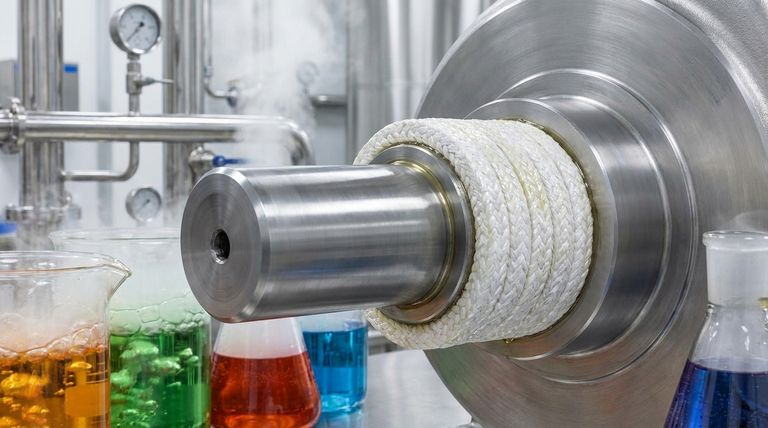
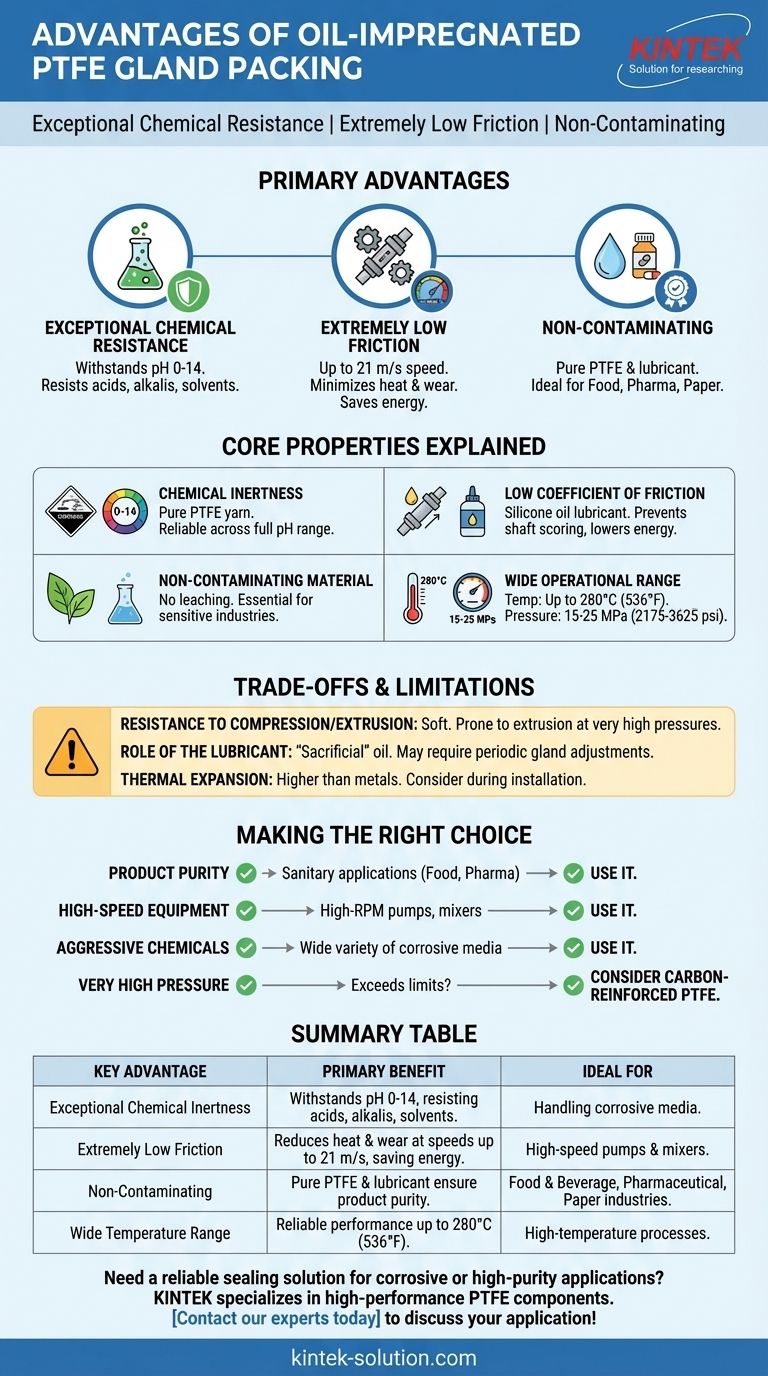
The primary advantages of oil-impregnated PTFE gland packing are its exceptional chemical resistance, extremely low friction, and non-contaminating properties. This combination makes it a specialized sealing solution for equipment that handles corrosive fluids, operates at high speeds, or is used in industries where product purity is non-negotiable.
