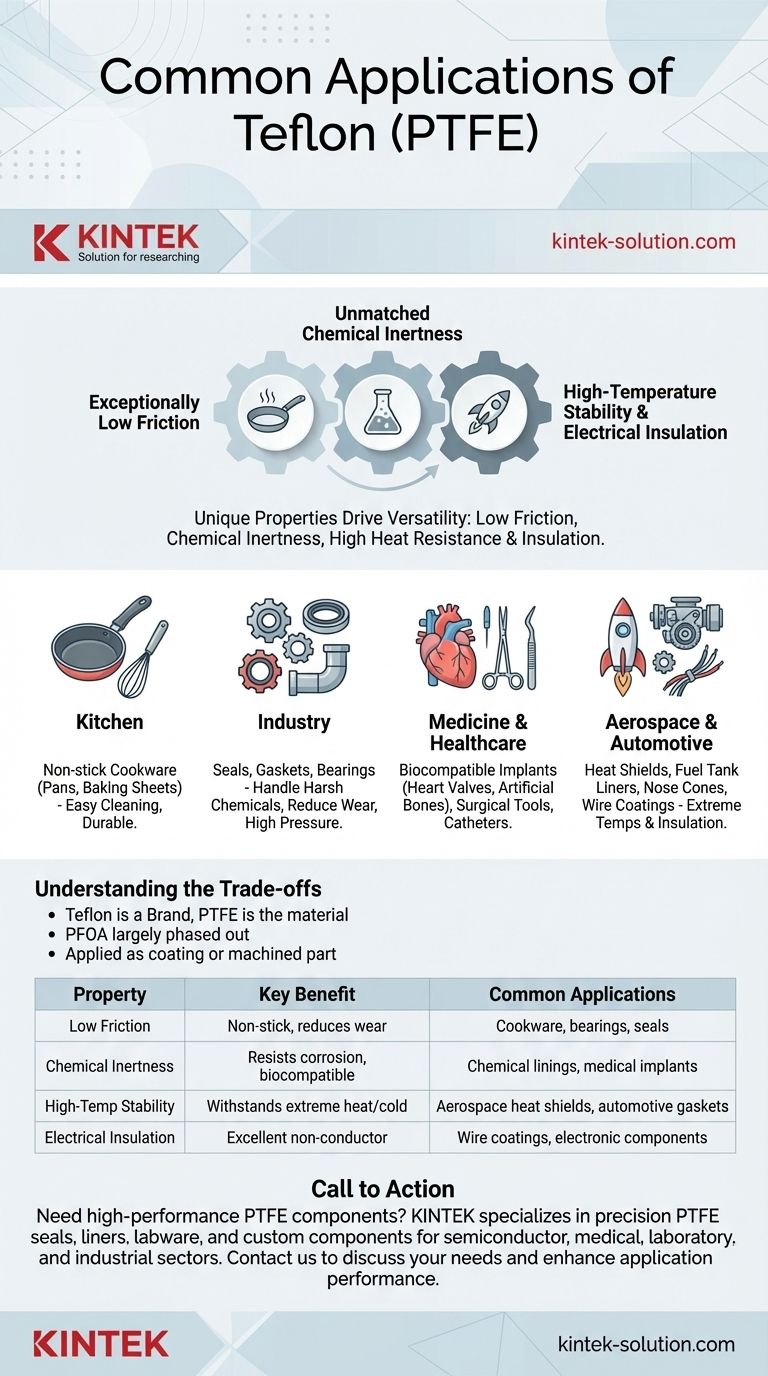
At its core, Teflon is most famously used for non-stick cookware, but its applications extend far beyond the kitchen. It is a critical material in industrial settings for seals and gaskets, in medicine for biocompatible implants and surgical tools, in aerospace for heat shields, and in electronics as a high-performance electrical insulator. Its versatility stems from a unique combination of properties that solve problems across dozens of industries.
The widespread use of Teflon isn't due to a single feature, but its rare combination of three core properties: exceptionally low friction, extreme chemical inertness, and high heat resistance. Understanding these three traits is the key to understanding why it's used in everything from frying pans to spacecraft.

