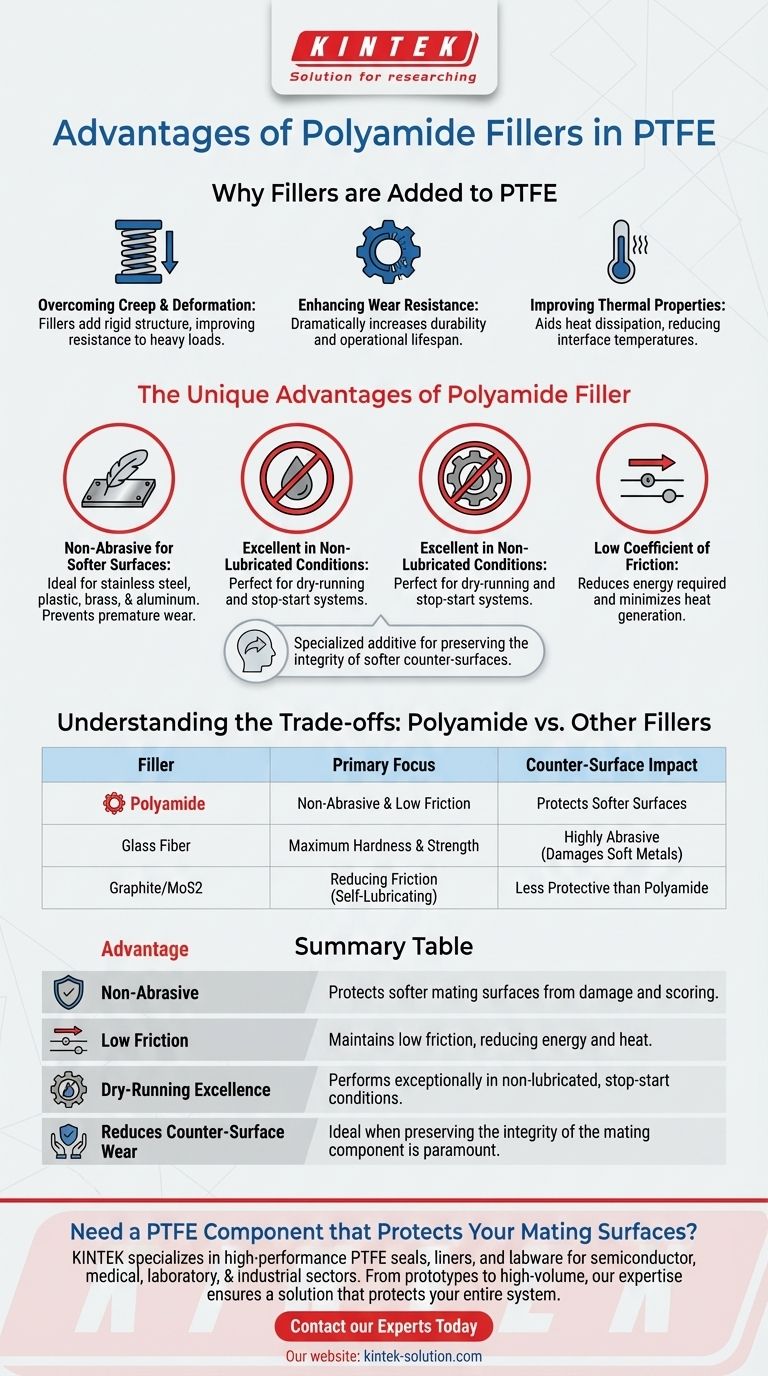
The primary advantages of using polyamide fillers in PTFE are its exceptionally low coefficient of friction and its non-abrasive nature, which makes it uniquely suited for dynamic applications against softer metals. It excels in non-lubricated, stop-start conditions where protecting the mating surface is a critical design requirement.
While most PTFE fillers add hardness and general wear resistance, polyamide is a specialized additive chosen when preserving the integrity of the counter-surface is paramount. It solves the problem of wear on softer materials like aluminum, brass, or plastic, which more aggressive fillers might damage.

Why Fillers are Added to PTFE
To understand the specific benefits of polyamide, it's essential to first recognize why pure, or "virgin," PTFE often requires modification. Virgin PTFE is a remarkable material but has inherent limitations.
Overcoming Creep and Deformation
Virgin PTFE is mechanically soft and can deform or "creep" over time, especially when subjected to a constant, heavy load. Fillers add a rigid structure to the PTFE matrix, significantly improving its resistance to this deformation.
