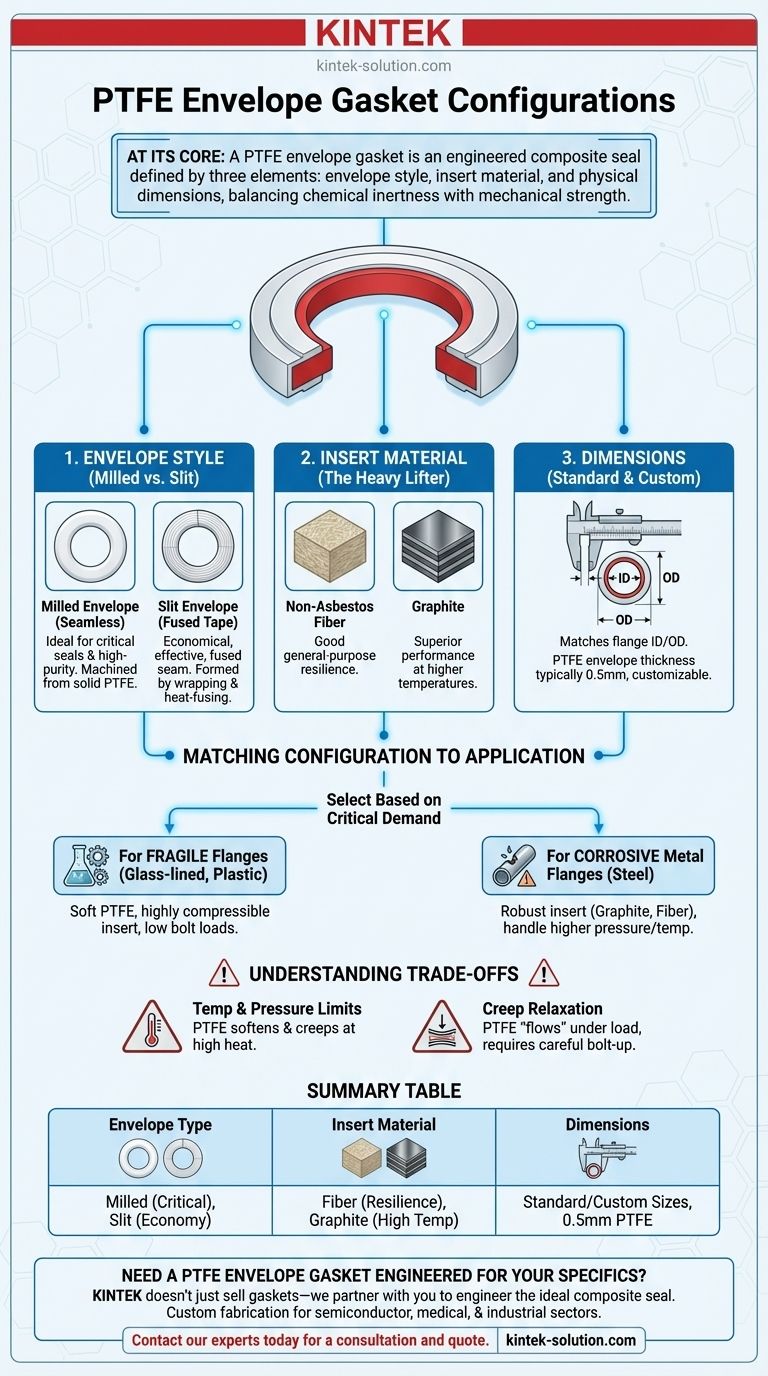
At its core, a PTFE envelope gasket's configuration is defined by three primary elements: the style of the PTFE envelope itself (milled or slit), the type of insert material it contains, and its physical dimensions. These components work together, combining the superior chemical resistance of PTFE with the mechanical properties of the insert material to create a highly specialized seal.
The essential takeaway is that you are not simply choosing a gasket, but rather engineering a composite seal. The configuration you select must balance the chemical inertness of the PTFE envelope against the mechanical strength, resilience, and temperature resistance of the insert material to perfectly match your application's demands.
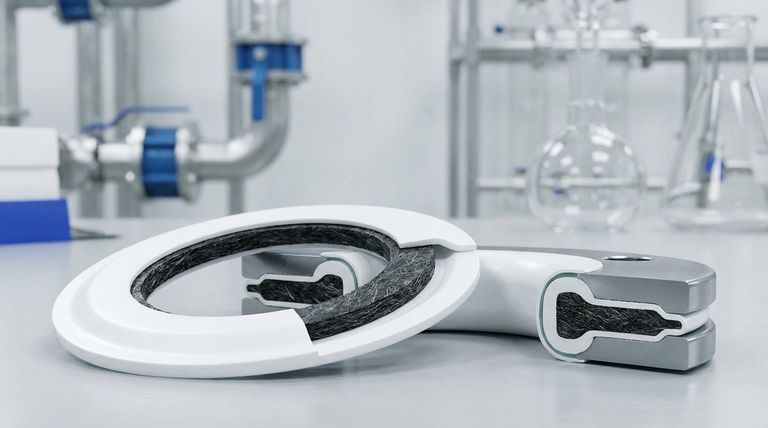

The Anatomy of a PTFE Envelope Gasket
A PTFE envelope gasket is a composite design. It consists of a softer, chemically resistant outer "envelope" made from PTFE that encloses a more robust core "insert" material. This design intelligently leverages the best properties of both materials.
