At their core, PTFE-lined plug valves offer elite chemical resistance for corrosive and hazardous materials, but this protection comes with significant operational trade-offs. Their primary benefits are excellent sealing and a simple, durable design. The main drawbacks are the high force required to turn the valve and potential flow restriction depending on the port design.
The decision to use a PTFE-lined plug valve is a strategic trade-off. You are choosing the ultimate protection against corrosion at the cost of higher actuation force and the need to carefully consider the valve's impact on flow characteristics.

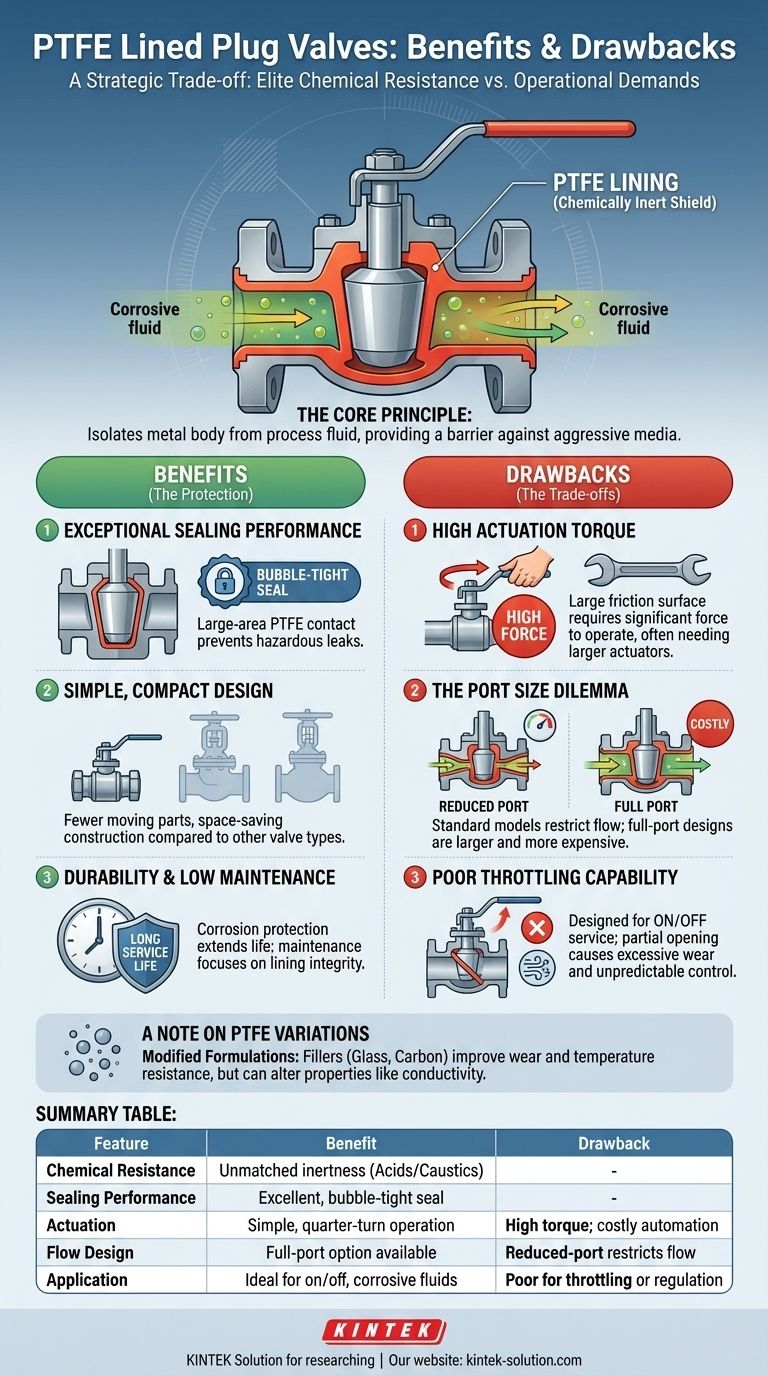
The Core Principle: A Shield Against Aggressive Media
The fundamental purpose of a PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) lining is to isolate the valve's metallic body from the process fluid. This creates a chemically inert barrier, making the valve suitable for services where corrosion is the primary concern.
How the Lining Works
The valve's internal body and the plug itself are completely encapsulated with a thick layer of PTFE. This ensures that the only material the process fluid touches is the highly non-reactive lining, preventing corrosion of the structural cast iron or steel body.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually immune to almost all chemicals, acids, and caustic substances. This makes it the material of choice for applications involving aggressive fluids where exotic and expensive metal alloys would otherwise be required.