Enhancing Wear Resistance
While PTFE has a very low friction coefficient, it is not highly resistant to abrasive wear. Fillers dramatically increase the material's durability and operational lifespan in dynamic sealing and bearing applications.
Improving Thermal Properties
Fillers can improve the thermal conductivity of PTFE, allowing heat generated at the mating surface to dissipate more effectively. This reduces interface temperatures and enhances the material's overall stability and durability.
The Unique Advantages of Polyamide Filler
Polyamide stands apart from other common fillers by prioritizing surface compatibility and low-friction performance over raw hardness.
Non-Abrasive for Softer Surfaces
This is the defining characteristic of polyamide-filled PTFE. Unlike hard fillers such as glass, polyamide is non-abrasive. This makes it the ideal choice for applications involving softer mating surfaces like stainless steel, plastic, brass, and aluminum.
Using a harder filler in these cases could lead to rapid wear and scoring of the counter-surface, causing premature failure of the entire assembly.
Excellent in Non-Lubricated Conditions
Polyamide is a synthetic polymer that performs exceptionally well in dry-running or non-lubricated systems. Its inherent properties are perfect for applications with frequent stop-start motion, where a consistent lubricating film cannot be maintained.
Low Coefficient of Friction
While many fillers can increase wear resistance, some do so at the cost of increased friction. Polyamide helps maintain a very low friction coefficient, reducing the energy required to operate the system and minimizing heat generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Polyamide vs. Other Fillers
Choosing a filler is an engineering decision based on specific application demands. Polyamide is a specialized solution, not a universal upgrade.
Polyamide vs. Glass Fiber
Glass is the most common and cost-effective PTFE filler, providing excellent compressive strength and general durability. However, it is highly abrasive and will damage soft metal surfaces. Glass is for hard-on-hard applications where strength is the top priority.
Polyamide vs. Graphite
Graphite is an excellent filler for reducing friction and is self-lubricating. It is often used with other fillers like glass or carbon to combine properties. While both reduce friction, polyamide's primary advantage remains its non-abrasive quality for protecting soft mating surfaces.
Polyamide vs. Molybdenum Disulfide (MoS2)
Often used in combination with bronze or glass, MoS2 increases solidity and smoothness while lowering the friction coefficient. It acts as a solid lubricant, particularly beneficial in dynamic seals, but does not provide the same level of protection for soft surfaces as polyamide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select your filled PTFE based on the demands of the entire mechanical system, not just the seal or bearing itself.
- If your primary focus is preserving a soft mating surface (like aluminum or plastic): Polyamide is the superior choice due to its non-abrasive nature.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance in a hard-on-hard system: Glass-filled PTFE is the robust and cost-effective industry standard.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in a dynamic, well-lubricated system: Graphite or Molybdenum Disulfide are excellent additives, often blended with other fillers.
- If your primary focus is a non-lubricated, stop-start application: Polyamide is specifically engineered to excel in these dry-running conditions.
Ultimately, selecting the correct filler requires understanding that you are engineering not just a component, but a complete system interface.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-Abrasive | Protects softer mating surfaces (aluminum, brass, plastic) from damage and scoring. |
| Low Friction | Maintains a low coefficient of friction, reducing energy use and heat generation. |
| Dry-Running Excellence | Performs exceptionally well in non-lubricated or stop-start conditions. |
| Reduces Counter-Surface Wear | Ideal when preserving the integrity of the mating component is paramount. |
Need a PTFE Component that Protects Your Mating Surfaces?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. If your application involves soft metals like aluminum or brass, or requires reliable performance in non-lubricated, stop-start conditions, our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures a solution that protects your entire system.
Contact our experts today to discuss how polyamide-filled PTFE can enhance your application's durability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the typical mechanical and thermal properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Low Friction & Extreme Temp Performance
- What are the primary functions of flat washers? Ensuring Secure, Durable, and Damage-Free Joints
- What is PTFE's resistance to fluorine under different conditions? Avoid Costly Failures with Temperature-Specific Data
- What are the disadvantages of PTFE/Teflon? Understanding Its Mechanical and Fabrication Limits
- What electrical properties make PTFE valuable for industrial applications? Discover the Key to Elite Insulation
- How does PTFE perform when exposed to sulfuric acid? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What makes PTFE an ideal material for corrosion-resistant applications? Unmatched Chemical Inertness for Harsh Environments
- What are the key steps in PTFE coating molding? A Guide to Durable, Non-Stick Surfaces



