Envelope Type: Milled vs. Slit
The manufacturing method of the envelope is a primary configuration choice.
A milled envelope is machined from a single, solid cylinder of PTFE. This creates a seamless gasket face, which is ideal for providing the most reliable seal, especially in critical or high-purity applications.
A slit envelope is formed by wrapping and heat-fusing PTFE tape. While highly effective and more economical, this method leaves a small, fused seam on the outer diameter of the gasket.
The Critical Role of the Insert Material
The insert provides the gasket's mechanical strength, resilience, and resistance to temperature and pressure. While the PTFE envelope provides the chemical seal, the insert does the heavy lifting.
Common insert materials mentioned for specific applications include non-asbestos fiber and graphite, but many others can be used depending on service needs. A fiber insert provides good general-purpose resilience, while a graphite insert offers superior performance at higher temperatures.
Dimensional Specifications
PTFE envelope gaskets can be manufactured to nearly any dimension required for your flange.
They are available in standard and non-standard sizes, with specified inner and outer diameters. Common production often starts from 12mm in diameter and can be customized upwards. The PTFE envelope itself typically has a thickness of 0.5mm, but this can also be adjusted as required by the application.
Matching Configuration to Application
The primary goal of configuring a PTFE envelope gasket is to match it to the specific demands of the flange and the process media.
For Fragile or Non-Metallic Flanges
Applications involving enamel, glass-lined, or plastic flanges benefit most from this gasket type.
The soft, conformable PTFE envelope protects the brittle flange surfaces from damage during bolt-up. A resilient, compressible insert material is chosen to achieve a tight seal with the lower bolt loads that these types of flanges can tolerate.
For Standard Metal Flanges in Corrosive Service
When sealing standard steel or rubber-lined steel flanges against aggressive chemicals, the PTFE envelope is the key feature.
Here, the configuration focus shifts to the insert. A more robust insert, such as graphite or a high-strength fiber composite, can be selected to handle higher pressures and temperatures, while the PTFE envelope provides the universal chemical resistance needed to protect the insert and the flange.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE envelope gaskets have specific limitations driven by their composite nature. Understanding these is key to successful implementation.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
The primary limiting factor is the PTFE envelope itself. While the insert may be rated for high temperatures, PTFE begins to soften and can be prone to creep (cold flow) at elevated temperatures, which limits the gasket's overall pressure-retaining capability.
The Challenge of Creep Relaxation
PTFE is a relatively soft material that can "flow" or deform under a constant load, a phenomenon known as creep. This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and sealing stress over time. The insert material is chosen specifically to resist this, but it remains a fundamental characteristic to manage.
Installation Sensitivity
The composite structure requires careful installation. Uneven or excessive bolt torque can damage the thin PTFE envelope, compromising the chemical seal before the gasket ever enters service. A careful, star-pattern tightening sequence is critical.
Selecting the Right Configuration
Your choice should be guided by the single most critical demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is universal chemical resistance: Prioritize the PTFE envelope itself. Select an insert material (like compressed fiber) that meets the basic mechanical requirements of your system.
- If your primary focus is protecting fragile flanges: The key is the soft PTFE envelope combined with a highly compressible insert that can achieve a seal at very low bolt stress.
- If your primary focus is higher temperatures or pressures in a corrosive environment: Select a mechanically robust insert like graphite to handle the load, relying on the PTFE envelope for the chemical barrier.
By breaking down the configuration into its core components, you can confidently specify a gasket that provides both the chemical compatibility and mechanical integrity your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Configuration Element | Key Options | Primary Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Envelope Type | Milled, Slit | Milled for critical seals; Slit for economy |
| Insert Material | Fiber, Graphite, Others | Fiber for resilience; Graphite for high temperature |
| Dimensions | Standard & Custom Sizes | Matches flange ID/OD; Envelope thickness typically 0.5mm |
Need a PTFE Envelope Gasket Engineered for Your Specifics?
At KINTEK, we don't just sell gaskets—we partner with you to engineer the ideal composite seal. Whether you're protecting fragile glass-lined flanges in a lab or sealing aggressive chemicals in a semiconductor process, our expertise ensures your configuration balances PTFE's chemical inertness with the right insert's mechanical strength.
We specialize in custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Let us help you achieve a perfect, reliable seal.
Contact our experts today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when choosing between O-rings, square rings, quad rings, or flat gaskets? Optimize Your Seal Selection
- Why are PTFE washers considered cost-effective despite their higher initial cost? Maximize ROI with Long-Term Savings
- Why are PTFE washers resistant to water and moisture? Unlocking the Power of Hydrophobic Sealing
- Why is specialized equipment needed for PTFE impeller manufacturing? Precision Machining for Critical Performance
- How does the chemical resistance of custom Teflon rotary shaft seals benefit industrial applications? Ensure Unmatched Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What are the cost and availability differences between PTFE and stainless steel impellers? A Guide to Material Selection
- What are critical installation practices for PTFE O-rings? Avoid Leaks and Ensure a Perfect Seal
- How does the chemical resistance of PTFE gaskets benefit ball valve applications? Ensure Leak-Free, Non-Contaminating Seals



















