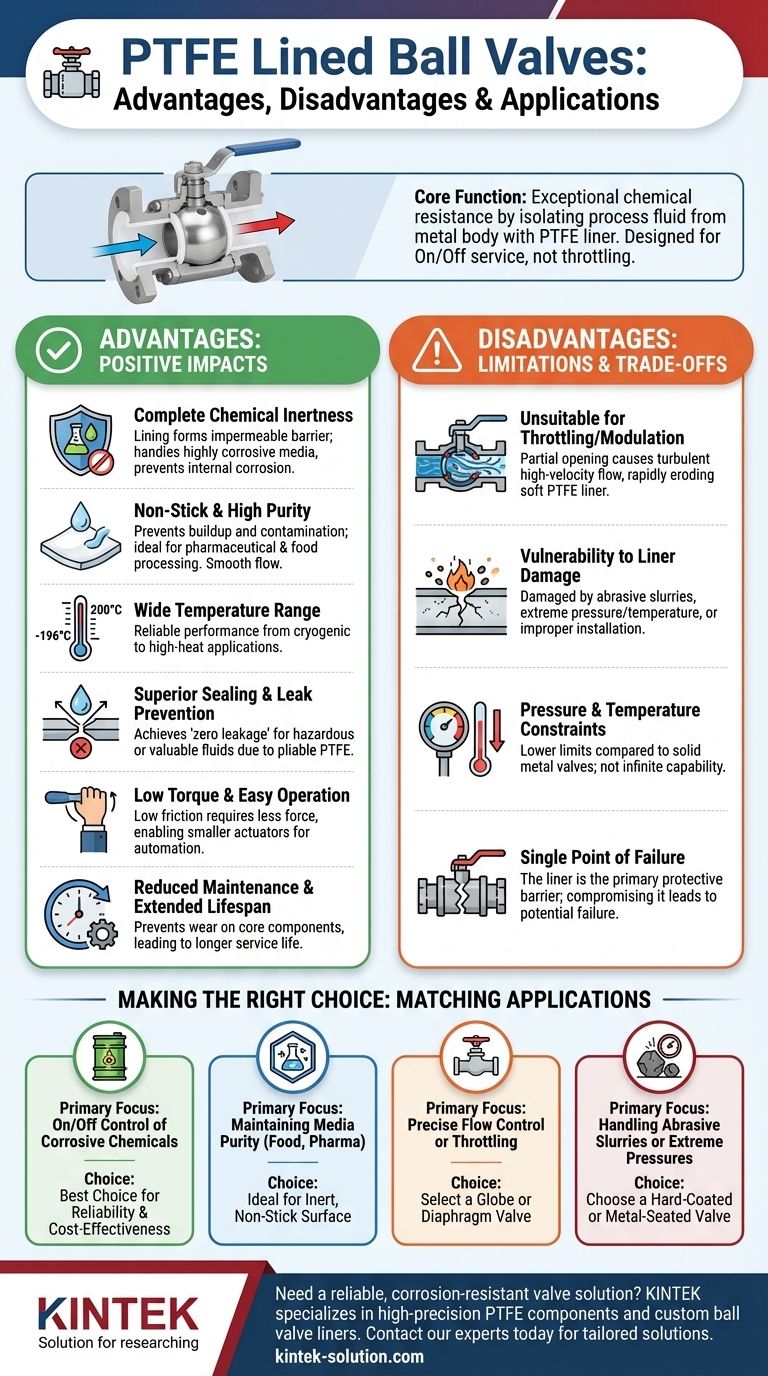
At its core, a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) lined ball valve offers exceptional chemical resistance by isolating the process fluid from the valve's metal body. Its primary advantages are its ability to handle highly corrosive media and provide a tight, leak-proof seal with low operating effort. The main disadvantage is that it is designed for simple on/off service and is unsuitable for throttling or modulating flow.
A PTFE lined ball valve is a specialist, not a generalist. It provides an unparalleled, cost-effective solution for on/off control of corrosive and high-purity fluids but lacks the versatility for precise flow regulation or handling abrasive materials.

The Core Advantage: Complete Chemical Inertness
The fundamental purpose of a PTFE lining is to create an impermeable barrier between the fluid you are transporting and the structural metal of the valve. This design principle delivers several key benefits.
How the Lining Creates a Protective Barrier
All wetted parts of the valve—the body, ball, and stem—are lined with a uniform layer of PTFE (or similar fluoropolymers like PFA/FEP). This means the corrosive acid, alkali, or solvent only ever comes into contact with the chemically inert liner, not the cast iron or steel body. This completely prevents corrosion of the valve's core components.