While many packing materials offer either chemical resistance or low friction, oil-impregnated PTFE excels by delivering both simultaneously. This makes it a superior choice for dynamic sealing applications in sanitary or highly corrosive environments.

Core Properties Explained
To understand where this packing truly shines, it's essential to break down its key characteristics. Each property addresses a specific operational challenge in pumps, valves, and other rotating equipment.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
The packing is constructed from pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) yarn. PTFE is renowned for being one of the most chemically inert materials used in industry.
This allows it to operate reliably across the entire pH range of 0 to 14, meaning it can withstand nearly all industrial acids, alkalis, and solvents without degrading.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
The PTFE yarn is impregnated with a special silicone oil lubricant. This treatment dramatically reduces the friction between the packing and the rotating shaft.
The key benefit is minimal heat generation, even at high peripheral speeds (up to 21 m/s). This prevents shaft scoring, reduces wear on equipment, and lowers energy consumption.
Non-Contaminating Material
Both the pure PTFE and the specialized lubricant are chosen for their purity. They do not leach or shed particles that could contaminate the process fluid.
This makes oil-impregnated PTFE packing ideal for sensitive industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and paper manufacturing, where product contamination is unacceptable.
Wide Operational Range
Beyond its chemical resistance, this packing performs reliably across a broad range of conditions.
It maintains its integrity at temperatures up to 280°C (536°F) and can handle pressures between 15 to 25 MPa (2175 to 3625 psi), depending on the specific application and equipment condition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single sealing solution is perfect for every scenario. Understanding the limitations of oil-impregnated PTFE is crucial for proper application and avoiding premature failure.
Resistance to Compression and Extrusion
Standard oil-impregnated PTFE packing is relatively soft. In very high-pressure applications, it can be prone to extrusion, where the packing material is squeezed out of the gland housing.
For applications involving extreme pressures or worn equipment, a more structurally robust packing, such as one woven from sintered or carbon-reinforced PTFE yarns, may be a better choice due to its higher dimensional stability.
The Role of the Lubricant
The silicone oil is a "sacrificial" component. Over time and under pressure, this lubricant can be gradually squeezed out of the packing.
This may require periodic gland adjustments (tightening) to maintain an effective seal. It is a normal part of the maintenance cycle for this type of packing.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to metals. This must be considered during installation. Overtightening a cold pump can lead to excessive friction and heat once the system reaches its operating temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct packing requires matching the material's strengths to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is product purity: The non-contaminating nature of this packing makes it the default choice for sanitary applications in food, pharma, or fine chemicals.
- If your primary focus is high-speed equipment: The low-friction properties are critical for preventing heat buildup and shaft damage in high-RPM pumps and mixers.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: Its ability to withstand the full pH range provides unmatched reliability when dealing with a wide variety of corrosive media.
- If your primary focus is very high pressure: You should carefully evaluate if the pressure exceeds the packing's limits and consider a more extrusion-resistant alternative like a carbon-reinforced PTFE packing.
By understanding these distinct advantages and limitations, you can deploy oil-impregnated PTFE packing effectively to enhance equipment reliability and service life.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Primary Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Exceptional Chemical Inertness | Withstands pH 0-14, resisting acids, alkalis, and solvents. | Handling corrosive media. |
| Extremely Low Friction | Reduces heat and wear at speeds up to 21 m/s, saving energy. | High-speed pumps and mixers. |
| Non-Contaminating | Pure PTFE and lubricant ensure product purity. | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Paper industries. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Reliable performance up to 280°C (536°F). | High-temperature processes. |
Need a reliable sealing solution for corrosive or high-purity applications?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom gland packings. Our precision production ensures seals that deliver exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, and non-contaminating performance for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can fabricate from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact requirements. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and enhance your equipment's reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for Teflon encapsulated silicone o-rings? A Guide to Optimal Sealing Performance
- What are some modern applications of PTFE due to its electrical insulative properties? | High-Frequency & Extreme Environment Solutions
- What is the process flow for PTFE compression molding? A 4-Step Guide to Durable PTFE Preforms
- How is structured PTFE manufactured? The Process Behind High-Performance PTFE Components
- What tools and techniques are recommended for machining PTFE? Achieve Precision and a Clean Finish
- In what applications are solid Teflon O-rings most suitable? Maximize Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What challenges should be identified for an O-ring application? A Guide to Ensuring Seal Success
- How does PTFE differ from other sealing materials like elastomers or polyurethane? A Guide to Extreme Performance Seals



