The Properties That Drive Teflon's Versatility
Teflon is a brand name, most commonly for the polymer polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Its value comes not from what it does, but from what it doesn't do—it doesn't stick, it doesn't react, and it doesn't conduct electricity.
Exceptionally Low Friction (The Non-Stick Surface)
This is Teflon's most famous characteristic. It has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, which is why things slide off it so easily.
This property is essential for non-stick cookware, where it prevents food from adhering. It's also critical in industrial applications like self-lubricating bearings, gears, and seals that need to operate smoothly with minimal wear.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Teflon is highly non-reactive and resists corrosion from the vast majority of chemicals. This inertness makes it an invaluable material for handling aggressive substances.
It is used to create linings for pipes, tanks, and laboratory equipment in the chemical industry. This same non-reactive quality makes it biocompatible, meaning it can be safely used inside the human body for medical implants, artificial heart valves, and catheters.
High-Temperature Stability
Teflon can withstand a wide range of temperatures without degrading, maintaining its properties in both high-heat and cryogenic environments.
This makes it suitable for cookware, but also for demanding automotive and aerospace components. It is used for gaskets and seals in engines, as well as for heat shields and fuel tank liners on spacecraft.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
Teflon is an outstanding electrical insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity. This makes it a perfect material for protecting wires and electronic components.
You will find it used as a coating for wires and cables, especially in high-performance applications like aerospace and computing where signal integrity and safety are paramount.
Common Applications by Industry
While the underlying properties are the "why," seeing the material in context shows its true impact.
In the Kitchen
This is the most familiar application. Pans, skillets, and baking sheets are coated with Teflon to provide a durable, heat-resistant, and easy-to-clean non-stick surface.
In Industry
Industrial settings rely on Teflon for seals, gaskets, and bearings that must withstand harsh chemicals and high pressures without failing. Its low-friction nature reduces wear and tear on machinery.
In Medicine and Healthcare
Because the body does not reject it, Teflon is used for artificial bones, heart valves, and dentures. It also provides low-friction, sterile coatings for surgical instruments, catheters, and pharmaceutical packaging.
In Aerospace and Automotive
In high-performance vehicles, Teflon appears as coatings on wires, gaskets, and seals. Its ability to withstand extreme temperatures makes it essential for nose cones and heat shields on aircraft and spacecraft.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and understanding Teflon's context is key to appreciating its use.
"Teflon" is a Brand, Not a Single Material
The name Teflon refers to a family of fluoropolymers, with PTFE being the most common. Different formulations are optimized for different tasks, from flexible coatings to rigid, structural parts.
Historical Manufacturing Concerns
Early manufacturing processes for Teflon coatings used a chemical called PFOA, which raised significant health and environmental concerns. Since then, the industry has largely phased out PFOA in favor of other technologies, but this history is an important part of the material's story.
Application Method is Crucial
Teflon can be applied as a thin spray-on coating, as seen on cookware, or it can be machined from a solid block to create parts like gaskets and bearings. The form it takes is entirely dependent on the problem it is meant to solve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right material for a job depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to overcome.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: Teflon's non-stick quality is ideal for cookware, mechanical bearings, and medical device coatings.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: Its inertness makes it the standard for lining pipes, tanks, and laboratory equipment.
- If your primary focus is electrical safety: Its superior insulating properties are essential for coating wires and protecting electronic components.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: Its non-reactive nature is critical for medical implants, surgical tools, and pharmaceutical processing.
Ultimately, Teflon's ubiquitous presence is a direct result of its powerful and unique combination of physical and chemical properties.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Friction | Non-stick, reduces wear | Cookware, bearings, seals |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion, biocompatible | Chemical linings, medical implants |
| High-Temp Stability | Withstands extreme heat/cold | Aerospace heat shields, automotive gaskets |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent non-conductor | Wire coatings, electronic components |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your project?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures solutions that meet your exact specifications for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction.
Contact us today to discuss your custom PTFE fabrication needs and discover how we can enhance your application's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















