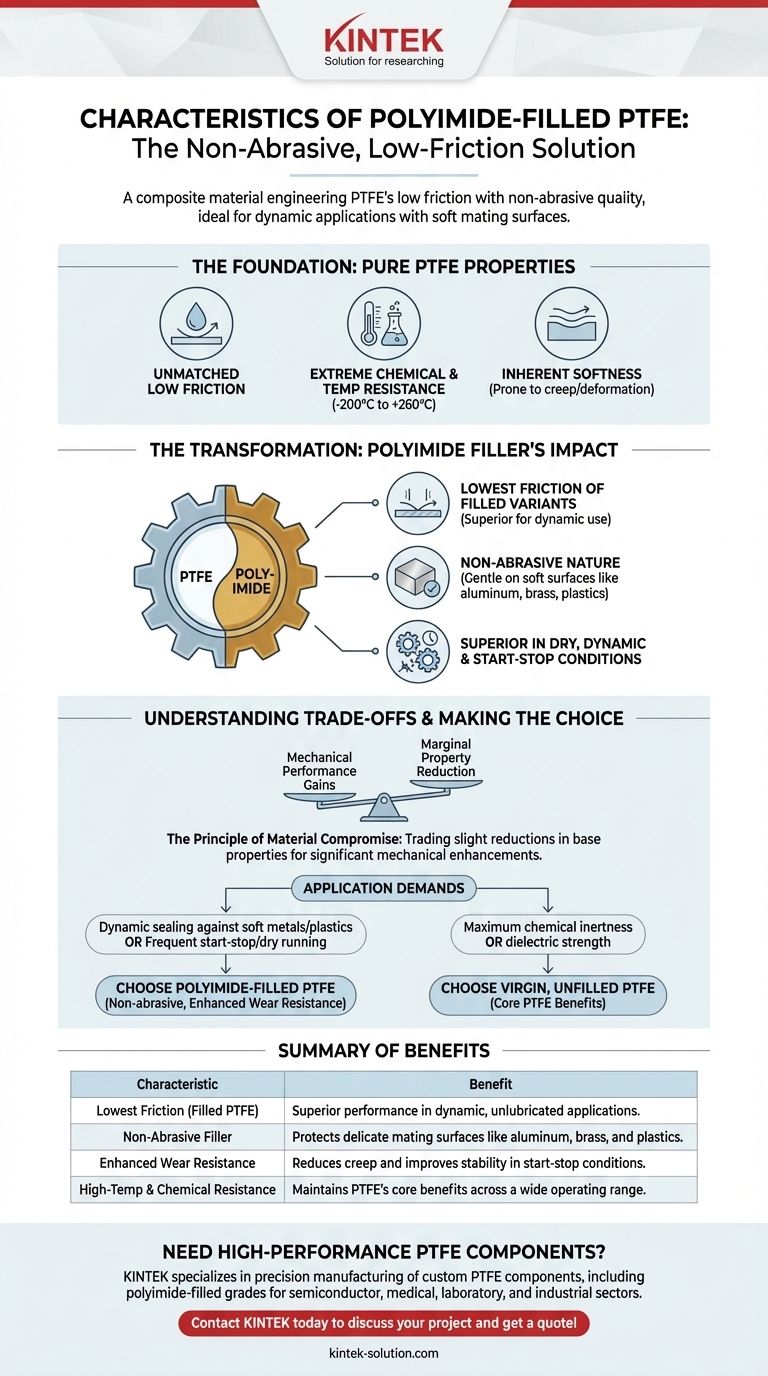
At its core, polyimide-filled PTFE is a composite material engineered to combine the extreme low friction of PTFE with a non-abrasive quality. This makes it uniquely suited for dynamic applications involving soft mating surfaces like aluminum, steel, or other plastics, where pure PTFE might be too soft or abrasive fillers would cause damage.
The central advantage of adding polyimide to PTFE is gaining exceptional performance in unlubricated, start-stop applications against delicate surfaces. It offers the lowest friction among common PTFE fillers while being gentle on its counterpart materials.

The Foundation: Understanding Pure PTFE's Properties
To appreciate the role of the polyimide filler, we must first understand the base material. Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a remarkable polymer with a unique combination of characteristics.
### Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This inherent slipperiness is its most famous attribute.
### Extreme Chemical and Temperature Resistance
It is virtually inert to almost all chemicals and maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, typically from –200°C to +260°C (–328°F to +500°F).
### Inherent Softness
While versatile, pure PTFE is a relatively soft material. In demanding mechanical applications, it can be prone to deformation or "creep" under load.
How Polyimide Filler Transforms PTFE
Adding polyimide as a filler specifically enhances the mechanical properties of PTFE for dynamic sealing and bearing applications without compromising its core benefits.
### The Lowest Friction of Filled Variants
While all PTFE is low-friction, the polyimide-filled grade is often cited as having the lowest friction coefficient among all commonly filled PTFE materials.
### A Non-Abrasive Nature for Delicate Surfaces
This is the key differentiator. Unlike glass or carbon fillers, polyimide is non-abrasive. This characteristic is critical for applications where the mating hardware is made of softer materials like aluminum, brass, stainless steel, or plastics.
### Superior Performance in Dry, Dynamic Conditions
Polyimide-filled PTFE excels in applications that are unlubricated (dry running) or involve frequent changes in motion (start-stop). The filler improves wear resistance and stability under these demanding conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material choice is without compromise. While polyimide filler provides significant mechanical advantages, it's important to understand the broader context.
### The Principle of Material Compromise
Adding any filler to a pure polymer can slightly alter its other properties. The exceptional chemical resistance or dielectric properties of virgin PTFE may be marginally reduced by the addition of a filler.
### Focusing on the Application's Goal
The choice to use a filled PTFE is a deliberate engineering decision. You are trading a small degree of certain base properties to gain a large improvement in mechanical performance, such as wear resistance and compatibility with soft metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material depends entirely on the primary demands of your specific environment and goals.
- If your primary focus is dynamic sealing against soft metal or plastic: Polyimide-filled PTFE is an ideal choice due to its non-abrasive nature.
- If your application involves frequent start-stop motion or runs without lubrication: The enhanced wear characteristics of this material make it a superior option over pure PTFE.
- If your absolute priority is maximum chemical inertness or dielectric strength: Virgin, unfilled PTFE may be the more appropriate selection for your needs.
Ultimately, choosing polyimide-filled PTFE is a strategic decision for when you need the benefits of PTFE in a demanding mechanical role.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lowest Friction (Filled PTFE) | Superior performance in dynamic, unlubricated applications. |
| Non-Abrasive Filler | Protects delicate mating surfaces like aluminum, brass, and plastics. |
| Enhanced Wear Resistance | Reduces creep and improves stability in start-stop conditions. |
| High-Temp & Chemical Resistance | Maintains PTFE's core benefits across a wide operating range. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your delicate applications?
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including polyimide-filled grades. We deliver the superior wear resistance and non-abrasive performance you need for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
From prototypes to high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components meet exact specifications. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















