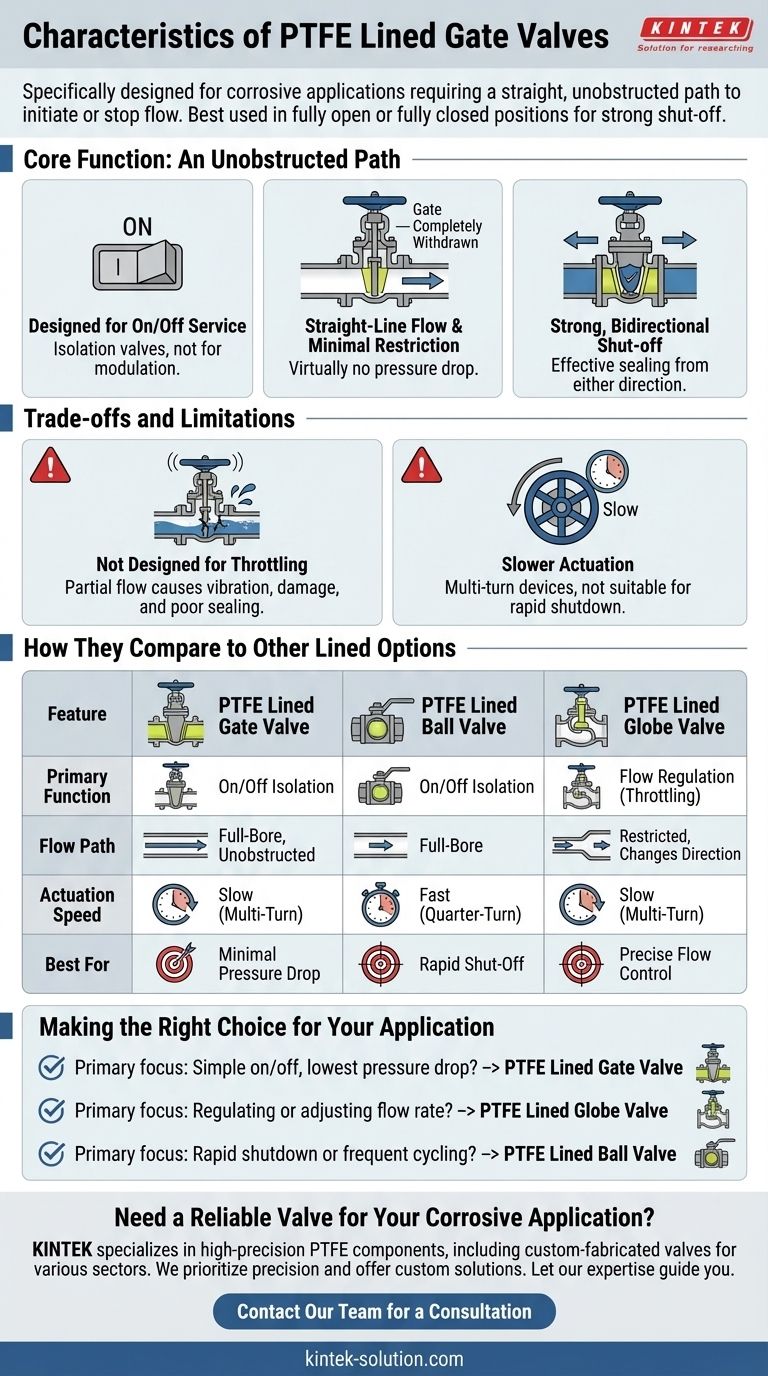
When evaluating valves for corrosive service, a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Lined Gate Valve serves a very specific purpose. It is designed primarily to initiate or stop flow in applications that require a straight, unobstructed path and minimal flow restriction. These valves are best used in a fully open or fully closed position, providing strong shut-off properties in either flow direction.
Choosing the right lined valve is about more than just chemical compatibility. You must match the valve's mechanical design to your system's operational needs. A PTFE Lined Gate Valve excels at simple on/off duty where flow restriction is unacceptable, but it is not a universal solution.