Non-Stick Properties for Purity and Flow
PTFE is famous for its non-stick surface. In a valve, this property prevents media from adhering to or building up on the internal surfaces. This is critical in pharmaceutical or food processing applications where purity is paramount and ensures a smooth, unobstructed flow path, minimizing pressure drop.
Wide Temperature and Application Range
PTFE linings perform reliably across a broad temperature spectrum, often cited from -196°C to 200°C (-320°F to 392°F). This versatility makes them a default choice in demanding industries like chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, oil and gas, and power generation where aggressive media is common.
Engineering and Operational Benefits
Beyond chemical resistance, the choice of PTFE as a liner introduces significant mechanical and operational advantages that contribute to system reliability and efficiency.
Superior Sealing and Leak Prevention
PTFE is a soft, pliable material. When the valve is closed, the PTFE-lined ball presses firmly against the PTFE seat, creating an exceptionally tight seal. This design can often achieve "zero leakage," which is critical for containing hazardous chemicals or preventing loss of valuable product.
Low Torque and Ease of Operation
The extremely low coefficient of friction of PTFE means very little force is required to turn the ball from the open to the closed position. This low-torque operation allows for smaller, less expensive actuators for automated systems and makes manual operation significantly easier.
Reduced Maintenance and Extended Lifespan
By preventing internal corrosion and media buildup, the PTFE lining dramatically reduces wear and tear on the valve's core components. This translates directly to a longer service life and lower maintenance requirements compared to unlined metal valves in corrosive service.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No valve design is without its compromises. Understanding the limitations of PTFE lined ball valves is crucial for selecting the right component and avoiding premature failure.
Unsuitable for Throttling or Flow Control
Ball valves are designed for on/off service. When a ball valve is partially open (throttling), it creates a narrow opening that forces fluid through at high velocity. This turbulent flow can rapidly erode the soft PTFE seats and lining, leading to seal failure. For flow regulation, a globe or diaphragm valve is a more appropriate choice.
Vulnerability to Liner Damage
While durable, the PTFE lining is the valve's single point of failure. It can be damaged by:
- Abrasive Media: Slurries or fluids with suspended solids can scratch and wear away the liner, compromising its integrity.
- Extreme Conditions: Exceeding the specified pressure or temperature limits can cause the liner to deform, crack, or even collapse, leading to catastrophic failure.
- Improper Installation: Mechanical stress or mishandling during installation can easily damage the lining.
Pressure and Temperature Constraints
While the temperature range is wide, it is not infinite. PTFE has absolute temperature and pressure limits that are generally lower than those of solid metal valves. In very high-pressure or high-temperature applications, a metal-seated valve may be necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve is about matching its specific strengths to your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is on/off control of corrosive chemicals: The PTFE lined ball valve is the industry standard and likely your best choice for reliability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is maintaining media purity (food, pharma): The inert, non-stick PTFE surface makes it an ideal solution to prevent contamination and buildup.
- If your primary focus is precise flow control or throttling: You must select a different valve type, such as a globe valve, to avoid damaging the valve and ensure stable control.
- If your primary focus is handling abrasive slurries or extreme pressures: A hard-coated or metal-seated ball valve is a more robust and reliable option.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE lined ball valve is an excellent decision when its specialized capabilities align perfectly with your process requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent for corrosive acids, alkalis, and solvents | Not suitable for abrasive slurries or solids |
| Operation | Low torque, easy on/off control, tight seal | Unsuitable for throttling or flow modulation |
| Performance | Wide temperature range (-196°C to 200°C), non-stick surface | Pressure and temperature limits lower than solid metal valves |
| Maintenance | Long service life, reduced maintenance in corrosive service | Liner is vulnerable to damage if limits are exceeded |
Need a reliable, corrosion-resistant valve solution for your semiconductor, medical, or industrial process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom ball valve liners and seals. Our expertise ensures your valves deliver maximum chemical resistance, purity, and longevity.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and get a solution that perfectly matches your process needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE coatings benefit industrial manufacturing? Enhance Equipment Life & Efficiency
- How do PTFE sealed ball bearings enhance riding performance? Achieve Faster, Longer-Lasting Speed
- How many types of PTFE gaskets are there and what are their general uses? A Guide to Chemical-Resistant Sealing
- How do fillers enhance PTFE's properties? Unlock Superior Wear Resistance & Stability
- How does the durability of Teflon sheets benefit printing operations? Boost Quality & Cut Costs
- What are the processing methods for PTFE? A Guide to Compression Molding and Machining
- What design parameters are specified for PTFE sliding bearings? Ensure Structural Safety and Performance
- Why are FEP and PTFE encapsulated O-rings used in the food and pharmaceutical industries? Ensure Purity and Compliance



