Analyzing the Key Benefits
When deployed in the right application, these valves provide distinct advantages rooted in their design and material properties.
Exceptional Sealing Performance
The design uses a tapered plug that wedges securely into a matching tapered body. This large-area contact between the PTFE-lined components creates an exceptionally tight, bubble-free seal when the valve is closed, which is critical for preventing leaks of hazardous media.
Simple, Compact Design
Compared to other valve types like gate or globe valves, plug valves have a simpler construction with fewer moving parts. They are typically more compact, which is a valuable benefit in systems where space is limited.
Durability and Low Maintenance
Because the valve body is shielded from corrosion, the valve's service life is significantly extended. Maintenance is primarily focused on the integrity of the lining and sealing adjustments rather than dealing with rust or material degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Drawbacks
The unique design of the PTFE-lined plug valve also introduces specific operational challenges that must be understood before selection.
High Actuation Torque
This is the most significant drawback. The large surface area of the tapered plug pressed firmly against the body lining creates high static friction. Despite PTFE's slick surface, a substantial amount of force (torque) is required to "break" the plug free and rotate it. This often necessitates larger, more expensive actuators for automated systems.
The Port Size Dilemma: Reduced vs. Full
PTFE-lined plug valves come in two main configurations that directly impact flow.
- Reduced Port: Most standard models have a reduced port, meaning the opening through the plug is smaller than the pipe's diameter. This creates a flow restriction and a pressure drop across the valve.
- Full Port: Full-port (or full-bore) designs are available, offering an unrestricted flow path. However, these valves are physically larger and more expensive.
Poor Throttling Capability
Like ball valves, plug valves are quarter-turn devices designed for simple on/off service. They are not designed for throttling or regulating flow. Attempting to use one in a partially open position can cause excessive wear on the lining and unpredictable flow control.
A Note on PTFE Variations
To overcome some of PTFE's inherent material weaknesses, manufacturers often use modified formulations.
The Role of Fillers
Standard PTFE can be susceptible to wear and deformation. By adding fillers like glass or carbon, manufacturers can improve the lining's rigidity, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, especially under changing temperatures.
Impact of Modified Linings
These fillers enhance mechanical properties but can alter other characteristics. For example, a carbon-filled liner is more conductive than pure PTFE. This is a critical detail in applications where electrical insulation is a factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve requires aligning its capabilities with your system's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive or pure media: The superior chemical resistance of a PTFE-lined plug valve is its defining strength and often makes it the best choice.
- If your primary focus is frequent cycling or automated control: The high actuation torque is a major consideration that will increase the cost and size of the required actuator.
- If your primary focus is maximizing flow and minimizing pressure drop: You must specify a more expensive full-port design to avoid the restrictions inherent in standard, reduced-port models.
Ultimately, a PTFE-lined plug valve is a specialized solution where understanding its distinct operational demands is the key to leveraging its unparalleled corrosion protection.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Drawback |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Unmatched inertness; handles aggressive acids/caustics | - |
| Sealing Performance | Excellent, bubble-tight seal for hazardous media | - |
| Actuation | Simple, quarter-turn operation | High torque required; costly automation |
| Flow Design | Full-port option available for minimal pressure drop | Standard reduced-port models restrict flow |
| Application | Ideal for on/off service with corrosive fluids | Poor for throttling or flow regulation |
Need a Reliable PTFE Component Solution?
Selecting the right valve is critical, but so is having a trusted manufacturing partner for the PTFE components themselves. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision production of high-performance PTFE parts—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We understand the demanding environments your equipment faces. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our custom fabrication ensures your components meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, sealing, and durability.
Let us help you build a more reliable and efficient system. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE-coated O-rings contribute to system reliability? Enhance Seal Life and Performance
- What are PTFE rods and how are they manufactured? A Guide to Their Properties and Production
- Why are gaskets made of Teflon used in construction? Prevent Galvanic Corrosion Between Dissimilar Metals
- When is machining preferred for PTFE part fabrication? For High-Precision, Complex, or Low-Volume Needs
- Which types of filled PTFE offer high resistance to extrusion? Moly, Glass/Moly, and Polyimide
- How do PTFE bearings benefit laboratory instruments? Ensure Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- How do spring energized PTFE seals differ from other radial seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- How does carbon filler cause corrosion when combined with aluminum? Understanding Galvanic Corrosion Risks



