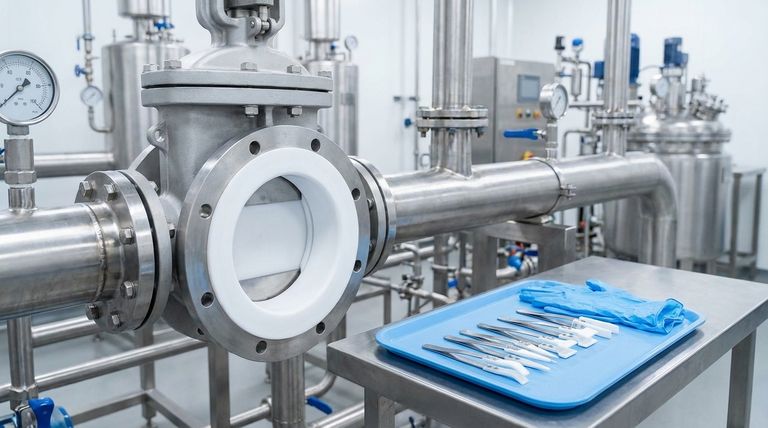

The Core Function: An Unobstructed Path
A PTFE Lined Gate Valve operates like a simple gate blocking a channel. Its primary strengths are derived from this straightforward mechanical design.
Designed for On/Off Service
These valves are not intended for modulation or throttling. They are isolation valves, meant to be kept either fully open to allow flow or fully closed to stop it completely.
Straight-Line Flow and Minimal Restriction
When the valve is open, the disc (the "gate") is completely withdrawn from the flow path. This creates a full, straight-line port that introduces virtually no pressure drop or flow obstruction, which is critical for many processes.
Strong, Bidirectional Shut-off
The design allows for a tight seal when the valve is closed. Because the gate mechanism is symmetrical, these valves are bidirectional, meaning they can effectively shut off flow from either direction without compromising performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The simplicity of the gate valve's design also introduces specific operational constraints that are crucial to understand. Choosing this valve for the wrong task will lead to poor performance and potential system damage.
Not Designed for Throttling
Using a gate valve in a partially open position is a common mistake. The fluid flowing past the partially open gate can cause severe vibration and chatter, leading to seat and disc damage over time and compromising the valve's ability to seal.
Slower Actuation
Compared to quarter-turn valves like ball or butterfly valves, gate valves are multi-turn devices. They are not easy or quick to open and close, requiring multiple rotations of the handwheel. This makes them unsuitable for applications requiring rapid shutdown.
How Gate Valves Compare to Other Lined Options
To understand where a PTFE Lined Gate Valve fits, it's helpful to compare it to other common lined valves, each with its own distinct advantages.
vs. PTFE Lined Globe Valves
The key difference is function. Gate valves are for on/off control. Globe valves are specifically designed to regulate or throttle flow. If you need to precisely control the flow rate, a globe valve is the correct choice.
vs. PTFE Lined Ball Valves
The key difference is speed. A ball valve is a quarter-turn (90°) device, making it extremely fast to open or close. While they also provide good on/off control, gate valves typically offer an even less restricted flow path when fully open.
vs. PTFE Lined Plug Valves
Plug valves are also fast-acting on/off valves, but they often require more force (torque) to actuate due to higher friction. Their primary advantage is often a very robust and simple sealing mechanism.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve is a matter of aligning its inherent characteristics with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is simple on/off control with the lowest possible pressure drop: The unobstructed path of a PTFE Lined Gate Valve makes it the ideal candidate.
- If your primary focus is regulating or adjusting the flow rate: A PTFE Lined Globe Valve is specifically designed for throttling and is the correct tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is rapid shutdown or frequent cycling: The quarter-turn speed of a PTFE Lined Ball Valve is far better suited for this need.
Ultimately, understanding a valve's fundamental design is the key to ensuring reliable and efficient system performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Lined Gate Valve | PTFE Lined Ball Valve | PTFE Lined Globe Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | On/Off Isolation | On/Off Isolation | Flow Regulation (Throttling) |
| Flow Path | Full-Bore, Unobstructed | Full-Bore | Restricted, Changes Direction |
| Actuation Speed | Slow (Multi-Turn) | Fast (Quarter-Turn) | Slow (Multi-Turn) |
| Best For | Minimal Pressure Drop | Rapid Shut-Off | Precise Flow Control |
Need a Reliable Valve for Your Corrosive Application?
Selecting the right PTFE component is critical for the performance and longevity of your system. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom-fabricated valves—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications.
Let our expertise guide you to the optimal solution. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE over rubber in rotary shaft seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key steps in designing PTFE slide bearings for a specific application? Achieve Optimal Performance and Reliability
- What is the best choice for thinner dielectric layers in PTFE-based materials? Ceramic-Filled Composites for High-Frequency Stability
- In which applications are EPDM valve seats most suitable? A Guide to Water & Steam Systems
- What is PTFE and why is it used in mechanical seals? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What are the pressure limitations for PTFE ball valve seats? Understanding the Critical Role of Valve Size
- Why is PTFE ideal for aerospace applications? The Ultimate Material for Extreme Conditions
- How does PTFE paste extrusion work? A Guide to Manufacturing High-Strength Components



















